Mild Traumatic Brain Injury with Social Defeat Stress Alters Anxiety, Contextual Fear Extinction, and Limbic Monoamines in Adult Rats
- PMID: 27147992
- PMCID: PMC4835499
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2016.00071
Mild Traumatic Brain Injury with Social Defeat Stress Alters Anxiety, Contextual Fear Extinction, and Limbic Monoamines in Adult Rats
Abstract
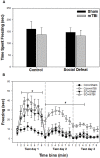
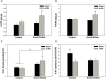
Mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) produces symptoms similar to those typifying posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in humans. We sought to determine whether a rodent model of stress concurrent with mTBI produces characteristics of PTSD such as impaired contextual fear extinction, while also examining concurrent alterations to limbic monoamine activity in brain regions relevant to fear and anxiety states. Male rats were exposed to social stress or control conditions immediately prior to mTBI induction, and 6 days later were tested either for anxiety-like behavior using the elevated plus maze (EPM), or for contextual fear conditioning and extinction. Brains were collected 24 h after EPM testing, and tissue from various limbic regions analyzed for content of monoamines, their precursors and metabolites using HPLC with electrochemical detection. Either social defeat or mTBI alone decreased time spent in open arms of the EPM, indicating greater anxiety-like behavior. However, this effect was enhanced by the combination of treatments. Further, rats exposed to both social defeat and mTBI exhibited greater freezing within extinction sessions compared to all other groups, suggesting impaired contextual fear extinction. Social defeat combined with mTBI also had greater effects on limbic monoamines than either insult alone, particularly with respect to serotonergic effects associated with anxiety and fear learning. The results suggest social stress concurrent with mTBI produces provides a relevant animal model for studying the prevention and treatment of post-concussive psychobiological outcomes.
Keywords: anxiety; fear conditioning; mild traumatic brain injury; monoamine; posttraumatic stress disorder; social stress.
Figures



References
-
- Almeida-Suhett C. P., Prager E. M., Pidoplichko V., Figueiredo T. H., Marini A. M., Li Z., et al. (2014). Reduced GABAergic inhibition in the basolateral amygdala and the development of anxiety-like behaviors after mild traumatic brain injury. PLoS ONE 9:e102627 10.1371/journal.pone.0102627 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barr J. L., Scholl J. L., Solanki R. R., Watt M. J., Lowry C. A., Renner K. J., et al. (2013). Influence of chronic amphetamine treatment and acute withdrawal on serotonin synthesis and clearance mechanisms in the rat ventral hippocampus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 37 479–490. 10.1111/ejn.12050 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

