Laboratory Diagnosis of Congenital Toxoplasmosis
- PMID: 27147724
- PMCID: PMC5035424
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00487-16
Laboratory Diagnosis of Congenital Toxoplasmosis
Abstract
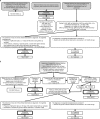
Recent studies have demonstrated that screening and treatment for toxoplasmosis during gestation result in a decrease of vertical transmission and clinical sequelae. Early treatment was associated with improved outcomes. Thus, laboratory methods should aim for early identification of infants with congenital toxoplasmosis (CT). Diagnostic approaches should include, at least, detection of Toxoplasma IgG, IgM, and IgA and a comprehensive review of maternal history, including the gestational age at which the mother was infected and treatment. Here, we review laboratory methods for the diagnosis of CT, with emphasis on serological tools. A diagnostic algorithm that takes into account maternal history is presented.
Copyright © 2016 Pomares and Montoya.
Figures
References
-
- Peyron F, Wallon M, Kieffer F, Garweg JG. 2015. Toxoplasmosis, p. 949–1042. In Wilson CB, Nizet V, Maldonado Y, Remington JS, Klein JO (ed), Remington and Klein's infectious diseases of the fetus and newborn infant. Elsevier Health Sciences, Oxford, United Kingdom.
-
- Cortina-Borja M, Tan HK, Wallon M, Paul M, Prusa A, Buffolano W, Malm G, Salt A, Freeman K, Petersen E, Gilbert RE, European Multicentre Study on Congenital Toxoplasmosis (EMSCOT). 2010. Prenatal treatment for serious neurological sequelae of congenital toxoplasmosis: an observational prospective cohort study. PLoS Med 7:e1000351. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1000351. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous