Assessment of red blood cell distribution width as a prognostic marker in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- PMID: 27147570
- PMCID: PMC5078056
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.9055
Assessment of red blood cell distribution width as a prognostic marker in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Abstract
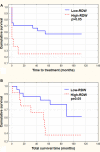
Red blood cell distribution width (RDW) is a quantitative measure of the variability in size of circulating erythrocytes. It was recently reported that RDW is a prognostic factor for infection diseases, cardiovascular and pulmonary diseases, as well as some neoplasms. Moreover, RDW is remarkably strong predictor of longevity, including all causes of death, for adults aged 45 years and older. To explain this occurrence it was proposed that persistent IGFs/mTOR signaling is one of the factors that play a role in affecting the RDW and mortality.The above observations induced us to analyze the prognostic role of RDW in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) being the most frequent type of adult leukemia in Western countries. The obtained results have shown that RDW may be considered as a potential CLL prognostic marker. Elevated RDW level at the moment of diagnosis was associated with advanced disease and presence of other poor prognostic factors. It is also connected with overall survival indicating shorter time in patients with elevated RDW. It is possible that the presently observed correlation between mortality and RDW of the CLL patients is affected by their metabolic (IGF-1/mTOR driven)- rather than chronological- aging. The patients with high level of RDW are expected to have an increased persistent level of IGF-1/mTOR signaling. Within the framework of personalized therapy, these CLL patients therefore would be expected to be more sensitive to the treatment with mTOR inhibitors.
Keywords: CD38; CLL; RDW; ZAP-70; mTOR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Higher red blood cell distribution width at diagnose is a simple negative prognostic factor in chronic phase-chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: A retrospective study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Mar 12;100(10):e24003. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000024003. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33725811 Free PMC article.
-
Validation and potential mechanisms of red cell distribution width as a prognostic marker in heart failure.J Card Fail. 2010 Mar;16(3):230-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2009.11.003. Epub 2009 Dec 29. J Card Fail. 2010. PMID: 20206898 Free PMC article.
-
Red blood cell distribution width predicts long-term mortality in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury: a retrospective database study.Sci Rep. 2020 Mar 12;10(1):4563. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-61516-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32165684 Free PMC article.
-
Red cell distribution width and mortality in older adults: a meta-analysis.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2010 Mar;65(3):258-65. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glp163. Epub 2009 Oct 30. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2010. PMID: 19880817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the B cell receptor pathway in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Leuk Lymphoma. 2012 Dec;53(12):2362-70. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2012.695781. Leuk Lymphoma. 2012. PMID: 22616724 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic role of RDW in hematological malignancies: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Cell Int. 2018 Apr 23;18:61. doi: 10.1186/s12935-018-0558-3. eCollection 2018. Cancer Cell Int. 2018. PMID: 29713244 Free PMC article.
-
Red Blood Cell Distribution Width Is a Predictive Factor of Anthracycline-Induced Cardiotoxicity.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020 Oct 30;7:594685. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.594685. eCollection 2020. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020. PMID: 33330656 Free PMC article.
-
Red cell distribution width and common disease onsets in 240,477 healthy volunteers followed for up to 9 years.PLoS One. 2018 Sep 13;13(9):e0203504. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203504. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30212481 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Red blood cell distribution width and platelet counts are independent prognostic factors and improve the predictive ability of IPI score in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients.BMC Cancer. 2019 Nov 11;19(1):1084. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6281-1. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31711453 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic role of pretreatment red blood cell distribution width in patients with cancer: A meta-analysis of 49 studies.J Cancer. 2019 Jul 10;10(18):4305-4317. doi: 10.7150/jca.31598. eCollection 2019. J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31413750 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Calligaris-Cappio F, Hamblin TJ. B-Cell Chronic Lymphocytic leukemia: A Bird of a Different Feather. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:399–408. - PubMed
-
- Chiorazzi N, Rai KR, Ferrarini M. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:804–815. - PubMed
-
- Hamblin TJ, Oscier DG. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: the nature of the leukemic cells. Blood Rev. 1997;11:119–122. - PubMed
-
- Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E, Aldler H, Rattan S, Keating M, Rai K, Rassenti L, Kipps T, Negrini M, et al. Frequent deletions and downregulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:15524–15529. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

