Role of Fyn-mediated NMDA receptor function in prediabetic neuropathy in mice
- PMID: 27146985
- PMCID: PMC4978791
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00229.2016
Role of Fyn-mediated NMDA receptor function in prediabetic neuropathy in mice
Abstract
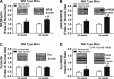
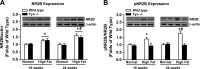
Diabetic neuropathy is a common complication of diabetes. This study evaluated the role of Fyn kinase and N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) in the spinal cord in diabetic neuropathy using an animal model of high-fat diet-induced prediabetes. We found that prediabetic wild-type mice exhibited tactile allodynia and thermal hypoalgesia after a 16-wk high-fat diet, relative to normal diet-fed wild-type mice. Furthermore, prediabetic wild-type mice exhibited increased tactile allodynia and thermal hypoalgesia at 24 wk relative to 16 wk. Such phenomena were correlated with increased expression and activation of NR2B subunit of NMDARs, as well as Fyn-NR2B interaction in the spinal cord. Fyn(-/-) mice developed prediabetes after 16-wk high-fat diet treatment and exhibited thermal hypoalgesia, without showing tactile allodynia or altered expression and activation of NR2B subunit, relative to normal diet-fed Fyn(-/-) mice. Finally, intrathecal administrations of Ro 25-6981 (selective NR2B subunit-containing NMDAR antagonist) dose-dependently alleviated tactile allodynia, but not thermal hypoalgesia, at 16 and 24 wk in prediabetic wild-type mice. Our results suggested that Fyn-mediated NR2B signaling plays a critical role in regulation of prediabetic neuropathy and that the increased expression/function of NR2B subunit-containing NMDARs may contribute to the progression of neuropathy in type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: Fyn kinase; NMDA; neuropathic pain; prediabetes; spinal cord.
Copyright © 2016 the American Physiological Society.
Figures


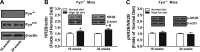
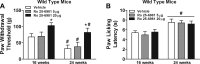
Similar articles
-
Contribution of the spinal cord BDNF to the development of neuropathic pain by activation of the NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in rats with spinal nerve ligation.Exp Neurol. 2010 Apr;222(2):256-66. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2010.01.003. Epub 2010 Jan 14. Exp Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20079352
-
Role of the spinal cord NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in the development of neuropathic pain.Exp Neurol. 2009 Feb;215(2):298-307. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.10.018. Epub 2008 Nov 12. Exp Neurol. 2009. PMID: 19046970
-
Role of A3 adenosine receptor in diabetic neuropathy.J Neurosci Res. 2016 Oct;94(10):936-46. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23774. Epub 2016 Jun 19. J Neurosci Res. 2016. PMID: 27319979
-
Role of sigma 1 receptor in high fat diet-induced peripheral neuropathy.Biol Chem. 2017 Sep 26;398(10):1141-1149. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2017-0117. Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28525360
-
Protein Kinase C (PKC)-mediated TGF-β Regulation in Diabetic Neuropathy: Emphasis on Neuro-inflammation and Allodynia.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024;24(7):777-788. doi: 10.2174/0118715303262824231024104849. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 37937564 Review.
Cited by
-
BDNF Contributes to Spinal Long-Term Potentiation and Mechanical Hypersensitivity Via Fyn-Mediated Phosphorylation of NMDA Receptor GluN2B Subunit at Tyrosine 1472 in Rats Following Spinal Nerve Ligation.Neurochem Res. 2017 Oct;42(10):2712-2729. doi: 10.1007/s11064-017-2274-0. Epub 2017 May 11. Neurochem Res. 2017. PMID: 28497343
-
Pathogenic gene connections in type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a bioinformatics analysis and mouse model investigations experiments.Nutr Diabetes. 2024 Aug 6;14(1):60. doi: 10.1038/s41387-024-00323-0. Nutr Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 39107295 Free PMC article.
-
Crumbling Pathogenesis and Biomarkers for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy.Biomedicines. 2025 Feb 8;13(2):413. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13020413. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40002826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Function of Adenosine 2A Receptor in High-Fat Diet-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy.J Diabetes Res. 2020 May 22;2020:7856503. doi: 10.1155/2020/7856503. eCollection 2020. J Diabetes Res. 2020. PMID: 32566683 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe T, Matsumura S, Katano T, Mabuchi T, Takagi K, Xu L, Yamamoto A, Hattori K, Yagi T, Watanabe M, Nakazawa T, Yamamoto T, Mishina M, Nakai Y, Ito S. Fyn kinase-mediated phosphorylation of NMDA receptor NR2B subunit at Tyr1472 is essential for maintenance of neuropathic pain. Eur J Neurosci 22: 1445–1454, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Bai HP, Liu P, Wu YM, Guo WY, Guo YX, Wang XL. Activation of spinal GABAB receptors normalizes N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor in diabetic neuropathy. J Neurol Sci 341: 68–72, 2014. - PubMed
-
- Boulton AJ, Vinik AI, Arezzo JC, Bril V, Feldman EL, Freeman R, Malik RA, Maser RE, Sosenko JM, Ziegler D. Diabetic neuropathies: a statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 28: 956–962, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Boyce S, Wyatt A, Webb JK, O'Donnell R, Mason G, Rigby M, Sirinathsinghji D, Hill RG, Rupniak NM. Selective NMDA NR2B antagonists induce antinociception without motor dysfunction: correlation with restricted localisation of NR2B subunit in dorsal horn. Neuropharmacology 38: 611–623, 1999. - PubMed
-
- Bujalska M. Effect of cannabinoid receptor agonists on streptozotocin-induced hyperalgesia in diabetic neuropathy. Pharmacology 82: 193–200, 2008. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

