Apolipoprotein E lipoprotein particles inhibit amyloid-β uptake through cell surface heparan sulphate proteoglycan
- PMID: 27151330
- PMCID: PMC4857252
- DOI: 10.1186/s13024-016-0099-y
Apolipoprotein E lipoprotein particles inhibit amyloid-β uptake through cell surface heparan sulphate proteoglycan
Abstract
Background: The accumulation, aggregation and deposition of amyloid-β (Aβ) peptides in the brain are central to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Alzheimer's disease risk increases significantly in individuals carrying one or two copies of APOE ε4 allele compared to individuals with an ε3/ε3 genotype. Growing evidence has demonstrated that apolipoprotein E (apoE) strongly influences AD pathogenesis by controlling Aβ aggregation and metabolism. Heparan sulphate proteoglycans (HSPGs) are abundant cell surface molecules that bind to both apoE and Aβ. HSPGs have been associated with Aβ aggregation and deposition. Although several lines of research have shown that apoE influences Aβ clearance in the brain, it is not clear how apoE influences HSPG-mediated cellular uptake of Aβ.
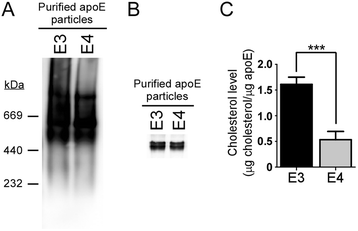
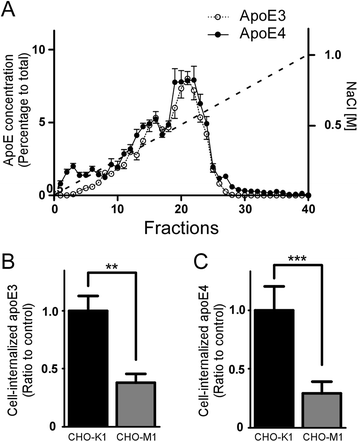
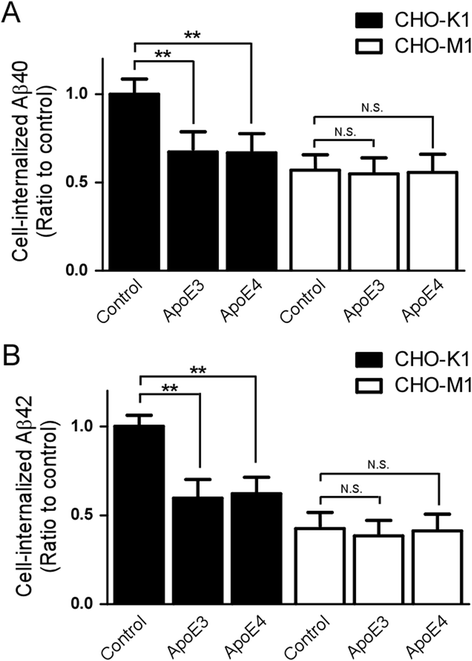
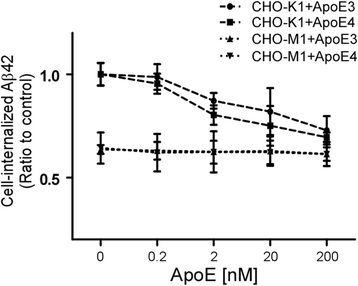
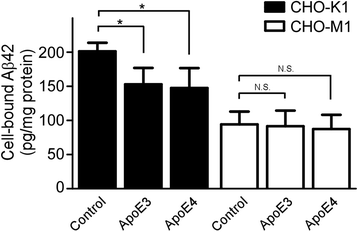
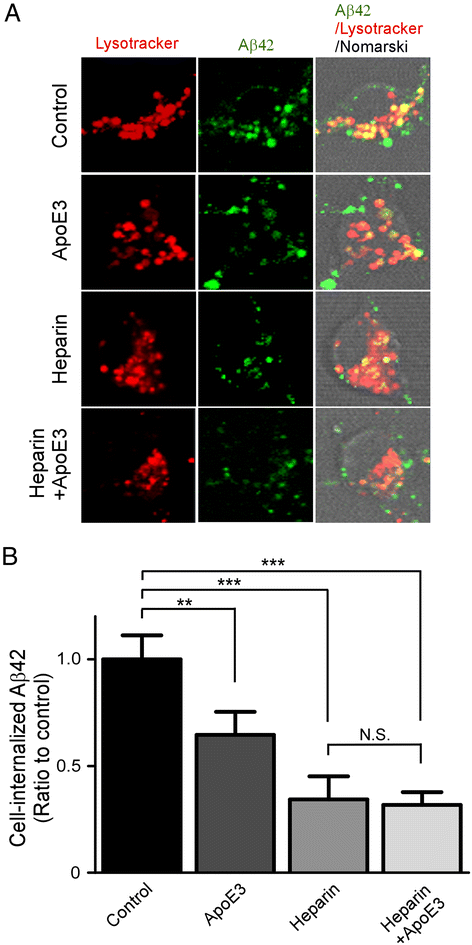
Results: In this study, we show that apoE lipoprotein particles from conditioned media of immortalized astrocytes isolated from human APOE-targeted replacement (TR) mice significantly suppress cellular Aβ42 and Aβ40 uptake through cell surface HSPG. ApoE3 and apoE4 particles have similar binding affinity to heparin, while apoE4 particles are likely hypolipidated compared to apoE particles. We also found that the apoE particles antagonize Aβ binding to cell surface, and inhibited Aβ uptake in a concentration-dependent manner in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells. While the effect was not apoE isoform-dependent, the suppressive effect of apoE particles on Aβ uptake was not observed in HSPG-deficient CHO cells. We further demonstrated that apoE particles reduced the internalization of Aβ in mouse primary neurons, an effect that is eliminated by the presence of heparin.
Conclusions: Taken together, our findings indicate that apoE particles irrespective of isoform inhibit HSPG-dependent cellular Aβ uptake. Modulating the ability of apoE particles to affect Aβ cellular uptake may hold promises for developing new strategies for AD therapy.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Aβ; Cellular uptake; HSPG; apoE.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heparan sulphate proteoglycan and the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 constitute major pathways for neuronal amyloid-beta uptake.J Neurosci. 