A Rat Model of Alzheimer's Disease Based on Abeta42 and Pro-oxidative Substances Exhibits Cognitive Deficit and Alterations in Glutamatergic and Cholinergic Neurotransmitter Systems
- PMID: 27148049
- PMCID: PMC4837344
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2016.00083
A Rat Model of Alzheimer's Disease Based on Abeta42 and Pro-oxidative Substances Exhibits Cognitive Deficit and Alterations in Glutamatergic and Cholinergic Neurotransmitter Systems
Abstract
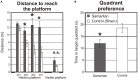
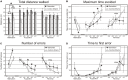
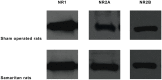
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is one of the most serious human, medical, and socioeconomic burdens. Here we tested the hypothesis that a rat model of AD (Samaritan; Taconic Pharmaceuticals, USA) based on the application of amyloid beta42 (Abeta42) and the pro-oxidative substances ferrous sulfate heptahydrate and L-buthionine-(S, R)-sulfoximine, will exhibit cognitive deficits and disruption of the glutamatergic and cholinergic systems in the brain. Behavioral methods included the Morris water maze (MWM; long-term memory version) and the active allothetic place avoidance (AAPA) task (acquisition and reversal), testing spatial memory and different aspects of hippocampal function. Neurochemical methods included testing of the NR1/NR2A/NR2B subunits of NMDA receptors in the frontal cortex and CHT1 transporters in the hippocampus, in both cases in the right and left hemisphere separately. Our results show that Samaritan rats(™) exhibit marked impairment in both the MWM and active place avoidance tasks, suggesting a deficit of spatial learning and memory. Moreover, Samaritan rats exhibited significant changes in NR2A expression and CHT1 activity compared to controls rats, mimicking the situation in patients with early stage AD. Taken together, our results corroborate the hypothesis that Samaritan rats are a promising model of AD in its early stages.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; animal model; cognition; hippocampus; learning and memory; neurochemistry of the acetylcholine system; sporadic AD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Time-dependent effect of oligomeric amyloid-β (1-42)-induced hippocampal neurodegeneration in rat model of Alzheimer's disease.Neurol Res. 2019 Feb;41(2):139-150. doi: 10.1080/01616412.2018.1544745. Epub 2018 Nov 19. Neurol Res. 2019. PMID: 30453864
-
Analysis of sensitivity to MK-801 treatment in a novel active allothetic place avoidance task and in the working memory version of the Morris water maze reveals differences between Long-Evans and Wistar rats.Neurosci Res. 2006 Aug;55(4):383-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2006.04.007. Epub 2006 May 19. Neurosci Res. 2006. PMID: 16712995
-
Subtle learning and memory impairment in an idiopathic rat model of Alzheimer's disease utilizing cholinergic depletions and β-amyloid.Brain Res. 2016 Sep 1;1646:12-24. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.05.033. Epub 2016 May 18. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 27208489
-
Rodent models of memory dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease and normal aging: moving beyond the cholinergic hypothesis.Life Sci. 1994;55(25-26):2037-49. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(94)00384-x. Life Sci. 1994. PMID: 7997063 Review.
-
[Aging of memory mechanisms].C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1994;188(5-6):469-86. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1994. PMID: 7780790 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Network Proteomics of the Lewy Body Dementia Brain Reveals Presynaptic Signatures Distinct from Alzheimer's Disease.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 24:2024.01.23.576728. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.23.576728. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Mol Neurodegener. 2024 Aug 6;19(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13024-024-00749-1. PMID: 38328211 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Network proteomics of the Lewy body dementia brain reveals presynaptic signatures distinct from Alzheimer's disease.Mol Neurodegener. 2024 Aug 6;19(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13024-024-00749-1. Mol Neurodegener. 2024. PMID: 39107789 Free PMC article.
-
Amelioration of Alzheimer's disease pathology and cognitive deficits by immunomodulatory agents in animal models of Alzheimer's disease.Neural Regen Res. 2019 Jul;14(7):1158-1176. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.251192. Neural Regen Res. 2019. PMID: 30804241 Free PMC article.
-
Age-Related Increase of Insulin-Degrading Enzyme Is Inversely Correlated with Cognitive Function in APPswe/PS1dE9 Mice.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Apr 22;24:2446-2455. doi: 10.12659/msm.909596. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 29680859 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling of Alzheimer's Disease to Study the Efficacy of Cell Therapy (Review).Bull Exp Biol Med. 2023 Aug;175(4):524-529. doi: 10.1007/s10517-023-05899-8. Epub 2023 Sep 28. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 37768457
References
-
- Arendt T., Bigl V., Arendt A., Tennstedt A. (1983). Loss of neurons in the nucleus basalis of Meynert in Alzheimer’s disease, paralysis agitans and Korsakoff’s disease. Acta. Neuropathol. 61, 101–108. - PubMed
-
- Bahník Š. (2014). Carousel Maze Manager (Version 0.4.0) Software Available from https://github.com/bahniks/CM_Manager_0_4_0
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

