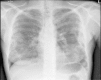
Sulfasalazine: A rare cause of acute eosinophilic pneumonia
- PMID: 27144116
- PMCID: PMC4840476
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2016.03.006
Sulfasalazine: A rare cause of acute eosinophilic pneumonia
Abstract
Sulfasalazine is a compound of 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) and sulfapyridine joined by an azo bond. It is a widely used drug in the treatment of chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Fatal toxicity of sulfasalazine arises from its effects on the bone marrow and the resulting blood dyscrasias. Pulmonary toxicity from sulfasalazine is a rather rare finding. Here, we present the case of a patient who developed acute eosinophilic pneumonia with sulfasalazine use.
Keywords: ASA, Aminosalicylic Acid; BAL, Bronchoalveolar Lavage; CRP, C-reactive protein; Drug induced lung disease; Eosinophilic pneumonia; Interstitial lung disease; MGG, May-Grunwald-Giemsa; TNF-α, Tumour necrosis factor alpha.
Figures
References
-
- Parry S.D., Barbatzas C., Peel E.T., Barton J.R. Sulphasalazine and lung toxicity. Eur. Respir. J. 2002;19:756–764. - PubMed
-
- Baillie J. Sulfasalazine and pulmonary infiltrates. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1984;79:77. - PubMed
-
- Scherpenisse J., van der Valk P.D., van den Bosch J.M., van Hees P.A., Nadorp J.H. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 1988;10(2):218–220. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous