Milk-derived bioactive peptides and their health promoting effects: a potential role in atherosclerosis
- PMID: 27151091
- PMCID: PMC5338169
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.13002
Milk-derived bioactive peptides and their health promoting effects: a potential role in atherosclerosis
Abstract
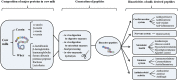
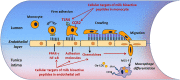
Bioactive peptides derived from milk proteins are food components that, in addition to their nutritional value, retain many biological properties and have therapeutic effects in several health disorders, including cardiovascular disease. Amongst these, atherosclerosis is the underlying cause of heart attack and strokes. It is a progressive dyslipidaemic and inflammatory disease where accumulation of oxidized lipids and inflammatory cells leads to the formation of an atherosclerotic plaque in the vessel wall. Milk-derived bioactive peptides can be released during gastrointestinal digestion, food processing or by enzymatic and bacterial fermentation and are considered to promote diverse beneficial effects such as lipid lowering, antihypertensive, immnomodulating, anti-inflammatory and antithrombotic effects. In this review, an overview of the diverse biological effects of these compounds is given, particularly focusing on their beneficial properties on cardiovascular disease and proposing novel mechanisms of action responsible for their bioactivity. Attempts to prevent cardiovascular diseases target modifications of several risk factors such as high blood pressure, obesity, high blood concentrations of lipids or insulin resistance. Milk-derived bioactive peptides are a source of health-enhancing components and the potential health benefit of these compounds has a growing commercial potential. Consequently, they have been incorporated as ingredients in functional foods, as dietary supplements and as pharmaceuticals to promote health and reduce risk of chronic diseases.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; bioactive peptides; cardiovascular disease; immunomodulation; inflammation; milk proteins.
© 2016 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Schanbacher FL, Talhouk RS, Murray FA. Biology and origin of bioactive peptides in milk. Livest Prod Sci 1997; 50: 105–23.
-
- Wong DW, Camirand WM, Pavlath AE. Structures and functionalities of milk proteins. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 1996; 36: 807–44. - PubMed
-
- Korhonen H, Pihlanto A. Technological options for the production of health‐promoting proteins and peptides derived from milk and colostrum. Curr Pharm Des 2007; 13: 829–43. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto N. Antihypertensive peptides derived from food proteins. Biopolymers 1997; 43: 129–34. - PubMed
-
- Lahov E, Regelson W. Antibacterial and immunostimulating casein‐derived substances from milk: casecidin, isracidin peptides. Food Chem Toxicol 1996; 34: 131–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

