Learning Bayesian Networks from Correlated Data
- PMID: 27146517
- PMCID: PMC4857179
- DOI: 10.1038/srep25156
Learning Bayesian Networks from Correlated Data
Abstract
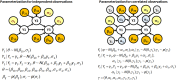
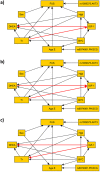
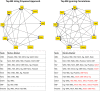
Bayesian networks are probabilistic models that represent complex distributions in a modular way and have become very popular in many fields. There are many methods to build Bayesian networks from a random sample of independent and identically distributed observations. However, many observational studies are designed using some form of clustered sampling that introduces correlations between observations within the same cluster and ignoring this correlation typically inflates the rate of false positive associations. We describe a novel parameterization of Bayesian networks that uses random effects to model the correlation within sample units and can be used for structure and parameter learning from correlated data without inflating the Type I error rate. We compare different learning metrics using simulations and illustrate the method in two real examples: an analysis of genetic and non-genetic factors associated with human longevity from a family-based study, and an example of risk factors for complications of sickle cell anemia from a longitudinal study with repeated measures.
Figures




References
-
- Friedman N., Linial M., Nachman I. & Pe’er D. Using bayesian networks to analyze expression data. Journal of Computational Biology 7, 601–20 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Lauritzen S. L. & Sheehan N. A. Graphical models for genetic analysis. Statistical Science 18, 489–514 (2004).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

