Prediction of Mortality in Incident Hemodialysis Patients: A Validation and Comparison of CHADS2, CHA2DS2, and CCI Scores
- PMID: 27148867
- PMCID: PMC4858249
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154627
Prediction of Mortality in Incident Hemodialysis Patients: A Validation and Comparison of CHADS2, CHA2DS2, and CCI Scores
Abstract
Background: The CHADS2 and CHA2DS2 scores are usually applied for stroke prediction in atrial fibrillation patients, and the Charlson comorbidity index (CCI) is a commonly used scale for assessing morbidity. The role in assessing mortality with score system in hemodialysis is not clear and comparisons are lacking. We aimed at evaluating CHADS2, CHA2DS2, and CCI scores to predict mortality in incident hemodialysis patients.
Methods: Using data from the Nation Health Insurance system of Taiwan (NHIRD) from 1 January 2005 to 31 December 2009, individuals ≧20 y/o who began hemodialysis identified by procedure code and receiving dialysis for > 3 months were included for our study. Renal transplantation patients after dialysis or PD patients were excluded. We calculated the CHADS2, CHA2DS2, and CCI score according to the ICD-9 code and categorized the patients into three groups in each system: 0-1, 2-3, over 4. A total of 3046 incident hemodialysis patients enrolled from NHIRD were examined for an association between the separate scoring systems (CHADS2, CHA2DS2, and CCI score) and mortality.
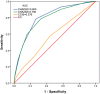
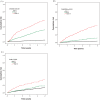
Results: CHADS2 and CHA2DS2 scores revealed good predictive value for total mortality (CHADS2 AUC = 0.805; CHA2DS2 AUC = 0.790). However, the CCI score did not reveal a similarly satisfying result (AUC = 0.576).
Conclusions: Our results show that CHADS2 and CHA2DS2 scores can be applied for mortality prediction in incident hemodialysis patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Incidence and prediction of ischemic stroke among atrial fibrillation patients with end-stage renal disease requiring dialysis.Heart Rhythm. 2014 Oct;11(10):1752-9. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2014.06.021. Epub 2014 Jun 18. Heart Rhythm. 2014. PMID: 24952148
-
Charlson Comorbidity Index is a predictor of outcomes in incident hemodialysis patients and correlates with phase angle and hospitalization.Int J Artif Organs. 2004 Apr;27(4):330-6. doi: 10.1177/039139880402700409. Int J Artif Organs. 2004. PMID: 15163067
-
Pre-stroke CHADS2 and CHA2DS2-VASc scores are useful in stratifying three-month outcomes in patients with and without atrial fibrillation.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013;36(4):273-80. doi: 10.1159/000353670. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013. PMID: 24135809
-
Atrial fibrillation: Utility of CHADS2 and CHA2DS2-VASc scores as predictors of readmission, mortality and resource utilization.Int J Cardiol. 2017 Oct 15;245:162-167. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.06.090. Int J Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28874288
-
Meta-analysis of CHADS2 versus CHA2DS2-VASc for predicting stroke and thromboembolism in atrial fibrillation patients independent of anticoagulation.Tex Heart Inst J. 2015 Feb 1;42(1):6-15. doi: 10.14503/THIJ-14-4353. eCollection 2015 Feb. Tex Heart Inst J. 2015. PMID: 25873792 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An artificial intelligence model to predict mortality among hemodialysis patients: A retrospective validated cohort study.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 29;15(1):27699. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06576-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40730809 Free PMC article.
-
Bariatric Surgery Did Not Increase the Risk of Gallstone Disease in Obese Patients: a Comprehensive Cohort Study.Obes Surg. 2019 Feb;29(2):464-473. doi: 10.1007/s11695-018-3532-1. Obes Surg. 2019. PMID: 30417273
-
Choice of antithrombotic therapy for patients with atrial fibrillation undergoing carotid angioplasty and stenting: a nationwide population-based study.Sci Rep. 2022 Jan 26;12(1):1417. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-05546-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35082380 Free PMC article.
-
Fasting blood glucose and the risk of all-cause mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus undergoing hemodialysis.Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2024 Sep;43(5):680-689. doi: 10.23876/j.krcp.23.098. Epub 2024 Jan 26. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2024. PMID: 38325864 Free PMC article.
-
The CHA2DS2-VASC Score Predicts Mortality in Patients Undergoing Coronary Angiography.Life (Basel). 2023 Oct 9;13(10):2026. doi: 10.3390/life13102026. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895408 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weller JM, Port FK, Swartz RD, Ferguson CW, Williams GW, Jacobs JF Jr. Analysis of survival of end-stage renal disease patients. Kidney Int. 1982;21(1):78–83. . - PubMed
-
- Wright LF. Survival in patients with end-stage renal disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 1991;17(1):25–8. . - PubMed
-
- Khan IH, Catto GR, Edward N, MacLeod AM. Death during the first 90 days of dialysis: a case control study. Am J Kidney Dis. 1995;25(2):276–80. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical