Patient enrollment and logistical problems top the list of difficulties in clinical research: a cross-sectional survey
- PMID: 27145883
- PMCID: PMC4855713
- DOI: 10.1186/s12874-016-0151-1
Patient enrollment and logistical problems top the list of difficulties in clinical research: a cross-sectional survey
Abstract
Background: Many medical research projects encounter difficulties. The objective of this study was to assess the self-reported frequency of difficulties encountered by medical researchers while conducting research and to identify factors associated with their occurrence.
Methods: The authors conducted a cross-sectional survey in 2010 among principal investigators of 996 study protocols approved by the Research Ethics Committee in Geneva, Switzerland, between 2001 and 2005. The authors asked principal investigators to rate the level of difficulty (1: none, to 5: very great) encountered across the research process.
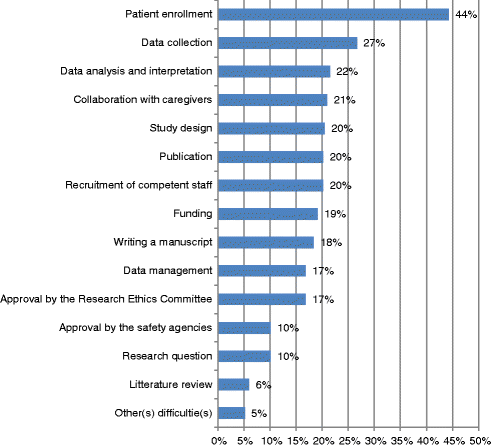
Results: 588 questionnaires were sent back (participation rate 59.0 %). 391 (66.5 %) studies were completed at the time of the survey. Investigators reported that the most frequent difficulties were related to patient enrollment (44.3 %), data collection (26.7 %), data analysis and interpretation (21.5 %), collaboration with caregivers (21.0 %), study design (20.4 %), publication in peer-reviewed journal (20.2 %), hiring of competent study personnel (20.2 %), and getting funding (19.2 %). On average, investigators reported 2.8 difficulties per project (SD 2.8, range 0 to 12). In multivariable analysis, the number of difficulties was higher for studies initiated by public sponsors (vs. private), single center studies (vs. multicenter), and studies about treatment, diagnosis or prognosis (i.e., clinical vs. other studies).
Conclusions: Medical researchers reported substantial logistical difficulties in conducting clinical research.
Keywords: Barriers; Clinical research; Difficulties; Medical researchers; Research protocols; Switzerland.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evidence-based medicine Training: Kazakhstan experience.Int J Risk Saf Med. 2015;27 Suppl 1:S95-6. doi: 10.3233/JRS-150705. Int J Risk Saf Med. 2015. PMID: 26639732
-
[Difficulties with conducting clinical trials in France].Therapie. 2001 Jul-Aug;56(4):341-7. Therapie. 2001. PMID: 11677850 French.
-
A national survey of provisions in clinical-trial agreements between medical schools and industry sponsors.N Engl J Med. 2002 Oct 24;347(17):1335-41. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa020349. N Engl J Med. 2002. PMID: 12397192
-
Recruiting long-term survivors of European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer phase III clinical trials into quality of life studies: challenges and opportunities.Eur J Cancer. 2014 Jul;50(11):1957-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2014.04.018. Epub 2014 May 9. Eur J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24820932 Clinical Trial.
-
Challenges to and lessons learned from conducting palliative care research.J Pain Symptom Manage. 2009 Mar;37(3):387-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2008.03.014. Epub 2008 Aug 19. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2009. PMID: 18715749 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Declining Use of Corticosteroids for Crohn's Disease Has Implications for Study Recruitment: Results of a Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial.J Can Assoc Gastroenterol. 2020 Nov 20;4(5):214-221. doi: 10.1093/jcag/gwaa037. eCollection 2021 Oct. J Can Assoc Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 34617003 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective Preference Assessment of a Pharmacological Clinical Trial to Alter the Progression of Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis After ACL Reconstruction.Orthop J Sports Med. 2025 Mar 11;13(3):23259671241311906. doi: 10.1177/23259671241311906. eCollection 2025 Mar. Orthop J Sports Med. 2025. PMID: 40078595 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with patient willingness to participate in anaesthesia clinical trials: a vignette-based cross-sectional study.BMC Med Res Methodol. 2020 Mar 19;20(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12874-020-00949-5. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2020. PMID: 32192447 Free PMC article.
-
Microphysiological systems for the modeling of wound healing and evaluation of pro-healing therapies.J Mater Chem B. 2020 Aug 19;8(32):7062-7075. doi: 10.1039/d0tb00544d. J Mater Chem B. 2020. PMID: 32756718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors influencing the statistical planning, design, conduct, analysis and reporting of trials in health care: A systematic review.Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2022 Jan 29;26:100897. doi: 10.1016/j.conctc.2022.100897. eCollection 2022 Apr. Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2022. PMID: 35198793 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cook DJ, Blythe D, Rischbieth A, Hebert PC, Zytaruk N, Menon K, Erikson S, Fowler R, Heels-Ansdell D, Meade MO. Enrollment of intensive care unit patients into clinical studies: a trinational survey of researchers’ experiences, beliefs, and practices. Crit Care Med. 2008;36(7):2100–5. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31817c00b0. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources