Particulate Oxidative Burden as a Predictor of Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Children with Asthma
- PMID: 27152705
- PMCID: PMC5047770
- DOI: 10.1289/EHP175
Particulate Oxidative Burden as a Predictor of Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Children with Asthma
Abstract
Background: Epidemiological studies have provided strong evidence that fine particulate matter (PM2.5; aerodynamic diameter ≤ 2.5 μm) can exacerbate asthmatic symptoms in children. Pro-oxidant components of PM2.5 are capable of directly generating reactive oxygen species. Oxidative burden is used to describe the capacity of PM2.5 to generate reactive oxygen species in the lung.
Objective: In this study we investigated the association between airway inflammation in asthmatic children and oxidative burden of PM2.5 personal exposure.
Methods: Daily PM2.5 personal exposure samples (n = 249) of 62 asthmatic school-aged children in Montreal were collected over 10 consecutive days. The oxidative burden of PM2.5 samples was determined in vitro as the depletion of low-molecular-weight antioxidants (ascorbate and glutathione) from a synthetic model of the fluid lining the respiratory tract. Airway inflammation was measured daily as fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO).
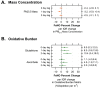
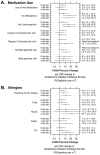
Results: A positive association was identified between FeNO and glutathione-related oxidative burden exposure in the previous 24 hr (6.0% increase per interquartile range change in glutathione). Glutathione-related oxidative burden was further found to be positively associated with FeNO over 1-day lag and 2-day lag periods. Results further demonstrate that corticosteroid use may reduce the FeNO response to elevated glutathione-related oxidative burden exposure (no use, 15.8%; irregular use, 3.8%), whereas mold (22.1%), dust (10.6%), or fur (13.1%) allergies may increase FeNO in children with versus children without these allergies (11.5%). No association was found between PM2.5 mass or ascorbate-related oxidative burden and FeNO levels.
Conclusions: Exposure to PM2.5 with elevated glutathione-related oxidative burden was associated with increased FeNO.
Citation: Maikawa CL, Weichenthal S, Wheeler AJ, Dobbin NA, Smargiassi A, Evans G, Liu L, Goldberg MS, Godri Pollitt KJ. 2016. Particulate oxidative burden as a predictor of exhaled nitric oxide in children with asthma. Environ Health Perspect 124:1616-1622; http://dx.doi.org/10.1289/EHP175.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no actual or potential competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Altuǧ H, Gaga EO, Döǧeroǧlu T, Brunekreef B, Hoek G, Van Doorn W. Effects of ambient air pollution on respiratory tract complaints and airway inflammation in primary school children. Sci Total Environ. 2014;479–480:201–209. - PubMed
-
- Anderson HR, Favarato G, Atkinson RW. Long-term exposure to air pollution and the incidence of asthma: meta-analysis of cohort studies. Air Qual Atmos Health. 2013;6:47–56.
-
- Ashutosh K. Nitric oxide and asthma: a review. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2000;6:21–25. - PubMed
-
- ATS/ERS (American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society) ATS/ERS recommendations for standardized procedures for the online and offline measurement of exhaled lower respiratory nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide, 2005. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;171:912–930. - PubMed
-
- Ayres JG, Borm P, Cassee FR, Castranova V, Donaldson K, Ghio A, et al. Evaluating the toxicity of airborne particulate matter and nanoparticles by measuring oxidative potential—a workshop report and consensus statement. Inhal Toxicol. 2008;20:75–99. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

