Non-absorbable disaccharides versus placebo/no intervention and lactulose versus lactitol for the prevention and treatment of hepatic encephalopathy in people with cirrhosis
- PMID: 27153247
- PMCID: PMC7004252
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003044.pub4
Non-absorbable disaccharides versus placebo/no intervention and lactulose versus lactitol for the prevention and treatment of hepatic encephalopathy in people with cirrhosis
Abstract
Background: Non-absorbable disaccharides (lactulose and lactitol) are recommended as first-line treatment for hepatic encephalopathy. The previous (second) version of this review included 10 randomised clinical trials (RCTs) evaluating non-absorbable disaccharides versus placebo/no intervention and eight RCTs evaluating lactulose versus lactitol for people with cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy. The review found no evidence to either support or refute the use of the non-absorbable disaccharides and no differences between lactulose versus lactitol.
Objectives: To assess the beneficial and harmful effects of i) non-absorbable disaccharides versus placebo/no intervention and ii) lactulose versus lactitol in people with cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy.
Search methods: We carried out electronic searches of the Cochrane Hepato-Biliary Group Controlled Trials Register, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL 2015, Issue 10), MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Science Citation Index Expanded to 19 October 2015; manual searches of meetings and conference proceedings; checks of bibliographies; and correspondence with investigators and pharmaceutical companies.
Selection criteria: We included RCTs, irrespective of publication status, language, or blinding.
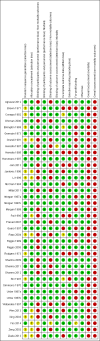
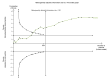
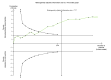
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors, working independently, retrieved data from published reports and correspondence with investigators. The primary outcomes were mortality, hepatic encephalopathy, and serious adverse events. We presented the results of meta-analyses as risk ratios (RR) and mean differences (MD) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). We assessed the quality of the evidence using 'Grading of Recommendations Assessment Development and Evaluation' (GRADE) and bias control using the Cochrane Hepato-Biliary Group domains. Our analyses included regression analyses of publication bias and other small study effects, Trial Sequential Analyses to detect type 1 and type 2 errors, and subgroup and sensitivity analyses.
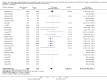
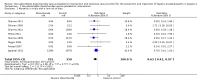
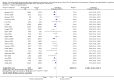
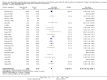
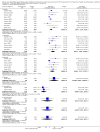
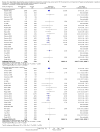
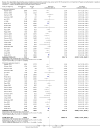
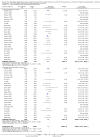
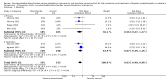
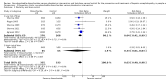
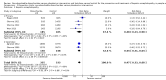
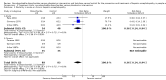
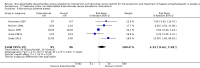
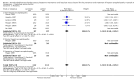
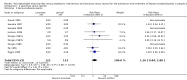
Main results: We included 38 RCTs with a total of 1828 participants. Eight RCTs had a low risk of bias in the assessment of mortality. All trials had a high risk of bias in the assessment of the remaining outcomes. Random-effects meta-analysis showed a beneficial effect of non-absorbable disaccharides versus placebo/no intervention on mortality when including all RCTs with extractable data (RR 0.59, 95% CI 0.40 to 0.87; 1487 participants; 24 RCTs; I(2) = 0%; moderate quality evidence) and in the eight RCTs with a low risk of bias (RR 0.63, 95% CI 0.41 to 0.97; 705 participants). The Trial Sequential Analysis with the relative risk reduction (RRR) reduced to 30% confirmed the findings when including all RCTs, but not when including only RCTs with a low risk of bias or when we reduced the RRR to 22%. Compared with placebo/no intervention, the non-absorbable disaccharides were associated with beneficial effects on hepatic encephalopathy (RR 0.58, 95% CI 0.50 to 0.69; 1415 participants; 22 RCTs; I(2) = 32%; moderate quality evidence). Additional analyses showed that non-absorbable disaccharides can help to reduce serious adverse events associated with the underlying liver disease including liver failure, hepatorenal syndrome, and variceal bleeding (RR 0.47, 95% CI 0.36 to 0.60; 1487 participants; 24 RCTs; I(2) = 0%; moderate quality evidence). We confirmed the results in Trial Sequential Analysis. Tests for subgroup differences showed no statistical differences between RCTs evaluating prevention, overt, or minimal hepatic encephalopathy. The evaluation of secondary outcomes showed a potential beneficial effect of the non-absorbable disaccharides on quality of life, but we were not able to include the data in an overall meta-analysis (very low quality evidence). Non-absorbable disaccharides were associated with non-serious (mainly gastrointestinal) adverse events (very low quality evidence). None of the RCTs comparing lactulose versus lactitol evaluated quality of life. The review found no differences between lactulose and lactitol for the remaining outcomes (very low quality evidence).
Authors' conclusions: This review includes a large number of RCTs evaluating the prevention or treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. The analyses found evidence that non-absorbable disaccharides may be associated with a beneficial effect on clinically relevant outcomes compared with placebo/no intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
Lise L Gluud received payment for presentations given at scientific meetings sponsored by Norgine.
All review authors have conducted previous reviews on hepatic encephalopathy and two authors (Hendrik Vilstrup and Marsha Morgan) have conducted RCTs on hepatic encephalopathy. These previous research activities are an academic bias based on the definitions given in the Cochrane Hepato‐Biliary Group module.
Figures


















Update of
-
Non-absorbable disaccharides versus placebo/no intervention and lactulose versus lactitol for the prevention and treatment of hepatic encephalopathy in people with cirrhosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 18;4:CD003044. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003044.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 06;(5):CD003044. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003044.pub4. PMID: 27089005 Updated.
Comment in
-
Cochrane systematic review highlights the importance of lactulose in the management of hepatic encephalopathy.BMJ Support Palliat Care. 2018 Jun;8(2):238-239. doi: 10.1136/bmjspcare-2016-001255. Epub 2016 Dec 13. BMJ Support Palliat Care. 2018. PMID: 27965213 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Agrawal 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Agrawal A, Sharma BC, Sharma P, Sarin SK. Secondary prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis: an open‐label, randomized controlled trial of lactulose, probiotics, and no therapy. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2012;107:1043‐50. [PUBMED: 22710579] - PubMed
-
- Agrawal A, Sharma P, Sharma B, Sarin S. Secondary prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis: An open label, randomized controlled trial of lactulose, probiotics and no‐therapy [abstract]. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2010; Vol. 105:S105. [DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2010.320-5; CN‐01004953] - DOI - PubMed
Brown 1971 {published data only}
-
- Brown H, Trey C, McDermott WV Jr. Lactulose treatment of hepatic encephalopathy in outpatients. Archives of Surgery 1971;102:25‐7. [PUBMED: 5538764] - PubMed
Corazza 1982 {published data only}
-
- Corazza GR, Tacconi C, Zoli G. Use of pyridoxine‐alpha‐ketoglutarate (PAK) in hepatic encephalopathy. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology Research 1982;2(Suppl 1):7‐13. [CN‐00189390]
Dhiman 2000 {published data only}
-
- Dhiman RK, Sawhney MS, Chawla YK, Das G, Ram S, Dilawari JB. Efficacy of lactulose in cirrhotic patients with subclinical hepatic encephalopathy. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 2000;45:1549‐52. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Elkington 1969 {published data only}
-
- Elkington SG, Floch MH, Conn HO. Lactulose in the treatment of chronic portal‐systemic encephalopathy. A double‐blind clinical trial. New England Journal of Medicine 1969;281:408‐12. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Germain 1973 {published data only}
-
- Germain L, Frexinos J, Louis A, Ribet A. Double blind study of lactulose in 18 patients with chronic hepatic encephalopathy after portocaval shunt [Étude en double aveugle du lactulose chez 18 malades atteints d'encéphalopathie hépatique chronique après shunt porto‐cave]. Archives Francaises des Maladies de L'appareil Digestif 1973;62:293‐302. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Grandi 1991 {published data only}
-
- Grandi M, Sacchetti C, Pederzoli S, Celani MF. A clinical comparative study of crystalline pure lactulose and powder pure lactitol in portosystemic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients [Studio clinico di confronto tra lattulosio puro in cristalli e lactitolo puro in polvere nella encefalopatia porto‐sistemica del paziente cirrotico]. Minerva Gastroenterologica e Dietologica 1991;37:225‐30. [PMID: 1805974] - PubMed
Heredia 1987 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Heredia D, Caballeria J, Arroyo V, Ravelli G, Rodès J. Lactitol versus lactulose in the treatment of acute portal systemic encephalopathy (PSE). A controlled trial. Journal of Hepatology 1987;4:293‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Heredia 1988 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Heredia D, Teres J, Orteu N, Rodès J. Lactitol vs. lactulose in the treatment of chronic recurrent portal‐systemic encephalopathy. Journal of Hepatology 1988;7:106‐10. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Horsmans 1997 {published data only}
-
- Geubel AP, Solbreux PM, Horsmans Y, Desager JP, Harvengt C, Dive C. Effect of lactulose in cirrhotic patients with portalsystemic shunting and without clinical encephalopathy: A randomized controlled trial [abstract]. Acta Gastroenterologica Belgica 1991;54:C8. [CN‐00266808]
-
- Horsmans Y, Solbreux PM, Daenens C, Desager JP, Geubel AP. Lactulose improves psychometric testing in cirrhotic patients with subclinical encephalopathy. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 1997;11:165‐70. [PUBMED: 9042989] - PubMed
Jain 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Jain L, Sharma BC, Srivastava S, Puri SK, Sharma P, Sarin S. Serum endotoxin, inflammatory mediators, and magnetic resonance spectroscopy before and after treatment in patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2013;28:1187‐93. [PUBMED: 23425082] - PubMed
Jankovic 1996 {published data only}
-
- Jankovic G, Pavicevic V, Pavlovic A, Krstic M, Cabric I, Crnobaric M, et al. Lactitol in the treatment of acute hepatic encephalopathy in liver cirrhosis [Laktitol u therapiji akutne hepatičke encephalopatije]. Archives of Gastroenterohepatology 1996;15:22‐4. [CN‐00182347]
Li 1999 {published data only}
-
- Li Z, Zhang H, Hong Y, Yu D, Gui X. Clinical effect of lactulose in the treatment of subclinical hepatic encephalopathy. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional & Western Medicine on Liver Diseases 1999;9:13‐5.
McClain 1984 {published data only}
-
- McClain CJ, Potter TJ, Kromhout JP, Zieve L. The effect of lactulose on psychomotor performance tests in alcoholic cirrhotics without overt hepatic encephalopathy. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology 1984;6:325‐9. [PUBMED: 6481115] - PubMed
Mittal 2011 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Mittal VV, Sharma BC, Sharma P, Sarin SK. A randomized controlled trial comparing lactulose, probiotics, and L‐ornithine L‐aspartate in treatment of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2011;23:725‐32. [PUBMED: 21646910] - PubMed
-
- Mittal VV, Sharma P, Sharma B, Sarin SK. Treatment of minimal hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized controlled trial comparing lactulose, probiotics & L‐ornithine L‐aspartate with placebo [abstract]. Hepatology 2009; Vol. 50, issue Suppl 2:471A. [CN‐00739663] - PubMed
Morgan 1987a {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hawley KE, Morgan MY. A randomised controlled double‐blind trial of lactitol and lactulose in acute hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients [abstract]. Journal of Hepatology 1986; Vol. 3:86. - PubMed
-
- Hawley KE, Morgan MY. Lactitol vs lactulose in the treatment of acute hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients: a double‐blind randomised trial [abstract]. Hepatology 1986;6:1148. - PubMed
-
- Hawley KE, Morgan MY. Randomised controlled double blind trial of lactitol and lactulose in acute hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients [abstract]. Gut 1986;27:A1266. - PubMed
-
- Morgan MY, Hawley KE. Lactitol vs. lactulose in the treatment of acute hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients: a double‐blind, randomized trial. Hepatology 1987;7:1278‐84. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Morgan 1987b {published and unpublished data}
-
- Morgan MY, Hawley KE, Stambuk D. Lactitol versus lactulose in the treatment of chronic hepatic encephalopathy. A double‐blind, randomised, cross‐over study. Journal of Hepatology 1987;4:236‐44. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Morgan 1989 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Morgan MY, Alonso M, Stanger LC. Lactitol and lactulose for the treatment of subclinical hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients. A randomized cross‐over study. Journal of Hepatology 1989;8:208‐17. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Stanger LC, Alonso M, Morgan MY. Lactitol and lactulose for the treatment of subclinical hepatic encephalopathy: a randomised cross‐over study [abstract]. Journal of Hepatology 1988;7:179. - PubMed
Pai 1995 {published data only}
-
- Pai CH, Huang YS, Jeng WC, Chan CY, Lee SD. Treatment of porto‐systemic encephalopathy with lactulose: a randomized controlled study. Chinese Medical Journal 1995;55:31‐6. - PubMed
Prasad 2007 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Prasad S, Dhiman RK, Duseja A, Chawla YK, Sharma A, Agarwal R. Lactulose improves cognitive functions and health‐related quality of life in patients with cirrhosis who have minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2007;45:549‐59. [PUBMED: 17326150] - PubMed
Quero 1997 {published data only}
-
- Quero JC, Groeneweg M, Meulstee J, Hop WCJ, Schalm SW. Does a low‐dose of lactulose improve quality of life in patients with liver cirrhosis?. In: Record C, Al‐Mardini H editor(s). Advances in Hepatic Encephalopathy & Metabolism in Liver Disease: Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Ammonia. Vol. 64, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK: Ipswich Book Company Ltd, 1997:459‐65. [CN‐00363147]
-
- Quero JC, Groeneweg M, Meulstee J, Schalm SW. Does a low‐dose of lactulose improve quality of life in patients with liver cirrhosis? [abstract]. European Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 1996;18:A19. [CN‐00250860]
Raza 2004 {published data only}
Riggio 1989 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Riggio O, Balducci G, Ariosto F, Merli M, Pieche U, Pinto G, et al. Lactitol in prevention of recurrent episodes of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients with portal‐systemic shunt. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 1989;34:823‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Riggio O, Balducci G, Ariosto F, Merli M, Romiti A, Tremiterra S, et al. Lactitol in the treatment of severe chronic hepatic encephalopathy. A randomized cross‐over comparison with lactulose [abstract]. Journal of Hepatology 1988; Vol. 7:168.
