A widespread sequence-specific mRNA decay pathway mediated by hnRNPs A1 and A2/B1
- PMID: 27151978
- PMCID: PMC4863738
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.277392.116
A widespread sequence-specific mRNA decay pathway mediated by hnRNPs A1 and A2/B1
Abstract
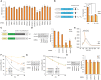
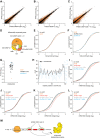
3'-untranslated regions (UTRs) specify post-transcriptional fates of mammalian messenger RNAs (mRNAs), yet knowledge of the underlying sequences and mechanisms is largely incomplete. Here, we identify two related novel 3' UTR motifs in mammals that specify transcript degradation. These motifs are interchangeable and active only within 3' UTRs, where they are often preferentially conserved; furthermore, they are found in hundreds of transcripts, many encoding regulatory proteins. We found that degradation occurs via mRNA deadenylation, mediated by the CCR4-NOT complex. We purified trans factors that recognize the motifs and identified heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs) A1 and A2/B1, which are required for transcript degradation, acting in a previously unknown manner. We used RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) to confirm hnRNP A1 and A2/B1 motif-dependent roles genome-wide, profiling cells depleted of these factors singly and in combination. Interestingly, the motifs are most active within the distal portion of 3' UTRs, suggesting that their role in gene regulation can be modulated by alternative processing, resulting in shorter 3' UTRs.
Keywords: 3′ UTR; CCR4–NOT deadenylase complex; cis-regulatory element; hnRNPs A2/B1 and A1; mRNA decay; post-transcriptional gene regulation.
© 2016 Geissler et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A position-specific 3'UTR sequence that accelerates mRNA decay.RNA Biol. 2016 Nov;13(11):1075-1077. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1225645. Epub 2016 Aug 26. RNA Biol. 2016. PMID: 27565004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between hnRNP A1 and a cis-acting element in the 3' UTR of CYP2A5 mRNA is central for high expression of the gene.FEBS Lett. 2003 Jan 30;535(1-3):147-52. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(02)03893-0. FEBS Lett. 2003. PMID: 12560094
-
hnRNPA2/B1 and nELAV proteins bind to a specific U-rich element in CDK5R1 3'-UTR and oppositely regulate its expression.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jun;1839(6):506-16. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.04.018. Epub 2014 May 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24792867
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of glucose transporter-1 by an AU-rich element in the 3'UTR and by hnRNP A2.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Jun 11;318(4):977-82. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.04.128. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. PMID: 15147968
-
Implications of polyadenylation in health and disease.Nucleus. 2014;5(6):508-19. doi: 10.4161/nucl.36360. Epub 2014 Oct 31. Nucleus. 2014. PMID: 25484187 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PERSIST platform provides programmable RNA regulation using CRISPR endoRNases.Nat Commun. 2022 May 11;13(1):2582. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30172-3. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35562172 Free PMC article.
-
HNRNPA2B1 as a trigger of RNA switch modulates the miRNA-mediated regulation of CDK6.iScience. 2021 Oct 25;24(11):103345. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103345. eCollection 2021 Nov 19. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34805798 Free PMC article.
-
The role of mRNA m6A methylation in the nervous system.Cell Biosci. 2019 Aug 20;9:66. doi: 10.1186/s13578-019-0330-y. eCollection 2019. Cell Biosci. 2019. PMID: 31452869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HNRNPA2B1: RNA-Binding Protein That Orchestrates Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotype in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Circulation. 2022 Oct 18;146(16):1243-1258. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.059591. Epub 2022 Aug 22. Circulation. 2022. PMID: 35993245 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudogenes in Cancer: State of the Art.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Aug 8;15(16):4024. doi: 10.3390/cancers15164024. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627052 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baltz AG, Munschauer M, Schwanhausser B, Vasile A, Murakawa Y, Schueler M, Youngs N, Penfold-Brown D, Drew K, Milek M, et al. 2012. The mRNA-bound proteome and its global occupancy profile on protein-coding transcripts. Mol Cell 46: 674–690. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
