Perioperative Rehabilitation in Operable Lung Cancer Patients (PROLUCA): A Feasibility Study
- PMID: 27151595
- PMCID: PMC5739160
- DOI: 10.1177/1534735416635741
Perioperative Rehabilitation in Operable Lung Cancer Patients (PROLUCA): A Feasibility Study
Abstract
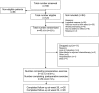
Introduction Surgical resection in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) may be associated with significant morbidity, functional limitations, and decreased quality of life. Objectives The safety and feasibility of a preoperative and early postoperative rehabilitation program in patients operated for NSCLC was determined in a nonhospital setting, with focus on high-intensity interval exercise. Methods Forty patients with biopsy-proven NSCLC stages I to IIIa referred for surgical resection at the Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery RT, Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen, were randomly assigned to 1 of 4 groups (3 intervention groups and 1 control group). The preoperative intervention consisted of a home-based exercise program, while the postoperative exercise program comprised a supervised group exercise program involving resistance and high-intensity interval cardiorespiratory exercise 2 hours weekly for 12 weeks combined with individual counseling. The study endpoints were inclusion rate, adherence, and number of adverse events. Results Forty patients (of 124 screened; 32%) were included and randomized into the 4 groups. The postoperative exercise was completed by 73% of the patients randomized to this intervention. No adverse events were observed, indicating that the early postoperative exercise program is safe. The preoperative home-based exercise program was not feasible due to interfering diagnostic procedures and fast-track surgery that left only 1 to 2 weeks between diagnosis and surgery. Conclusion The early postoperative exercise program for patients with NSCLC was safe and feasible, but in a fast-track set up, a preoperative home-based exercise program was not feasible for this population.
Keywords: NSCLC; exercise; lung cancer; perioperative intervention; rehabilitation.
© The Author(s) 2016.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Skokan L, Reed CE, Koh S, Ott GY, Silvestri GA. What happens to patients undergoing lung cancer surgery ? Surgery. 2002;1:21-30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical