Cost-effectiveness of neoadjuvant concurrent chemoradiotherapy versus esophagectomy for locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A population-based matched case-control study
- PMID: 27148413
- PMCID: PMC4846616
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.12326
Cost-effectiveness of neoadjuvant concurrent chemoradiotherapy versus esophagectomy for locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A population-based matched case-control study
Abstract
Background: Neoadjuvant concurrent chemoradiotherapy (NCCRT) is often considered for locally-advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (LA-ESCC) patients; however, no data regarding the cost-effectiveness of this treatment is available. Our study aimed to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of NCCRT versus esophagectomy for LA-ESCC at population level.
Methods: We identified LA-ESCC patients diagnosed within 2008-2009 and treated with either NCCRT or esophagectomy through the Taiwan Cancer Registry. We included potential confounding covariables (age, gender, residency, comorbidity, social-economic status, disease stage, treating hospital level and surgeon's experience, and the use of endoscopic ultrasound before treatment) and used propensity score (PS) to construct a 1:1 population. The duration of interest was three years within the date of diagnosis. Effectiveness was measured as overall survival. We took the payer's perspective and converted the cost to 2014 United States dollars (USD). In sensitivity analysis, we evaluated the potential impact of an unmeasured confounder on the statistical significance of incremental net benefit at suggested willingness-to-pay.
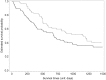
Results: Our study population constituted 150 PS matched subjects. The mean cost (2014 USD) and survival (year) were higher for NCCRT compared with esophagectomy (US$91,460 vs. $75,836 for cost; 2.2 vs. 1.8 for survival) with an estimated incremental cost-effectiveness ratio of US$39,060/life-year.
Conclusions: When compared to esophagectomy, NCCRT is likely to improve survival and is probably more cost-effective. Cost-effectiveness results should be interpreted with caution given our results were sensitive to potential unmeasured confounder(s) in sensitivity analysis.
Keywords: Cost‐effectiveness analysis; Taiwan; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; neoadjuvant concurrent chemoradiotherapy; propensity‐score matching.
Figures


References
-
- Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA, Luketich JD. Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet 2013; 381: 400–412. - PubMed
-
- Health Promotion Administration, Ministry of Health and Welfare . [Taiwan Cancer Registry Database 2008 Annual Report] (In Chinese). 2010. [Cited 28 Oct 2015.] Available at: http://tcr.cph.ntu.edu.tw/uploadimages/CA10_LF97.pdf
-
- Health Promotion Administration, Ministry of Health and Welfare . [Taiwan Cancer Registry Database 2011 Annual Report] (In Chinese). 2014. [Cited 28 Oct 2015.] Available at: http://tcr.cph.ntu.edu.tw/uploadimages/CA15_LF100_20140415.pdf
-
- Wang DB, Zhang X, Han HL, Xu YJ, Sun DQ, Shi ZL. Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy could improve survival outcomes for esophageal carcinoma: A meta‐analysis. Dig Dis Sci 2012; 57: 3226–3233. - PubMed
-
- Hong JC, Murphy JD, Wang SJ, Koong AC, Chang DT. Chemoradiotherapy before and after surgery for locally advanced esophageal cancer: A SEER‐Medicare analysis. Ann Surg Oncol 2013; 20: 3999–4007. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

