Nuclear receptor 4A1 (NR4A1) as a drug target for treating rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS)
- PMID: 27144436
- PMCID: PMC5058754
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.9112
Nuclear receptor 4A1 (NR4A1) as a drug target for treating rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS)
Abstract
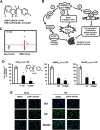
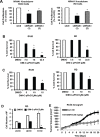
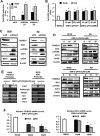
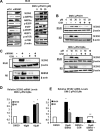
The orphan nuclear receptor NR4A1 is expressed in tumors from rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) patients and Rh30 and RD RMS cell lines, and we used RNA interference (RNAi) to investigate the role of this receptor in RMS cells. Knockdown of NR4A1 in Rh30 cells decreased cell proliferation, induced Annexin V staining and induced polyADPribose polymerase (PARP) cleavage and these results were similar to those observed in other solid tumors. Previous studies show that NR4A1 regulates expression of growth promoting/pro-survival genes with GC-rich promoters, activates mTOR through suppression of p53, and maintains low oxidative stress by regulating expression of isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) and thioredoxin domain containing 5 (TXNDC5). Results of RNAi studies demonstrated that NR4A1 also regulates these pathways and associated genes in RMS cells and thereby exhibits pro-oncogenic activity. 1,1-Bis(3-indolyl)-1-(p-substituted phenyl)methane (C-DIM) analogs containing p-hydroxyl (DIM-C-pPhOH) and p-carboxymethyl (DIM-C-pPhCO2Me) substituents are NR4A1 ligands that decreased NR4A1-dependent transactivation in RMS cells and inhibited RMS cell and tumor growth and induced apoptosis. Moreover, the effects of NR4A1 knockdown and the C-DIM/NR4A1 antagonists were comparable as inhibitors of NR4A1-dependent genes/pathways. Both NR4A1 knockdown and treatment with DIM-C-pPhOH and DIM-C-pPhCO2Me also induced ROS which activated stress genes and induced sestrin 2 which activated AMPK and inhibited mTOR in the mutant p53 RMS cells. Since NR4A1 regulates several growth-promoting/pro-survival pathways in RMS, the C-DIM/NR4A1 antagonists represent a novel mechanism-based approach for treating this disease alone or in combination and thereby reducing the adverse effects of current cytotoxic therapies.
Keywords: C-DIMs; NR4A1; NR4A1 antagonists; inhibition; rhabdomyosarcoma.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication and there has been no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nuclear Receptor 4A1 (NR4A1) as a Drug Target for Renal Cell Adenocarcinoma.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 2;10(6):e0128308. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128308. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26035713 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear receptor 4A1 as a drug target for breast cancer chemotherapy.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2015 Oct;22(5):831-40. doi: 10.1530/ERC-15-0063. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26229035
-
Potent inhibition of breast cancer by bis-indole-derived nuclear receptor 4A1 (NR4A1) antagonists.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Aug;177(1):29-40. doi: 10.1007/s10549-019-05279-9. Epub 2019 May 22. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 31119568 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting NR4A1 (TR3) in cancer cells and tumors.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2011 Feb;15(2):195-206. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2011.547481. Epub 2011 Jan 5. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2011. PMID: 21204731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The nuclear orphan receptor NR4A1 and NR4A3 as tumor suppressors in hematologic neoplasms.Curr Drug Targets. 2015;16(1):38-46. doi: 10.2174/1389450115666141120112818. Curr Drug Targets. 2015. PMID: 25410408 Review.
Cited by
-
Orphan nuclear receptor 4A1 (NR4A1) and novel ligands.Essays Biochem. 2021 Dec 17;65(6):877-886. doi: 10.1042/EBC20200164. Essays Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34096590 Free PMC article.
-
Bis-Indole-Derived NR4A1 Ligands and Metformin Exhibit NR4A1-Dependent Glucose Metabolism and Uptake in C2C12 Cells.Endocrinology. 2018 May 1;159(5):1950-1963. doi: 10.1210/en.2017-03049. Endocrinology. 2018. PMID: 29635345 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear receptor 4A1 (NR4A1) antagonists target paraspeckle component 1 (PSPC1) in cancer cells.Mol Carcinog. 2022 Jan;61(1):73-84. doi: 10.1002/mc.23362. Epub 2021 Oct 26. Mol Carcinog. 2022. PMID: 34699643 Free PMC article.
-
Flavonoids Quercetin and Kaempferol Are NR4A1 Antagonists and Suppress Endometriosis in Female Mice.Endocrinology. 2023 Aug 28;164(10):bqad133. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqad133. Endocrinology. 2023. PMID: 37652054 Free PMC article.
-
TXNDC5 is a cervical tumor susceptibility gene that stimulates cell migration, vasculogenic mimicry and angiogenesis by down-regulating SERPINF1 and TRAF1 expression.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 29;8(53):91009-91024. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18857. eCollection 2017 Oct 31. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29207620 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Paulino AC, Okcu MF. Rhabdomyosarcoma. Curr Probl Cancer. 2008;32:7–34. - PubMed
-
- Parham DM, Ellison DA. Rhabdomyosarcomas in adults and children: an update. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2006;130:1454–1465. - PubMed
-
- Kumar S, Perlman E, Harris CA, Raffeld M, Tsokos M. Myogenin is a specific marker for rhabdomyosarcoma: an immunohistochemical study in paraffin-embedded tissues. Mod Pathol. 2000;13:988–993. - PubMed
-
- Scrable HJ, Witte DP, Lampkin BC, Cavenee WK. Chromosomal localization of the human rhabdomyosarcoma locus by mitotic recombination mapping. Nature. 1987;329:645–647. - PubMed
-
- Barr FG, Galili N, Holick J, Biegel JA, Rovera G, Emanuel BS. Rearrangement of the PAX3 paired box gene in the paediatric solid tumour alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Nat Genet. 1993;3:113–117. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

