Effect of Onabotulinum Toxin A on Substance P and Receptor Neurokinin 1 in the Rat Ventral Prostate
- PMID: 27144785
- PMCID: PMC4854183
- DOI: 10.4172/2167-0250.1000131
Effect of Onabotulinum Toxin A on Substance P and Receptor Neurokinin 1 in the Rat Ventral Prostate
Abstract
Introduction: The objective of this work is to examine if sensory innervation impacts lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS). Onabotulinum toxin A (BoNTA) has been used for the treatment of overactive and neurogenic bladder and as a treatment for LUTS secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). The mechanism of how BoNTA impacts LUTS/BPH is unclear. In rats, BoNTA injection causes prostate denervation, apoptosis and atrophy. In clinical trials reduced prostate size and LUTS are observed inconsistently, suggesting a neurologic component. We will examine if BoNTA treatment inhibits substance P production in sensory nerve fibers in the rat prostate.
Methods: Twenty Sprague Dawley rats were divided into four groups including 1X PBS (control, n=6), 2.5 units Onabotulinum toxin A (BoNTA, n=6), 5 units BoNTA (n=6) injected into both lobes of the ventral prostate (VP) and sham surgery (n=2). Rats were Euthanized after one week. Substance P and its receptor neurokinin 1 localization and quantification were performed by counting the number of stained neurons and nerve bundles, by semi-quantitative immunohistochemical analysis and by western analysis.
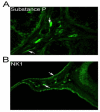
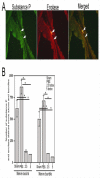
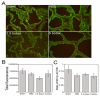
Results: Substance P was localized in neuronal axons and bundles in the stroma of the VP but not in the epithelium. Receptor neurokinin 1 was identified in neuronal bundles of the stroma and in columnar epithelium of the VP ducts. Substance P decreased ~90% after BoNTA treatment (p=0.0001) while receptor neurokinin 1 did not change by IHC (p=0.213) or Western (p=0.3675).
Conclusions: BoNTA treatment decreases substance P in the rat VP.
Keywords: BoNTA; LUTS/BPH; Prostate; Substance P.
Figures

References
-
- McVary KT. BPH: epidemiology and comorbidities. Am J Manag Care. 2006;12:S122–128. - PubMed
-
- Auffenberg GB, Helfand BT, McVary KT. Established medical therapy for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urol Clin North Am. 2009;36:443–459. v-vi. - PubMed
-
- Berry SJ, Coffey DS, Walsh PC, Ewing LL. The development of human benign prostatic hyperplasia with age. J Urol. 1984;132:474–479. - PubMed
-
- Füllhase C, Chapple C, Cornu JN, De Nunzio C, Gratzke C, et al. Systematic review of combination drug therapy for non-neurogenic male lower urinary tract symptoms. Eur Urol. 2013;64:228–243. - PubMed
-
- Abrams P. Update on AUA guideline on the management of benign prostatic hyperplasia: KT McVary, CG Roehrborn, JC Ulchaker and JT Wei. J Urol. 2012;187:358–359. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
