Common Genetic Variant Association with Altered HLA Expression, Synergy with Pyrethroid Exposure, and Risk for Parkinson's Disease: An Observational and Case-Control Study
- PMID: 27148593
- PMCID: PMC4853162
- DOI: 10.1038/npjparkd.2015.2
Common Genetic Variant Association with Altered HLA Expression, Synergy with Pyrethroid Exposure, and Risk for Parkinson's Disease: An Observational and Case-Control Study
Abstract
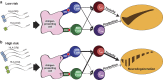
Background/objectives: The common non-coding single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs3129882 in HLA-DRA is associated with risk for idiopathic Parkinson's disease (PD). The location of the SNP in the major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II) locus implicates regulation of antigen presentation as a potential mechanism by which immune responses link genetic susceptibility to environmental factors in conferring lifetime risk for PD.
Methods: For immunophenotyping, blood cells from 81 subjects were analyzed by qRT-PCR and flow cytometry. A case-control study was performed on a separate cohort of 962 subjects to determine association of pesticide exposure and the SNP with risk of PD.
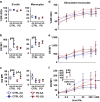
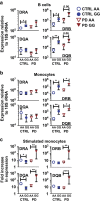
Results: Homozygosity for G at this SNP was associated with heightened baseline expression and inducibility of MHC class II molecules in B cells and monocytes from peripheral blood of healthy controls and PD patients. In addition, exposure to a commonly used class of insecticide, pyrethroids, synergized with the risk conferred by this SNP (OR = 2.48, p = 0.007), thereby identifying a novel gene-environment interaction that promotes risk for PD via alterations in immune responses.
Conclusions: In sum, these novel findings suggest that the MHC-II locus may increase susceptibility to PD through presentation of pathogenic, immunodominant antigens and/or a shift toward a more pro-inflammatory CD4+ T cell response in response to specific environmental exposures, such as pyrethroid exposure through genetic or epigenetic mechanisms that modulate MHC-II gene expression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Factor SA, Weiner WJ. Parkinson's Disease: Diagnosis and Clinical Management, 2nd edn. Demos Medical Publishing: New York, USA, 2007.
-
- Barnum CJ, Tansey MG. Neuroinflammation and non-motor symptoms: the dark passenger of Parkinson's disease? Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 2012; 12: 350–358. - PubMed
-
- Bower JH, Maraganore DM, Peterson BJ, McDonnell SK, Ahlskog JE, Rocca WA. Head trauma preceding PD: a case-control study. Neurology 2003; 60: 1610–1615. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

