Immunogenicity and reactogenicity of the human rotavirus vaccine, RIX4414 oral suspension, when co-administered with routine childhood vaccines in Chinese infants
- PMID: 27149266
- PMCID: PMC4964624
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2015.1085143
Immunogenicity and reactogenicity of the human rotavirus vaccine, RIX4414 oral suspension, when co-administered with routine childhood vaccines in Chinese infants
Abstract
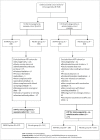
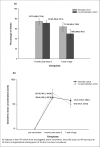
This study evaluated the immunogenicity of the human rotavirus (RV) vaccine (RIX4414) when co-administered with routine childhood vaccines in Chinese infants (NCT01171963). Healthy infants aged 6-16 weeks received 2 doses of either RIX4414 or placebo according to a 0, 1-month schedule. Infants received routine diphtheria-tetanus-acellular pertussis (DTPa) and oral poliovirus (OPV) vaccines either separately from or concomitantly with RIX4414/placebo (separate and co-administration cohorts, respectively). Anti-RV IgA seroconversion rates (one month post-dose-2) and seropositivity rates (at one year of age) were measured using ELISA. Immune responses against the DTPa and OPV antigens were measured one month post-DTPa dose-3 in the co-administration cohort. Solicited local and general symptoms were recorded for 8-days post-vaccination (total cohort). The according-to-protocol immunogenicity population included 511 infants in the separate cohort and 275 in the co-administration cohort. One month post-RIX4414 dose-2, anti-RV IgA seroconversion rates were 74.7% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 68.9-79.9) and 64.2% (95% CI: 55.4-72.3) in the separate and co-administration cohorts; seropositivity rates at one year of age were 71.5% (95% CI: 65.5-77.1) and 50.0% (95% CI: 40.9-59.1), respectively. One month post-DTPa dose-3, all infants in the co-administration cohort were seroprotected against diphtheria and tetanus, and seropositive for pertussis toxoid, pertactin and filamentous haemaglutinin. Two months post-OPV dose-3, seroprotection rates against anti-poliovirus types 1, 2 and 3 were >99% in the co-administration cohort. Reactogenicity profiles were similar in both cohorts. RIX4414 was immunogenic and well-tolerated in Chinese infants and did not appear to interfere with the immunogenicity and reactogenicity of co-administered routine childhood vaccines.
Keywords: China; DTPa; OPV; RIX4414; immunogenicity; reactogenicity; rotavirus; routine childhood vaccines.
Figures

References
-
- Kawai K, O'Brien MA, Goveia MG, Mast TC, El Khoury AC. Burden of rotavirus gastroenteritis and distribution of rotavirus strains in Asia: a systematic review. Vaccine 2012; 30:1244-54; PMID:22212128; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.12.092 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tate JE, Burton AH, Boschi-Pinto C, Steele AD, Duque J, Parashar UD. 2008 estimate of worldwide rotavirus-associated mortality in children younger than 5 years before the introduction of universal rotavirus vaccination programmes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis 2012; 12:136-41; PMID:22030330; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(11)70253-5 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rotavirus vaccines . WHO position paper - January 2013. Wkly Epidemiol Rec 2013; 88:49-64; PMID:23424730 - PubMed
-
- Yee EL, Fang ZY, Liu N, Hadler SC, Liang X, Wang H, Zhu X, Jiang B, Parashar U, Widdowson MA, et al. . Importance and challenges of accurately counting rotavirus deaths in China, 2002. Vaccine 2009; 27 Suppl 5:F46-9; PMID:19931719; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.08.065 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Duan ZJ, Liu N, Yang SH, Zhang J, Sun LW, Tang JY, Jin Y, Du ZQ, Xu J, Wu QB, et al. . Hospital-based surveillance of rotavirus diarrhea in the People's Republic of China, August 2003-July 2007. J Infect Dis 2009; 200 Suppl 1:S167-73; PMID:19817597; http://dx.doi.org/10.1086/605039 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
