Pathophysiological significance and therapeutic targeting of germinal center kinase in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 27151888
- PMCID: PMC4946202
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2016-02-696856
Pathophysiological significance and therapeutic targeting of germinal center kinase in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
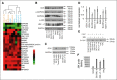
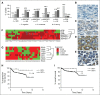
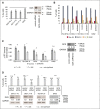
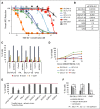
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common subtype of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, yet 40% to 50% of patients will eventually succumb to their disease, demonstrating a pressing need for novel therapeutic options. Gene expression profiling has identified messenger RNAs that lead to transformation, but critical events transforming cells are normally executed by kinases. Therefore, we hypothesized that previously unrecognized kinases may contribute to DLBCL pathogenesis. We performed the first comprehensive analysis of global kinase activity in DLBCL, to identify novel therapeutic targets, and discovered that germinal center kinase (GCK) was extensively activated. GCK RNA interference and small molecule inhibition induced cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in DLBCL cell lines and primary tumors in vitro and decreased the tumor growth rate in vivo, resulting in a significantly extended lifespan of mice bearing DLBCL xenografts. GCK expression was also linked to adverse clinical outcome in a cohort of 151 primary DLBCL patients. These studies demonstrate, for the first time, that GCK is a molecular therapeutic target in DLBCL tumors and that inhibiting GCK may significantly extend DLBCL patient survival. Because the majority of DLBCL tumors (∼80%) exhibit activation of GCK, this therapy may be applicable to most patients.
© 2016 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of Hippo-YAP signaling by insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in the tumorigenesis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.J Hematol Oncol. 2020 Jun 16;13(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00906-1. J Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32546241 Free PMC article.
-
The hematopoietic oncoprotein FOXP1 promotes tumor cell survival in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by repressing S1PR2 signaling.Blood. 2016 Mar 17;127(11):1438-48. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-08-662635. Epub 2016 Jan 4. Blood. 2016. PMID: 26729899
-
UCH-L1 is induced in germinal center B cells and identifies patients with aggressive germinal center diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Blood. 2016 Mar 24;127(12):1564-74. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-07-656678. Epub 2015 Dec 23. Blood. 2016. PMID: 26702068 Free PMC article.
-
The significance of FOXP1 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Leuk Lymphoma. 2017 May;58(5):1037-1051. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2016.1228932. Epub 2016 Sep 27. Leuk Lymphoma. 2017. PMID: 27678023 Review.
-
Novel drug targets for personalized precision medicine in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a comprehensive review.Mol Cancer. 2015 Dec 11;14:207. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0474-2. Mol Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26654227 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CUL4B regulates autophagy via JNK signaling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Cell Cycle. 2019 Feb;18(4):379-394. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2018.1560718. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Cell Cycle. 2019. PMID: 30612524 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the GCK pathway: a novel and selective therapeutic strategy against RAS-mutated multiple myeloma.Blood. 2021 Apr 1;137(13):1754-1764. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020006334. Blood. 2021. PMID: 33036022 Free PMC article.
-
GCK inhibition enhances iberdomide antimyeloma effects by promoting IKZF1 degradation via a CRBN-independent mechanism.Blood Neoplasia. 2025 Jun 19;2(3):100130. doi: 10.1016/j.bneo.2025.100130. eCollection 2025 Aug. Blood Neoplasia. 2025. PMID: 40792016 Free PMC article.
-
GNF-7, a novel FLT3 inhibitor, overcomes drug resistance for the treatment of FLT3‑ITD acute myeloid leukemia.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Nov 30;23(1):302. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-03142-y. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 38037057 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between HGAL and Grb2 proteins regulates B-cell receptor signaling.Blood Adv. 2019 Aug 13;3(15):2286-2297. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018016162. Blood Adv. 2019. PMID: 31362927 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lossos IS. Molecular pathogenesis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(26):6351–6357. - PubMed
-
- Coiffier B, Lepage E, Briere J, et al. CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(4):235–242. - PubMed
-
- Habermann TM, Weller EA, Morrison VA, et al. Rituximab-CHOP versus CHOP alone or with maintenance rituximab in older patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(19):3121–3127. - PubMed
-
- Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature. 2000;403(6769):503–511. - PubMed
-
- Lenz G, Davis RE, Ngo VN, et al. Oncogenic CARD11 mutations in human diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Science. 2008;319(5870):1676–1679. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

