Comparison of beta-endorphin and CGRP levels before and after treatment for severe schizophrenia
- PMID: 27143887
- PMCID: PMC4841412
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S101647
Comparison of beta-endorphin and CGRP levels before and after treatment for severe schizophrenia
Abstract
Objectives: Links between endorphins and dopaminergic transmission have not been fully explored in schizophrenia. Both endorphins excess and deficiency were postulated. CGRP is probably involved in dopaminergic transmission. The aim of this study was the evaluation of beta-endorphin (BE) and CGRP blood concentrations before and after treatment of severe schizophrenia.
Methods: Seventy patients treated with various antipsychotics, with severe symptoms of schizophrenia (51 with positive symptoms, 19 with negative symptoms), 15 first-degree relatives, and 44 healthy controls were included in the study. BE and CGRP blood concentrations were measured during patients severe schizophrenia and in their stable mental state after treatment. The results were compared with relatives and controls.
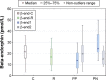
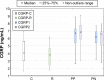
Results: BE and CGRP concentrations in patients with negative symptoms were higher than in relatives and in controls. BE levels in patients with positive symptoms were lower than in patients with negative symptoms (P<0.0000) and controls (P<0.0006). No significant changes in CGRP concentration were found in patient samples. CGRP levels in these samples were independent of treatment, but they were significantly higher than in relatives and controls. After the treatment, BE level decreased in patients with negative symptoms (P<0.0001) and increased in patients with positive symptoms (P<0.0000). No differences in BE concentration between patients in stable mental state, their relatives, and controls were found.
Conclusion: Effective antipsychotic treatment results in "normalization" of BE level. Specific changes in BE concentration could be involved in dopaminergic transmission and related to some symptoms of schizophrenia.
Keywords: CGRP; negative symptoms; neuroleptics; schizophrenia; β-endorphin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Relationship Between Antipsychotic Treatment and Plasma β-Endorphin Concentration in Patients with Schizophrenia.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2021 Feb 16;17:503-512. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S289821. eCollection 2021. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2021. PMID: 33623384 Free PMC article.
-
Pain perception in schizophrenia: influence of neuropeptides, cognitive disorders, and negative symptoms.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015 Aug 6;11:2023-31. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S87666. eCollection 2015. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015. PMID: 26273205 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory identification in patients with schizophrenia - the influence of β-endorphin and calcitonin gene-related peptide concentrations.Eur Psychiatry. 2017 Mar;41:16-20. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2016.09.004. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Eur Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28049076
-
Novel pharmacological approaches to the treatment of schizophrenia.Dan Med Bull. 2000 Jun;47(3):151-67. Dan Med Bull. 2000. PMID: 10913983 Review.
-
The acute efficacy of antipsychotics in schizophrenia: a review of recent meta-analyses.Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2018 Oct 8;8(11):303-318. doi: 10.1177/2045125318781475. eCollection 2018 Nov. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30344997 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Relationship Between Course of Illness and β-Endorphin Plasma Levels in Patients with Schizophrenia.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2019 Dec 31;15:3609-3614. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S225321. eCollection 2019. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2019. PMID: 32099366 Free PMC article.
-
The Endogenous Opioid System in Schizophrenia and Treatment Resistant Schizophrenia: Increased Plasma Endomorphin 2, and κ and μ Opioid Receptors Are Associated with Interleukin-6.Diagnostics (Basel). 2020 Aug 26;10(9):633. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10090633. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32858974 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship Between Antipsychotic Treatment and Plasma β-Endorphin Concentration in Patients with Schizophrenia.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2021 Feb 16;17:503-512. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S289821. eCollection 2021. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2021. PMID: 33623384 Free PMC article.
-
Odor perception and hedonics in chronic schizophrenia and in first episode psychosis.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2019 Mar 5;15:647-654. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S192523. eCollection 2019. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2019. PMID: 30880989 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma β-Endorphin Concentration and Antipsychotic Treatment Outcome in Schizophrenia: 1-Year Follow-Up.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Sep 6;26:e924307. doi: 10.12659/MSM.924307. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32892205 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Wied D, Sigling HO. Neuropeptides involved in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia and major depression. Neurotox Res. 2002;4:453–468. - PubMed
-
- Kream RM, Stefano GB, Ptáček R. Psychiatric implications of endogenous morphine: up-to-date review. Folia Biol. 2010;56(6):231–241. - PubMed
-
- Stefano GB, Goumon Y, Casares F, et al. Endogenous morphine. Trends Neurosci. 2000;23:436–442. - PubMed
-
- Fricchione GL, Mendoza A, Stefano GB. Morphine and its psychiatric implications. Adv Neuroimmunol. 1994;4(2):117–131. - PubMed
-
- Lipska BK, Weinberger DR. Delayed effects of neonatal hippocampal damage on haloperidol-induced catalepsy and apomorphine-induced stereotypic behaviors in the rat. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1993;15(75):213–222. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

