Comparative genomic analysis of six new-found integrative conjugative elements (ICEs) in Vibrio alginolyticus
- PMID: 27145747
- PMCID: PMC4857294
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-016-0692-9
Comparative genomic analysis of six new-found integrative conjugative elements (ICEs) in Vibrio alginolyticus
Abstract
Background: Vibrio alginolyticus is ubiquitous in marine and estuarine environments. In 2012-2013, SXT/R391-like integrative conjugative elements (ICEs) in environmental V. alginolyticus strains were discovered and found to occur in 8.9 % of 192 V. alginolyticus strains, which suggests that V. alginolyticus may be a natural pool possessing resourceful ICEs. However, complete ICE sequences originating from this bacterium have not been reported, which represents a significant barrier to characterizing the ICEs of this bacterium and exploring their relationships with other ICEs. In the present study, we acquired six ICE sequences from five V. alginolyticus strains and performed a comparative analysis of these ICE genomes.
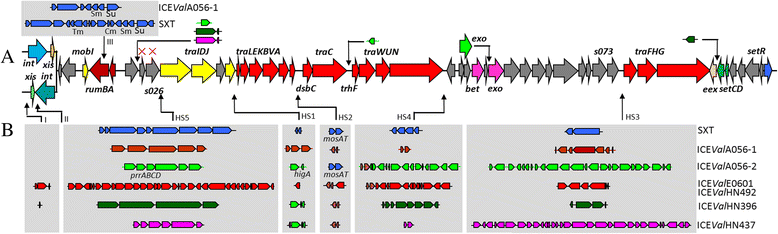
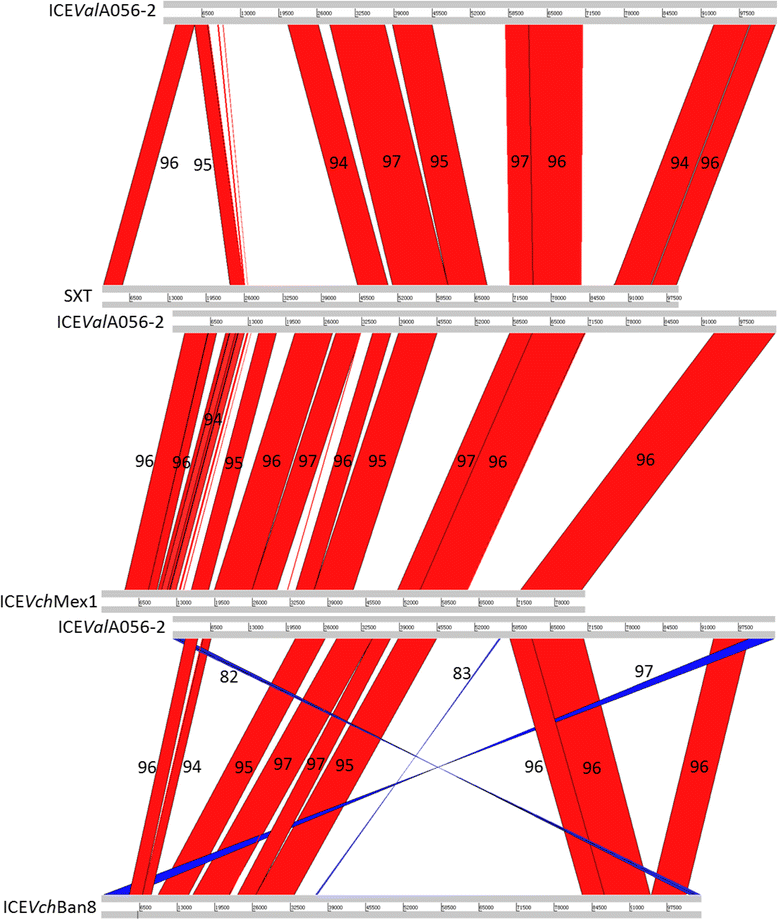
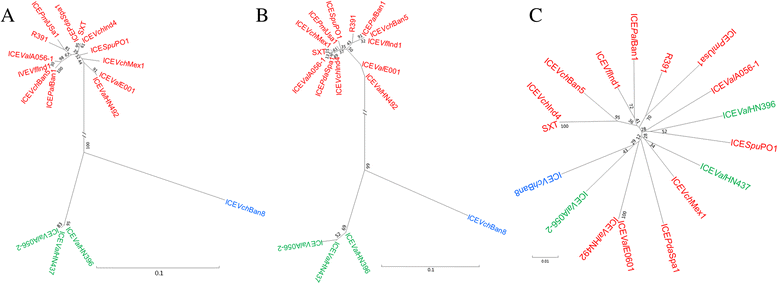
Results: A sequence analysis showed that there were only 14 variable bases dispersed between ICEValE0601 and ICEValHN492. ICEValE0601 and ICEValHN492 were treated as the same ICE. ICEValA056-1, ICEValE0601 and ICEValHN492 integrate into the 5' end of the host's prfC gene, and their Int and Xis share at least 97 % identity with their counterparts from SXT. ICEValE0601 or ICEValHN492 contain 50 of 52 conserved core genes in the SXT/R391 ICEs (not s025 or s026). ICEValA056-2, ICEValHN396 and ICEValHN437 have a different tRNA-ser integration site and a distinct int/xis module; however, the remaining backbone genes are highly similar to their counterparts in SXT/R391 ICEs. DNA sequences inserted into hotspot and variable regions of the ICEs are of various sizes. The variable genes of six ICEs encode a large array of functions to bestow various adaptive abilities upon their hosts, and only ICEValA056-1 contains drug-resistant genes. Many variable genes have orthologous and functionally related genes to those found in SXT/R391 ICEs, such as genes coding for a toxin-antitoxin system, a restriction-modification system, helicases and endonucleases. Six ICEs also contain a large number of unique genes or gene clusters that were not found in other ICEs. Six ICEs harbor more abundant transposase genes compared with other parts of their host genomes. A phylogenetic analysis indicated that transposase genes in these ICEs are highly diverse.
Conclusions: ICEValA056-1, ICEValE0601 and ICEValHN492 are typical members of the SXT/R391 family. ICEValA056-2, ICEValHN396 and ICEValHN437 form a new atypical group belonging to the SXT/R391 family. In addition to the many genes found to be present in other ICEs, six ICEs contain a large number of unique genes or gene clusters that were not found in other ICEs. ICEs may serve as a carrier for transposable genetic elements (TEs) and largely facilitate the dissemination of TEs.
Keywords: Comparative genomics; Integrative Conjugative Elements (ICEs); Transposable genetic Elements (TEs); Vibrio alginolyticus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Redefinition and Unification of the SXT/R391 Family of Integrative and Conjugative Elements.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Jun 18;84(13):e00485-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00485-18. Print 2018 Jul 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29654185 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the pan-genome of the SXT/R391 family of ICEs: molecular characterisation of new variable regions of SXT/R391-like ICEs detected in Pseudoalteromonas sp. and Vibrio scophthalmi.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2016 Aug;109(8):1141-52. doi: 10.1007/s10482-016-0716-3. Epub 2016 May 26. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2016. PMID: 27230650
-
Acquisition and evolution of SXT-R391 integrative conjugative elements in the seventh-pandemic Vibrio cholerae lineage.mBio. 2014 Aug 19;5(4):e01356-14. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01356-14. mBio. 2014. PMID: 25139901 Free PMC article.
-
[Bacterial SXT/R391 family from integrating conjugative elements--a review].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2014 May 4;54(5):471-9. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2014. PMID: 25199245 Review. Chinese.
-
The current ICE age: biology and evolution of SXT-related integrating conjugative elements.Plasmid. 2006 May;55(3):173-83. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2006.01.001. Epub 2006 Mar 13. Plasmid. 2006. PMID: 16530834 Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel Arsenate-Resistant Determinant Associated with ICEpMERPH, a Member of the SXT/R391 Group of Mobile Genetic Elements.Genes (Basel). 2019 Dec 16;10(12):1048. doi: 10.3390/genes10121048. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31888308 Free PMC article.
-
Redefinition and Unification of the SXT/R391 Family of Integrative and Conjugative Elements.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Jun 18;84(13):e00485-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00485-18. Print 2018 Jul 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29654185 Free PMC article.
-
Complete genomic sequence of the Vibrio alginolyticus bacteriophage Vp670 and characterization of the lysis-related genes, cwlQ and holA.BMC Genomics. 2018 Oct 11;19(1):741. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-5131-x. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30305030 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis and comparative genomics of R997, the first SXT/R391 integrative and conjugative element (ICE) of the Indian Sub-Continent.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 17;7(1):8562. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08735-y. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28819148 Free PMC article.
-
Toxin-antitoxin systems in pathogenic Vibrio species: a mini review from a structure perspective.3 Biotech. 2022 Jun;12(6):125. doi: 10.1007/s13205-022-03178-3. Epub 2022 May 7. 3 Biotech. 2022. PMID: 35542053 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Garriss G, Burrus V. Integrating conjugative elements of the SXT/R391 family. In: Roberts AP, Mullany P, editors. Bacterial integrative mobile genetic elements. Austin: Landes Biosciences; 2013. pp. 217–34.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

