Relationship Between Spiritual Coping and Survival in Patients with HIV
- PMID: 27149968
- PMCID: PMC4978670
- DOI: 10.1007/s11606-016-3668-4
Relationship Between Spiritual Coping and Survival in Patients with HIV
Abstract
Background: Studies of spirituality in initially healthy people have shown a survival advantage, yet there are fewer research studies in the medically ill, despite the widespread use of spirituality/religiousness to cope with serious physical illness. In addition, many studies have used limited measures such as religious service attendance.
Objective: We aimed to examine if, independent of medication adherence, the use of spirituality/religiousness to cope with HIV predicts survival over 17 years.
Design: This was a longitudinal study, started in 1997. Study materials were administered semi annually.
Participants: A diverse sample of 177 HIV patients initially in the mid-stage of disease (150-500 CD4-cells/mm(3); no prior AIDS-defining symptoms) participated in the study.
Main measures: Participants were administered a battery of psychosocial questionnaires and a blood draw. They completed interviews and essays to assess current stressors. Spiritual coping (overall/strategies) was rated by qualitative content analysis of interviews regarding stress and coping with HIV, and essays.
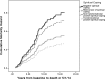
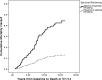
Key results: Controlling for medical variables (baseline CD4/viral load) and demographics, Cox regression analyses showed that overall positive spiritual coping significantly predicted greater survival over 17 years (mortality HR = 0.56, p = 0.039). Findings held even after controlling for health behaviors (medication adherence, substance use) and social support. Particular spiritual coping strategies that predicted longer survival included spiritual practices (HR = 0.26, p < 0.001), spiritual reframing (HR = 0.27, p = 0.006), overcoming spiritual guilt (HR = 0.24, p < 0.001), spiritual gratitude (HR = 0.40, p = 0.002), and spiritual empowerment (HR = 0.52, p = 0.024), indicating that people using these strategies were 2-4 times more likely to survive.
Conclusions: To our knowledge this is the first study showing a prospective relationship of spiritual coping in people who are medically ill with survival over such a long period of time, and also specifically identifies several strategies of spirituality that may be beneficial.
Keywords: HIV; spiritual coping; spiritual practices; spiritual reframing; spirituality; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they do not have a conflict of interest.
Funders
The parent study was funded by NIH: R01MH53791 and MH066697, (G. Ironson, PI) and the spiritual coping substudy was funded by the Templeton foundation (G. Ironson, PI; H. Kremer, Co-PI).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Spiritual coping predicts CD4-cell preservation and undetectable viral load over four years.AIDS Care. 2015;27(1):71-9. doi: 10.1080/09540121.2014.952220. Epub 2014 Oct 8. AIDS Care. 2015. PMID: 25297848
-
Longitudinal spiritual coping with trauma in people with HIV: implications for health care.AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2014 Mar;28(3):144-54. doi: 10.1089/apc.2013.0280. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2014. PMID: 24601735 Free PMC article.
-
Spiritual transformation, psychological well-being, health, and survival in people with HIV.Int J Psychiatry Med. 2009;39(3):263-81. doi: 10.2190/PM.39.3.d. Int J Psychiatry Med. 2009. PMID: 19967899
-
Spirituality and chronic illness.Image J Nurs Sch. 1998;30(3):275-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1547-5069.1998.tb01305.x. Image J Nurs Sch. 1998. PMID: 9753845 Review.
-
Spirituality and HIV disease: an integrated perspective.J Assoc Nurses AIDS Care. 2001 May-Jun;12(3):58-65. doi: 10.1016/s1055-3290(06)60144-1. J Assoc Nurses AIDS Care. 2001. PMID: 11387805 Review.
Cited by
-
Frequency of Private Prayer Predicts Survival Over 6 Years in a Nationwide U.S. Sample of Individuals with a Chronic Illness.J Relig Health. 2024 Aug;63(4):2910-2923. doi: 10.1007/s10943-023-01870-z. Epub 2023 Jul 29. J Relig Health. 2024. PMID: 37515683 Free PMC article.
-
Religion, Spirituality, and Risk of End-Stage Kidney Disease Among Adults of Low Socioeconomic Status in the Southeastern United States.J Health Care Poor Underserved. 2020;31(4):1727-1746. doi: 10.1353/hpu.2020.0129. J Health Care Poor Underserved. 2020. PMID: 33416749 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the role of religious beliefs in adherence to antiretroviral therapy among Pentecostal Christians living with HIV in sub-Saharan Africa: a scoping review.BMC Public Health. 2023 Sep 11;23(1):1768. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16616-5. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37697279 Free PMC article.
-
Praying for People You Know Predicts Survival over 17 Years Among People Living with HIV in the U.S.J Relig Health. 2022 Oct;61(5):4081-4095. doi: 10.1007/s10943-022-01622-5. Epub 2022 Aug 23. J Relig Health. 2022. PMID: 35999335 Free PMC article.
-
"Which comes first": Religious/spiritual engagement or health? Initial observations from longitudinal analyses.PLoS One. 2025 May 7;20(5):e0320410. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320410. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40333637 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

