Optimizing sedation in patients with acute brain injury
- PMID: 27145814
- PMCID: PMC4857238
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-016-1294-5
Optimizing sedation in patients with acute brain injury
Abstract
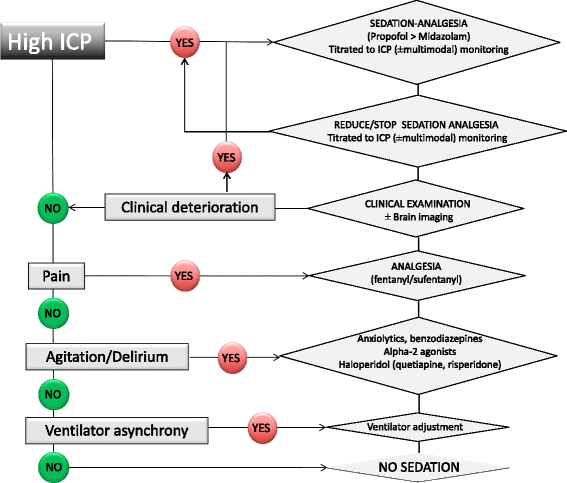
Daily interruption of sedative therapy and limitation of deep sedation have been shown in several randomized trials to reduce the duration of mechanical ventilation and hospital length of stay, and to improve the outcome of critically ill patients. However, patients with severe acute brain injury (ABI; including subjects with coma after traumatic brain injury, ischaemic/haemorrhagic stroke, cardiac arrest, status epilepticus) were excluded from these studies. Therefore, whether the new paradigm of minimal sedation can be translated to the neuro-ICU (NICU) is unclear. In patients with ABI, sedation has 'general' indications (control of anxiety, pain, discomfort, agitation, facilitation of mechanical ventilation) and 'neuro-specific' indications (reduction of cerebral metabolic demand, improved brain tolerance to ischaemia). Sedation also is an essential therapeutic component of intracranial pressure therapy, targeted temperature management and seizure control. Given the lack of large trials which have evaluated clinically relevant endpoints, sedative selection depends on the effect of each agent on cerebral and systemic haemodynamics. Titration and withdrawal of sedation in the NICU setting has to be balanced between the risk that interrupting sedation might exacerbate brain injury (e.g. intracranial pressure elevation) and the potential benefits of enhanced neurological function and reduced complications. In this review, we provide a concise summary of cerebral physiologic effects of sedatives and analgesics, the advantages/disadvantages of each agent, the comparative effects of standard sedatives (propofol and midazolam) and the emerging role of alternative drugs (ketamine). We suggest a pragmatic approach for the use of sedation-analgesia in the NICU, focusing on some practical aspects, including optimal titration and management of sedation withdrawal according to ABI severity.
Figures
References
-
- Oddo M, Steiner LA. Sedation and analgesia in the neurocritical care unit. In: Smith M, Kofke WA, Citerio G, editors. Oxford textbook of neurocritical care. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical