CD40 in coronary artery disease: a matter of macrophages?
- PMID: 27146510
- PMCID: PMC4856717
- DOI: 10.1007/s00395-016-0554-5
CD40 in coronary artery disease: a matter of macrophages?
Abstract
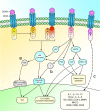
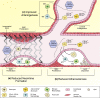
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also known as ischemic heart disease (IHD), is the leading cause of mortality in the western world, with developing countries showing a similar trend. With the increased understanding of the role of the immune system and inflammation in coronary artery disease, it was shown that macrophages play a major role in this disease. Costimulatory molecules are important regulators of inflammation, and especially, the CD40L-CD40 axis is of importance in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease. Although it was shown that CD40 can mediate macrophage function, its exact role in macrophage biology has not gained much attention in cardiovascular disease. Therefore, the goal of this review is to give an overview on the role of macrophage-specific CD40 in cardiovascular disease, with a focus on coronary artery disease. We will discuss the function of CD40 on the macrophage and its (proposed) role in the reduction of atherosclerosis, the reduction of neointima formation, and the stimulation of arteriogenesis.
Keywords: Arteriogenesis; Atherosclerosis; CD40; Ischemic heart disease; Macrophage; Neointima formation.
Figures
References
-
- Adawi A, Zhang Y, Baggs R, Rubin P, Williams J, Finkelstein J, Phipps RP. Blockade of CD40-CD40 ligand interactions protects against radiation-induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1998;89:222–230. - PubMed
-
- Advani R, Forero-Torres A, Furman RR, Rosenblatt JD, Younes A, Ren H, Harrop K, Whiting N, Drachman JG. Phase I study of the humanized anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody dacetuzumab in refractory or recurrent non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:4371–4377. - PubMed
-
- Albiero M, Rattazzi M, Menegazzo L, Boscaro E, Cappellari R, Pagnin E, Bertacco E, Poncina N, Dyar K, Ciciliot S, Iwabuchi K, Millioni R, Arrigoni G, Kraenkel N, Landmesser U, Agostini C, Avogaro A, Fadini GP. Myeloid calcifying cells promote atherosclerotic calcification via paracrine activity and allograft inflammatory factor-1 overexpression. Basic Res Cardiol. 2013;108:368. - PubMed
-
- Andre P, Prasad KS, Denis CV, He M, Papalia JM, Hynes RO, Phillips DR, Wagner DD. CD40L stabilizes arterial thrombi by a beta3 integrin–dependent mechanism. Nat Med. 2002;8:247–252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

