Sinusoidal communication in liver fibrosis and regeneration
- PMID: 27151183
- PMCID: PMC4992446
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.04.018
Sinusoidal communication in liver fibrosis and regeneration
Abstract
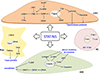
Cellular crosstalk is a process through which a message is transmitted within an individual cell (intracellular crosstalk) or between different cells (intercellular crosstalk). Intercellular crosstalk within the liver microenvironment is critical for the maintenance of normal hepatic functions and for cells survival. Hepatic cells are closely connected to each other, work in synergy, and produce molecules that modulate their differentiation and activity. This review summarises the current knowledge regarding paracrine communication networks in parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells in liver fibrosis due to chronic injury, and regeneration after partial hepatectomy.
Keywords: Cirrhosis; HSC; Hepatic stellate cells; Hepatocytes; Ischemia/reperfusion; Kupffer cells; LSEC; Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells; Portal hypertension; Regeneration; Transplantation.
Copyright © 2016 European Association for the Study of the Liver. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Cogger VC, Warren A, Fraser R, Ngu M, McLean AJ, le Couteur DG. Hepatic sinusoidal pseudocapillarization with aging in the non-human primate. Exp Gerontol. 2003;38:1101–1107. - PubMed
-
- McLean AJ, Cogger VC, Chong GC, Warren A, Markus AM, Dahlstrom JE, et al. Age-related pseudocapillarization of the human liver. J Pathol. 2003;200:112–117. - PubMed
-
- Schaffner F, Poper H. Capillarization of hepatic sinusoids in man. Gastroenterology. 1963;44:239–242. 239–242. - PubMed
-
- Urashima S, Tsutsumi m, Nakase K, Wang JS, Takada A. Studies on capillarization of the hepatic sinusoids in alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Alcohol Suppl. 1993;1B:77–84. 77–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

