Overexpression of micro ribonucleic acid-591 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion of malignant pleural mesothelioma cells
- PMID: 27148420
- PMCID: PMC4846623
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.12336
Overexpression of micro ribonucleic acid-591 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion of malignant pleural mesothelioma cells
Abstract
Background: Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is an aggressive cancer refractory to current therapies. Reduced expression of micro ribonucleic acid (miR)-591 in a range of cancer types has suggested it is a potent tumor suppressor, and overexpression has been shown to inhibit tumor cell growth. The role of miR-591 in MPM is largely unknown.
Methods: miR-591 was over-expressed in vitro using micro RNA mimics in three MPM cell lines (H513, H2052, H2373), and effects on tumor cell growth, proliferation, invasion, and target gene expression were assessed.
Results: miR-591 mimic was introduced into MPM cell lines to overexpress this microRNA. The cellular growth, proliferation, and invasive capability was significantly inhibited after overexpression of miR-591. Growth inhibition caused by miR-591 correlated with upregulation of p21 and Bax. Reduced invasive capability correlated with downregulation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and transforming growth factor-β1.
Conclusion: miR-591 is a potent tumor suppressor in MPM. Overexpression of miR-591 may represent a novel therapeutic approach for MPM.
Keywords: Malignant pleural mesothelioma; miR‐591; microRNA.
Figures
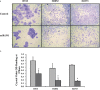
 , Control;
, Control;  , miR‐591.
, miR‐591.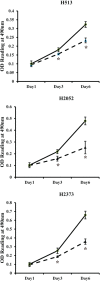
 , miR‐591;
, miR‐591;  , Control.
, Control.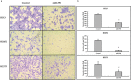
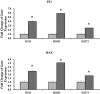
 , Control;
, Control;  , miR‐591.
, miR‐591.Similar articles
-
Restoring expression of miR-16: a novel approach to therapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma.Ann Oncol. 2013 Dec;24(12):3128-35. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt412. Epub 2013 Oct 22. Ann Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24148817
-
miR-1 induces growth arrest and apoptosis in malignant mesothelioma.Chest. 2013 Nov;144(5):1632-1643. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-2770. Chest. 2013. PMID: 23828229 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic silencing of microRNA-34b/c plays an important role in the pathogenesis of malignant pleural mesothelioma.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Aug 1;17(15):4965-74. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-3040. Epub 2011 Jun 14. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21673066
-
Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in malignant pleural mesothelioma.Cancer Res. 2002 Sep 15;62(18):5242-7. Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12234991
-
Manipulating microRNAs for the Treatment of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: Past, Present and Future.Front Oncol. 2020 Feb 7;10:105. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00105. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32117755 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Myocardial microRNAs associated with reverse remodeling in human heart failure.JCI Insight. 2017 Jan 26;2(2):e89169. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.89169. JCI Insight. 2017. PMID: 28138556 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-591 functions as tumor suppressor in breast cancer by targeting TCF4 and inhibits Hippo-YAP/TAZ signaling pathway.Cancer Cell Int. 2019 Apr 24;19:108. doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-0818-x. eCollection 2019. Cancer Cell Int. 2019. PMID: 31049030 Free PMC article.
-
ACTL6A suppresses p21Cip1 tumor suppressor expression to maintain an aggressive mesothelioma cancer cell phenotype.Oncogenesis. 2021 Oct 23;10(10):70. doi: 10.1038/s41389-021-00362-7. Oncogenesis. 2021. PMID: 34689163 Free PMC article.
-
Circ_0091581 Promotes the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Through Targeting miR-591/FOSL2 Axis.Dig Dis Sci. 2021 Sep;66(9):3074-3085. doi: 10.1007/s10620-020-06641-4. Epub 2020 Oct 11. Dig Dis Sci. 2021. PMID: 33040214
References
-
- Guo G, Chmielecki J, Goparaju C et al Whole‐exome sequencing reveals frequent genetic alterations in BAP1, NF2, CDKN2A, and CUL1 in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Cancer Res 2015; 75: 264–269. - PubMed
-
- Hashim D, Boffetta P. Occupational and environmental exposures and cancers in developing countries. Ann Glob Health 2014; 80: 393–411. - PubMed
-
- Balatti V, Maniero S, Ferracin M et al MicroRNAs dysregulation in human malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Thorac Oncol 2011; 6: 844–851. - PubMed
-
- Busacca S, Germano S, De Cecco L et al MicroRNA signature of malignant mesothelioma with potential diagnostic and prognostic implications. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2010; 42: 312–319. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

