Lip movements entrain the observers' low-frequency brain oscillations to facilitate speech intelligibility
- PMID: 27146891
- PMCID: PMC4900800
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.14521
Lip movements entrain the observers' low-frequency brain oscillations to facilitate speech intelligibility
Abstract
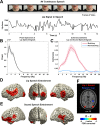
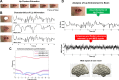
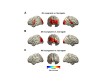
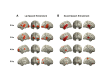
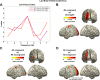
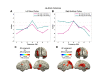
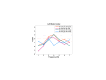
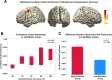
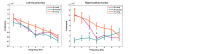
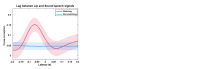
During continuous speech, lip movements provide visual temporal signals that facilitate speech processing. Here, using MEG we directly investigated how these visual signals interact with rhythmic brain activity in participants listening to and seeing the speaker. First, we investigated coherence between oscillatory brain activity and speaker's lip movements and demonstrated significant entrainment in visual cortex. We then used partial coherence to remove contributions of the coherent auditory speech signal from the lip-brain coherence. Comparing this synchronization between different attention conditions revealed that attending visual speech enhances the coherence between activity in visual cortex and the speaker's lips. Further, we identified a significant partial coherence between left motor cortex and lip movements and this partial coherence directly predicted comprehension accuracy. Our results emphasize the importance of visually entrained and attention-modulated rhythmic brain activity for the enhancement of audiovisual speech processing.
Keywords: electroencephalography; human; language; lip movements; magnetoencephalography; neuroscience; oscillations; speech.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Comment in
-
I see what you are saying.Elife. 2016 Jun 9;5:e17693. doi: 10.7554/eLife.17693. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27278639 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahissar E, Nagarajan S, Ahissar M, Protopapas A, Mahncke H, Merzenich MM. Speech comprehension is correlated with temporal response patterns recorded from auditory cortex. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2001;98:13367–13372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.201400998. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Behne D, Wang Y, Belsby SO, Kaasa S, Simonsen L, Back K. Visual field advantage in the perception of audiovisual speech segments. International Conference on Auditory-Visual Speech Processing. AVSP-2008; Queensland, Australia. 2008. pp. 47–50.
-
- Besl PJ, McKay HD. A method for registration of 3-D shapes. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. 1992;14:239–256. doi: 10.1109/34.121791. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

