Treating Post-traumatic Stress Disorder in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis: A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing the Efficacy of Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing and Relaxation Therapy
- PMID: 27148134
- PMCID: PMC4838623
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00526
Treating Post-traumatic Stress Disorder in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis: A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing the Efficacy of Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing and Relaxation Therapy
Abstract
Objective: Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a demyelinating autoimmune disease that imposes a significant emotional burden with heavy psychosocial consequences. Several studies have investigated the association between MS and mental disorders such as depression and anxiety, and recently researchers have focused also on Post-traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). This is the first study that investigates the usefulness of proposing a treatment for PTSD to patients with MS.
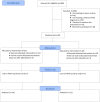
Methods: A randomized controlled trial with patients with MS diagnosed with PTSD comparing Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR; n = 20) and Relaxation Therapy (RT; n = 22). The primary outcome measure was the proportion of participants that no longer meet PTSD diagnosis as measured with Clinician Administered PTSD Scale 6-months after the treatment.
Results: The majority of patients were able to overcome their PTSD diagnosis after only 10 therapy sessions. EMDR treatment appears to be more effective than RT in reducing the proportion of patients with MS suffering from PTSD. Both treatments are effective in reducing PTSD severity, anxiety and depression symptoms, and to improve Quality of Life.
Conclusion: Although our results can only be considered preliminary, this study suggests that it is essential that PTSD symptoms are detected and that brief and cost-effective interventions to reduce PTSD and associated psychological symptoms are offered to patients, in order to help them to reduce the psychological burden associated with their neurological condition.
Trial registration: NCT01743664, https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01743664.
Keywords: EMDR; PTSD; multiple sclerosis; relaxation therapy; stress.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (1994). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th Edn Washington DC: American Psychiatric Pub.
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.
-
- Andrykowski M. A., Cordova M. J., McGrath P. C., Sloan D. A., Kenady D. E. (2000). Stability and change in posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms following breast cancer treatment: a 1-year follow-up. Psychooncology 9 69–78. 10.1002/(SICI)1099-1611(200001/02)9:1<69::AID-PON439>3.3.CO;2-I - DOI - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical