Role of Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress in Glucose Tolerance, Insulin Resistance, and Cardiac Diastolic Dysfunction
- PMID: 27151515
- PMCID: PMC4889180
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.115.003046
Role of Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress in Glucose Tolerance, Insulin Resistance, and Cardiac Diastolic Dysfunction
Abstract
Background: Diabetes mellitus (DM) is associated with mitochondrial oxidative stress. We have shown that myocardial oxidative stress leads to diastolic dysfunction in a hypertensive mouse model. Therefore, we hypothesized that diabetes mellitus could cause diastolic dysfunction through mitochondrial oxidative stress and that a mitochondria-targeted antioxidant (MitoTEMPO) could prevent diastolic dysfunction in a diabetic mouse model.
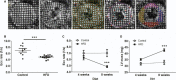
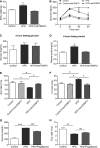
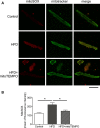
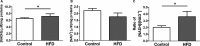
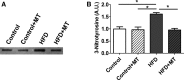
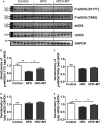
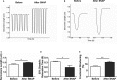
Methods and results: C57BL/6J mice were fed either 60 kcal % fat diet (high-fat diet [HFD]) or normal chow (control) for 8 weeks with or without concurrent MitoTEMPO administration, followed by in vivo assessment of diastolic function and ex vivo studies. HFD mice developed impaired glucose tolerance compared with the control (serum glucose=495±45 mg/dL versus 236±30 mg/dL at 60 minutes after intraperitoneal glucose injection, P<0.05). Myocardial tagged cardiac magnetic resonance imaging showed significantly reduced diastolic circumferential strain (Ecc) rate in the HFD mice compared with controls (5.0±0.3 1/s versus 7.4±0.5 1/s, P<0.05), indicating diastolic dysfunction in the HFD mice. Systolic function was comparable in both groups (left ventricular ejection fraction=66.4±1.4% versus 66.7±1.2%, P>0.05). MitoTEMPO-treated HFD mice showed significant reduction in mitochondria reactive oxygen species, S-glutathionylation of cardiac myosin binding protein C, and diastolic dysfunction, comparable to the control. The fasting insulin levels of MitoTEMPO-treated HFD mice were also comparable to the controls (P>0.05).
Conclusions: MitoTEMPO treatment prevented insulin resistance and diastolic dysfunction, suggesting that mitochondrial oxidative stress may be involved in the pathophysiology of both conditions.
Keywords: diastolic dysfunction; insulin resistance; mitochondrial oxidative stress.
© 2016 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures








References
-
- Schocken DD, Benjamin EJ, Fonarow GC, Krumholz HM, Levy D, Mensah GA, Narula J, Shor ES, Young JB, Hong Y. Prevention of heart failure: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Councils on Epidemiology and Prevention, Clinical Cardiology, Cardiovascular Nursing, and High Blood Pressure Research; Quality of Care and Outcomes Research Interdisciplinary Working Group; and Functional Genomics and Translational Biology Interdisciplinary Working Group. Circulation. 2008;117:2544–2565. - PubMed
-
- Owan TE, Hodge DO, Herges RM, Jacobsen SJ, Roger VL, Redfield MM. Trends in prevalence and outcome of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:251–259. - PubMed
-
- Redfield MM, Jacobsen SJ, Burnett JC Jr, Mahoney DW, Bailey KR, Rodeheffer RJ. Burden of systolic and diastolic ventricular dysfunction in the community: appreciating the scope of the heart failure epidemic. JAMA. 2003;289:194–202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

