MiR-211/STAT5A Signaling Modulates Migration of Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Improve its Therapeutic Efficacy
- PMID: 27145179
- PMCID: PMC5096301
- DOI: 10.1002/stem.2391
MiR-211/STAT5A Signaling Modulates Migration of Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Improve its Therapeutic Efficacy
Erratum in
-
Correction to: MiR-211/STAT5A Signaling Modulates Migration of Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Improve its Therapeutic Efficacy.Stem Cells. 2022 Jul 27;40(7):e2. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxac028. Stem Cells. 2022. PMID: 35648161 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
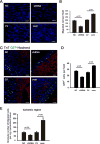
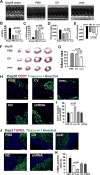
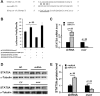
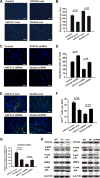
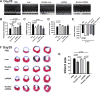
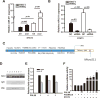
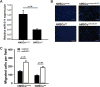
Our previous study showed that the therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) transplantation were improved by enhancing migration. MicroRNA-211 (miR-211) can modulate the migratory properties of some cell types by mechanisms that are not fully understood. This study was designed to investigate a possible role for miR-211 in MSC migration, and whether genetic manipulation of miR-211 in MSCs could be used to enhance its beneficial effects of cell transplantation. Transwell assays confirmed that MSCs migration of was significantly impaired by miR-211 knockdown but enhanced by miR-211 overexpression. MiR-211 overexpressing MSCs also exhibited significantly increased cell engraftment in the peri-infarct areas of female rat hearts 2 days after intravenous transplantation of male MSCs as shown by GFP tracking and SYR gene quantification. This conferred a significant decrease in infarct size and improved cardiac performance. By using a loss or gain of gene function approach, we demonstrated that miR-211 targeted STAT5A to modulate MSCs migration, possibly by interacting with MAPK signaling. Furthermore, the beneficial effects of miR-211 overexpression in MSCs were abolished by simultaneous overexpression of STAT5A whereas the negative effects of miR-211 silencing on MSC migration were rescued by simultaneous downregulation of STAT5A. Finally, using ChIP-PCR and luciferase assays, we provide novel evidence that STAT3 can directly bind to promoter elements that activate miR-211 expression. STAT3/miR-211/STAT5A signaling plays a key role in MSCs migration. Intravenous infusion of genetically modified miR-211 overexpressing MSCs conveys enhanced protection from adverse post-MI remodeling compared with unmodified MSCs. Stem Cells 2016;34:1846-1858.
Keywords: Mesenchymal stem cells; MicroRNA-211; Migration; Myocardial infarction; Retention; STAT5A.
© 2016 The Authors STEM CELLS published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of AlphaMed Press.
Conflict of interest statement
of Potential Conflicts of Interest The authors indicate no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hou D, Youssef EA, Brinton TJ, et al. Radiolabeled cell distribution after intramyocardial, intracoronary, and interstitial retrograde coronary venous delivery: Implications for current clinical trials. Circulation. 2005;112:I150–I156. - PubMed
-
- Bartunek J, Behfar A, Dolatabadi D, et al. Cardiopoietic stem cell therapy in heart failure: The C-CURE (Cardiopoietic stem Cell therapy in heart failURE) multicenter randomized trial with lineage-specified biologics. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61:2329–2338. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