2011 Feb 2;31(5):1644-51. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5491-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21289173 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E increases cell association of amyloid-β 40 through heparan sulfate and LRP1 dependent pathways.Amyloid. 2014 Jun;21(2):76-87. doi: 10.3109/13506129.2013.879643. Epub 2014 Feb 3. Amyloid. 2014. PMID: 24491019
-
Differential cellular accumulation/retention of apolipoprotein E mediated by cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Apolipoproteins E3 and E2 greater than e4.J Biol Chem. 1998 May 29;273(22):13452-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.22.13452. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9593678
-
The interaction of amyloid-beta with ApoE.Subcell Biochem. 2005;38:255-72. doi: 10.1007/0-387-23226-5_13. Subcell Biochem. 2005. PMID: 15709483 Review.
-
Unraveling APOE4's Role in Alzheimer's Disease: Pathologies and Therapeutic Strategies.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2025;26(4):259-281. doi: 10.2174/0113892037326839241014054430. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2025. PMID: 39722484 Review.
Cited by
-
Using human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) to investigate the mechanisms by which Apolipoprotein E (APOE) contributes to Alzheimer's disease (AD) risk.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 May;138:104788. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104788. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 32032733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Half a century of amyloids: past, present and future.Chem Soc Rev. 2020 Aug 7;49(15):5473-5509. doi: 10.1039/c9cs00199a. Epub 2020 Jul 7. Chem Soc Rev. 2020. PMID: 32632432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered substrate metabolism in neurodegenerative disease: new insights from metabolic imaging.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Oct 28;18(1):248. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02305-w. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 34711251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglial apolipoprotein E particles contribute to neuronal senescence and synaptotoxicity.iScience. 2024 May 16;27(6):110006. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110006. eCollection 2024 Jun 21. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38868202 Free PMC article.
-
ApoE Lipidation as a Therapeutic Target in Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 1;21(17):6336. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176336. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32882843 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

