Dopamine Autoreceptor Regulation of a Hypothalamic Dopaminergic Network
- PMID: 27149844
- PMCID: PMC4850423
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.03.062
Dopamine Autoreceptor Regulation of a Hypothalamic Dopaminergic Network
Abstract
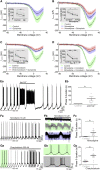
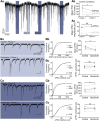
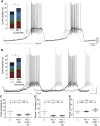
How autoreceptors contribute to maintaining a stable output of rhythmically active neuronal circuits is poorly understood. Here, we examine this issue in a dopamine population, spontaneously oscillating hypothalamic rat (TIDA) neurons, that underlie neuroendocrine control of reproduction and neuroleptic side effects. Activation of dopamine receptors of the type 2 family (D2Rs) at the cell-body level slowed TIDA oscillations through two mechanisms. First, they prolonged the depolarizing phase through a combination of presynaptic increases in inhibition and postsynaptic hyperpolarization. Second, they extended the discharge phase through presynaptic attenuation of calcium currents and decreased synaptic inhibition. Dopamine reuptake blockade similarly reconfigured the oscillation, indicating that ambient somatodendritic transmitter concentration determines electrical behavior. In the absence of D2R feedback, however, discharge was abolished by depolarization block. These results indicate the existence of an ultra-short feedback loop whereby neuroendocrine dopamine neurons tune network behavior to echoes of their own activity, reflected in ambient somatodendritic dopamine, and also suggest a mechanism for antipsychotic side effects.
Keywords: D2 receptor; arcuate nucleus; auto-inhibition; calcium currents; network oscillation; prolactin; tuberoinfundibular.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
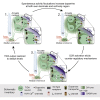
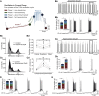
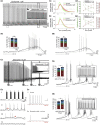
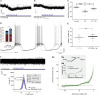
Comment in
-
Oscillating from Neurosecretion to Multitasking Dopamine Neurons.Cell Rep. 2016 Apr 26;15(4):681-682. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.04.013. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 27119847 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aghajanian G.K., Bunney B.S. Dopamine“autoreceptors”: pharmacological characterization by microiontophoretic single cell recording studies. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1977;297:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Andén N.E., Strömbom U. Adrenergic receptor blocking agents: effects on central noradrenaline and dopamine receptors and on motor activity. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 1974;38:91–103. - PubMed
-
- Annunziato L., Leblanc P., Kordon C., Weiner R.I. Differences in the kinetics of dopamine uptake in synaptosome preparations of the median eminence relative to other dopaminergically inervated brain regions. Neuroendocrinology. 1980;31:316–320. - PubMed
-
- Beckstead M.J., Grandy D.K., Wickman K., Williams J.T. Vesicular dopamine release elicits an inhibitory postsynaptic current in midbrain dopamine neurons. Neuron. 2004;42:939–946. - PubMed
-
- Bedran de Castro J.C., Khorram O., McCann S.M. Possible negative ultra-short loop feedback of luteinizing hormone releasing hormone (LHRH) in the ovariectomized rat. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1985;179:132–135. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

