Epithelioid Trophoblastic Tumor in a Postmenopausal Woman: A Case Report
- PMID: 27152314
- PMCID: PMC4854661
- DOI: 10.6118/jmm.2016.22.1.50
Epithelioid Trophoblastic Tumor in a Postmenopausal Woman: A Case Report
Abstract
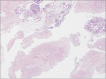
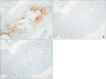
Epithelioid trophoblastic tumor (ETT) is a rare gestational trophoblastic neoplasm composed of intermediate trophoblasts. Most cases of ETT are reported in women of reproductive age following a prior gestation within 2 weeks to 30 years. ETT is extremely rare in postmenopausal women. It is commonly misdiagnosed as a poorly differentiated carcinoma or another type of gestational trophoblastic tumor. We report a case of ETT in a 56-year-old woman that developed 23 years after the patient's last pregnancy.
Keywords: Epithelioid trophoblastic tumor; Postmenopause; Uterus.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Shih IM, Kurman RJ. Epithelioid trophoblastic tumor: a neoplasm distinct from choriocarcinoma and placental site trophoblastic tumor simulating carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998;22:1393–1403. - PubMed
-
- Massenkeil G, Crombach G, Dominik S, De Bruyne F, Nitz U, Krussel J, et al. Metastatic choriocarcinoma in a postmenopausal woman. Gynecol Oncol. 1996;61:432–437. - PubMed
-
- McLellan R, Buscema J, Currie JL, Woodruff JD. Placental site trophoblastic tumor in a postmenopausal woman. Am J Clin Pathol. 1991;95:670–675. - PubMed
-
- Park SY, Park MH, Ko HS, Cha EJ, Sohn JS, Kim CJ. Epithelioid trophoblastic tumor presenting as an ovarian mass in a postmenopausal woman. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2014;33:35–39. - PubMed
-
- Shih IM, Kurman RJ. The pathology of intermediate trophoblastic tumors and tumor-like lesions. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2001;20:31–47. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

