Transient overexpression of exogenous APOBEC3A causes C-to-U RNA editing of thousands of genes
- PMID: 27149507
- PMCID: PMC5449087
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1184387
Transient overexpression of exogenous APOBEC3A causes C-to-U RNA editing of thousands of genes
Abstract
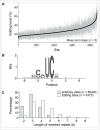
APOBEC3A cytidine deaminase induces site-specific C-to-U RNA editing of hundreds of genes in monocytes exposed to hypoxia and/or interferons and in pro-inflammatory macrophages. To examine the impact of APOBEC3A overexpression, we transiently expressed APOBEC3A in HEK293T cell line and performed RNA sequencing. APOBEC3A overexpression induces C-to-U editing at more than 4,200 sites in transcripts of 3,078 genes resulting in protein recoding of 1,110 genes. We validate recoding RNA editing of genes associated with breast cancer, hematologic neoplasms, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Alzheimer disease and primary pulmonary hypertension. These results highlight the fundamental impact of APOBEC3A overexpression on human transcriptome by widespread RNA editing.
Keywords: Cytidine deaminase; RNA editing; RNA seq; disease genes; epitranscriptomics.
Figures


Similar articles
-
APOBEC3A cytidine deaminase induces RNA editing in monocytes and macrophages.Nat Commun. 2015 Apr 21;6:6881. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7881. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 25898173 Free PMC article.
-
RNA editing enzyme APOBEC3A promotes pro-inflammatory M1 macrophage polarization.Commun Biol. 2021 Jan 22;4(1):102. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-01620-x. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 33483601 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial complex II regulates a distinct oxygen sensing mechanism in monocytes.Hum Mol Genet. 2017 Apr 1;26(7):1328-1339. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx041. Hum Mol Genet. 2017. PMID: 28204537 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of APOBEC3A and APOBEC3B in Human Papillomavirus Infection and Disease Progression.Viruses. 2017 Aug 21;9(8):233. doi: 10.3390/v9080233. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 28825669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolutionary analysis of RNA editing enzymes.Methods. 1998 May;15(1):41-50. doi: 10.1006/meth.1998.0604. Methods. 1998. PMID: 9614651 Review.
Cited by
-
Advantages and challenges associated with bisulfite-assisted nanopore direct RNA sequencing for modifications.RSC Chem Biol. 2023 Aug 23;4(11):952-964. doi: 10.1039/d3cb00081h. eCollection 2023 Nov 1. RSC Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 37920399 Free PMC article.
-
Therapy-induced APOBEC3A drives evolution of persistent cancer cells.Nature. 2023 Aug;620(7973):393-401. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06303-1. Epub 2023 Jul 5. Nature. 2023. PMID: 37407818 Free PMC article.
-
When MicroRNAs Meet RNA Editing in Cancer: A Nucleotide Change Can Make a Difference.Bioessays. 2018 Feb;40(2):10.1002/bies.201700188. doi: 10.1002/bies.201700188. Epub 2017 Dec 27. Bioessays. 2018. PMID: 29280160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased RNA Editing May Provide a Source for Autoantigens in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Cell Rep. 2018 Apr 3;23(1):50-57. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.03.036. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 29617672 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Editing Alters miRNA Function in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.Cancers (Basel). 2020 May 5;12(5):1159. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051159. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32380696 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nishikura K. Functions and regulation of RNA editing by ADAR deaminases. Annu Rev Biochem 2010; 79:321-49; PMID:20192758; http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-060208-105251 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bazak L, Haviv A, Barak M, Jacob-Hirsch J, Deng P, Zhang R, Isaacs FJ, Rechavi G, Li JB, Eisenberg E, et al.. A-to-I RNA editing occurs at over a hundred million genomic sites, located in a majority of human genes. Genome Res 2014; 24:365-76; PMID:24347612; http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/gr.164749.113 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ramaswami G, Lin W, Piskol R, Tan MH, Davis C, Li JB. Accurate identification of human alu and non-alu RNA editing sites. Nature methods 2012; 9:579-81; PMID:22484847; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1982 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li JB, Church GM. Deciphering the functions and regulation of brain-enriched A-to-I RNA editing. Nat Neurosci 2013; 16:1518-1522; PMID:24165678; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nn.3539 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Smith HC, Bennett RP, Kizilyer A, McDougall WM, Prohaska KM. Functions and regulation of the APOBEC family of proteins. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2012; 23:258-68; PMID:22001110; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.10.004 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
