iROS-gPseKNC: Predicting replication origin sites in DNA by incorporating dinucleotide position-specific propensity into general pseudo nucleotide composition
- PMID: 27147572
- PMCID: PMC5085147
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.9057
iROS-gPseKNC: Predicting replication origin sites in DNA by incorporating dinucleotide position-specific propensity into general pseudo nucleotide composition
Abstract
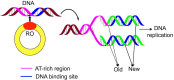
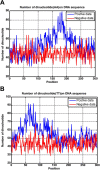
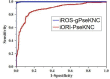
DNA replication, occurring in all living organisms and being the basis for biological inheritance, is the process of producing two identical replicas from one original DNA molecule. To in-depth understand such an important biological process and use it for developing new strategy against genetics diseases, the knowledge of duplication origin sites in DNA is indispensible. With the explosive growth of DNA sequences emerging in the postgenomic age, it is highly desired to develop high throughput tools to identify these regions purely based on the sequence information alone. In this paper, by incorporating the dinucleotide position-specific propensity information into the general pseudo nucleotide composition and using the random forest classifier, a new predictor called iROS-gPseKNC was proposed. Rigorously cross-validations have indicated that the proposed predictor is significantly better than the best existing method in sensitivity, specificity, overall accuracy, and stability. Furthermore, a user-friendly web-server for iROS-gPseKNC has been established at http://www.jci-bioinfo.cn/iROS-gPseKNC, by which users can easily get their desired results without the need to bother the complicated mathematics, which were presented just for the integrity of the methodology itself.
Keywords: general pseudo nucleotide composition; iROS-gPseKNC; origin of replication; position-specific dinucleotide propensity; random forest.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
iOri-Human: identify human origin of replication by incorporating dinucleotide physicochemical properties into pseudo nucleotide composition.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 25;7(43):69783-69793. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11975. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27626500 Free PMC article.
-
iRNAm5C-PseDNC: identifying RNA 5-methylcytosine sites by incorporating physical-chemical properties into pseudo dinucleotide composition.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 20;8(25):41178-41188. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17104. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28476023 Free PMC article.
-
pLoc-mVirus: Predict subcellular localization of multi-location virus proteins via incorporating the optimal GO information into general PseAAC.Gene. 2017 Sep 10;628:315-321. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.07.036. Epub 2017 Jul 18. Gene. 2017. PMID: 28728979
-
iDNA-Methyl: identifying DNA methylation sites via pseudo trinucleotide composition.Anal Biochem. 2015 Apr 1;474:69-77. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2014.12.009. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Anal Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25596338
-
iPPI-Esml: An ensemble classifier for identifying the interactions of proteins by incorporating their physicochemical properties and wavelet transforms into PseAAC.J Theor Biol. 2015 Jul 21;377:47-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2015.04.011. Epub 2015 Apr 20. J Theor Biol. 2015. PMID: 25908206
Cited by
-
iPhos-PseEn: identifying phosphorylation sites in proteins by fusing different pseudo components into an ensemble classifier.Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 9;7(32):51270-51283. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9987. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27323404 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of Newly Identified Brain eQTL Genes and Their Interactors in Schizophrenia.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018 Sep 7;12:433-442. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.05.026. Epub 2018 Jul 11. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018. PMID: 30195780 Free PMC article.
-
iSulfoTyr-PseAAC: Identify Tyrosine Sulfation Sites by Incorporating Statistical Moments via Chou's 5-steps Rule and Pseudo Components.Curr Genomics. 2019 May;20(4):306-320. doi: 10.2174/1389202920666190819091609. Curr Genomics. 2019. PMID: 32030089 Free PMC article.
-
Pse-Analysis: a python package for DNA/RNA and protein/ peptide sequence analysis based on pseudo components and kernel methods.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 21;8(8):13338-13343. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14524. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28076851 Free PMC article.
-
iCrotoK-PseAAC: Identify lysine crotonylation sites by blending position relative statistical features according to the Chou's 5-step rule.PLoS One. 2019 Nov 21;14(11):e0223993. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223993. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31751380 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zakrzewska-Czerwinska J, Jakimowicz D, Zawilak-Pawlik A, Messer W. Regulation of the initiation of chromosomal replication in bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2007;31:378–387. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Feng P, Lin H. Prediction of replication origins by calculating DNA structural properties. Febs Letters. 2012;586:934–938. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

