DrugGenEx-Net: a novel computational platform for systems pharmacology and gene expression-based drug repurposing
- PMID: 27151405
- PMCID: PMC4857427
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-016-1065-y
DrugGenEx-Net: a novel computational platform for systems pharmacology and gene expression-based drug repurposing
Abstract
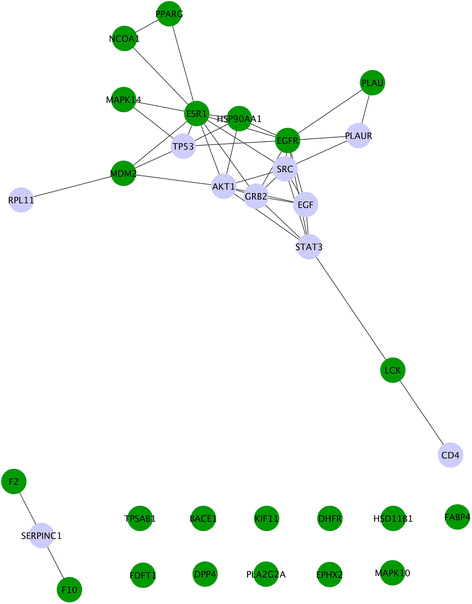
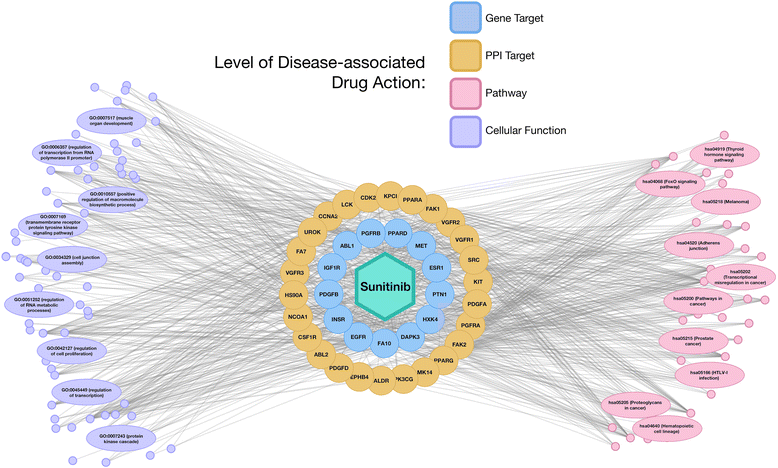
Background: The targeting of disease-related proteins is important for drug discovery, and yet target-based discovery has not been fruitful. Contextualizing overall biological processes is critical to formulating successful drug-disease hypotheses. Network pharmacology helps to overcome target-based bottlenecks through systems biology analytics, such as protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks and pathway regulation.
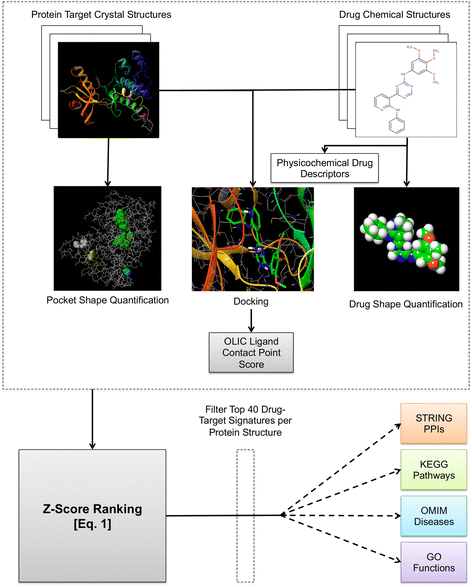
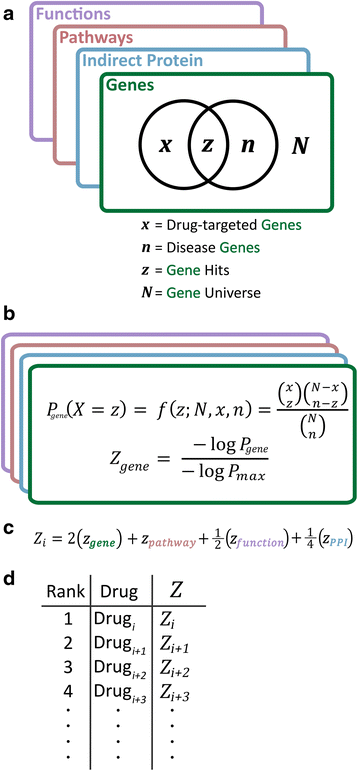
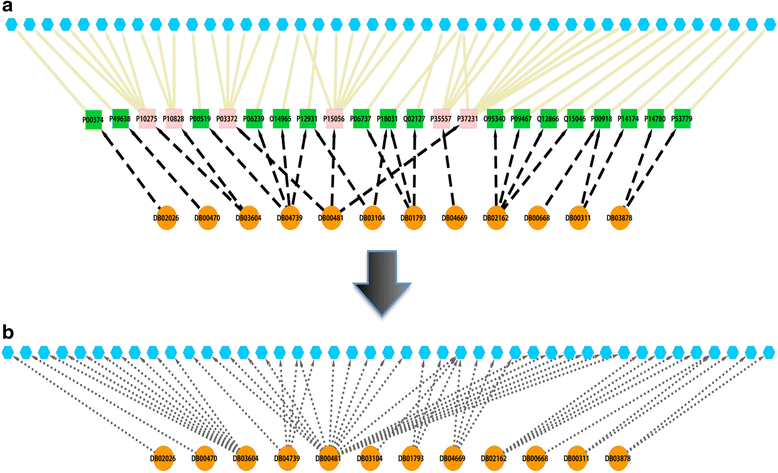
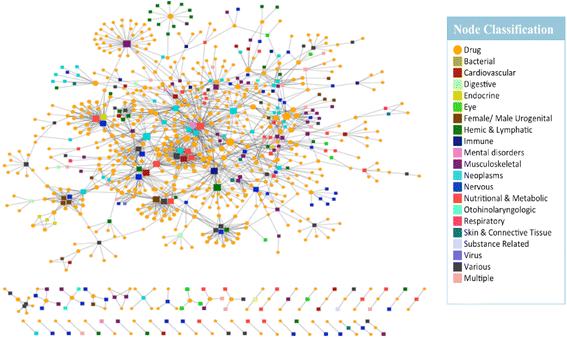
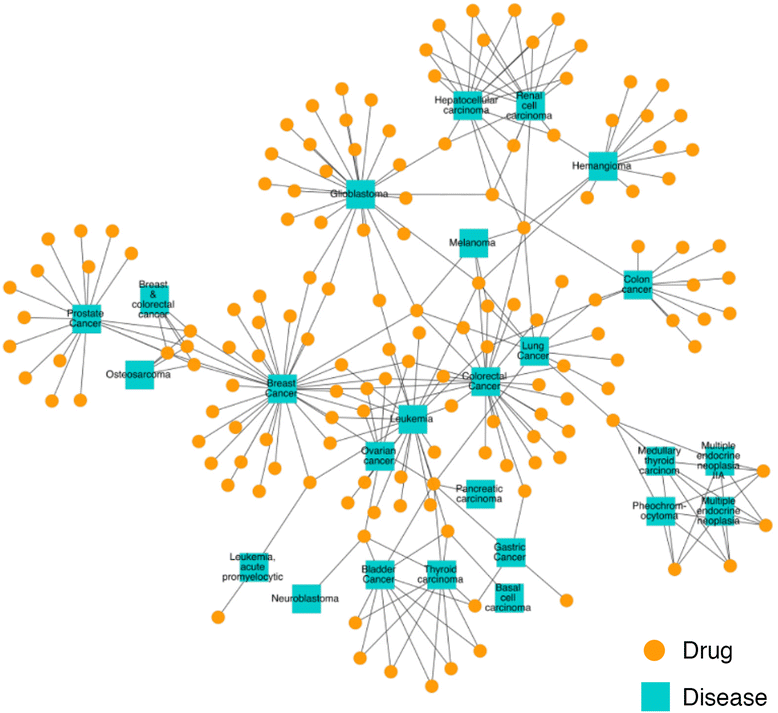
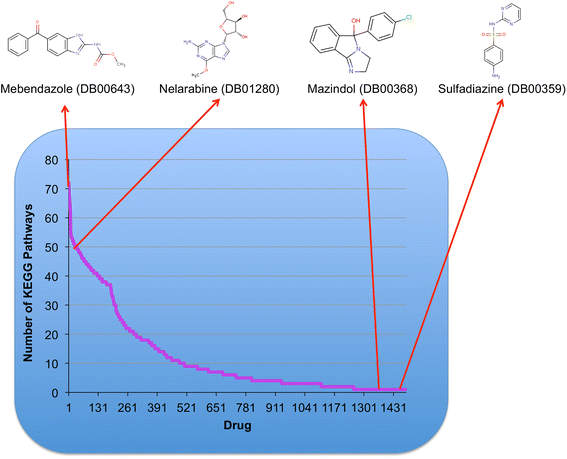
Results: We present a systems polypharmacology platform entitled DrugGenEx-Net (DGE-NET). DGE-NET predicts empirical drug-target (DT) interactions, integrates interaction pairs into a multi-tiered network analysis, and ultimately predicts disease-specific drug polypharmacology through systems-based gene expression analysis. Incorporation of established biological network annotations for protein target-disease, -signaling pathway, -molecular function, and protein-protein interactions enhances predicted DT effects on disease pathophysiology. Over 50 drug-disease and 100 drug-pathway predictions are validated. For example, the predicted systems pharmacology of the cholesterol-lowering agent ezetimibe corroborates its potential carcinogenicity. When disease-specific gene expression analysis is integrated, DGE-NET prioritizes known therapeutics/experimental drugs as well as their contra-indications. Proof-of-concept is established for immune-related rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease, as well as neuro-degenerative Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases.
Conclusions: DGE-NET is a novel computational method that predicting drug therapeutic and counter-therapeutic indications by uniquely integrating systems pharmacology with gene expression analysis. DGE-NET correctly predicts various drug-disease indications by linking the biological activity of drugs and diseases at multiple tiers of biological action, and is therefore a useful approach to identifying drug candidates for re-purposing.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; DrugGenEx-NET; Gene expression analysis; Inflammatory bowel disease; Parkinson’s disease; Polypharmacology; Rheumatoid arthritis; TMFS.
Figures


References
-
- Paul SM, Mytelka DS, Dunwiddie CT, Persinger CC, Munos BH, Lindborg SR, et al. How to improve R&D productivity: the pharmaceutical industry’s grand challenge. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010;9:203–14. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