-
- Riggio O, Balducci G, Ariosto F, Merli M, Tremiterra S, Ziparo V, et al. Lactitol in the treatment of chronic hepatic encephalopathy ‐ a randomized cross‐over comparison with lactulose. Hepato‐Gastroenterology 1990;37:524‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Riggio 2005 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Riggio O, Masini A, Efrati C, Nicolao F, Angeloni S, Salvatori FM, et al. Pharmacological prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: a randomized controlled study. Journal of Hepatology 2005;42:674‐9. [PUBMED: 15826716] - PubMed
-
- Riggio O, Masini A, Efrati C, Nicolao F, Attili AF, Merli M. Randomized controlled trial for the prevention of early post‐tips hepatic encephalopathy: comparison between rifaximin, lactitol and no treatment [abstract]. Hepatology 2001;34:1510.
Rodgers 1973 {published data only}
-
- Rodgers JB Jr, Kiley JE, Balint JA. Comparison of results of long‐term treatment of chronic hepatic encephalopathy with lactulose and sorbitol. American Journal of Gastroenterology 1973;60:459‐65. [PMID: 4587191] - PubMed
Sharma 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Sharma BC, Sharma P, Agrawal A, Sarin SK. Secondary prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy: an open‐label randomized controlled trial of lactulose versus placebo. Gastroenterology 2009;137:885‐91. [PUBMED: 19501587] - PubMed
Sharma 2011 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Sharma P, Agrawal A, Sharma BC, Sarin SK. Prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy in acute variceal bleed: a randomized controlled trial of lactulose versus no lactulose. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2011;26:996‐1003. [PUBMED: 21129028] - PubMed
Sharma 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Agrawal A, Sharma P, Sharma BC, Sarin SK. Primary prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: an open labelled randomized controlled trial of lactulose versus no lactulose [abstract]. Journal of Hepatology 2012;56(Suppl 2):S238. [CN‐00844674] - PubMed
-
- Chander SB, Praveen S, Amit A, Kumar SS. Primary prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: A open labelled randomized controlled trial of lactulose versus no lactulose [abstract]. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2010; Vol. 25:A13. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.06493.x; CN‐00789741] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sharma P, Sharma BC, Agrawal A, Sarin SK. Primary prophylaxis of overt hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: an open labelled randomized controlled trial of lactulose versus no lactulose. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2012;27:1329‐35. [PUBMED: 22606978] - PubMed
Shi 1997 {published data only}
-
- Shi H, Liu HY, Fu Z, Zhu L, Chen WZ. Lactitol in treatment of subclinical hepatic encephalopathy: a double blind placebo‐controlled randomised trial. Chinese Journal of Digestion 1997;17:221‐3.
Simmons 1970 {published data only}
-
- Simmons F, Goldstein H, Boyle JD. A controlled clinical trial of lactulose in hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterology 1970; Vol. 59:827‐32. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Uribe 1987a {published and unpublished data}
-
- Uribe M, Campollo O, Vargas F, Ravelli GP, Mundo F, Zapata L, et al. Acidifying enemas (lactitol and lactose) vs. nonacidifying enemas (tap water) to treat acute portal‐systemic encephalopathy: a double‐blind, randomized clinical trial. Hepatology 1987;7:639‐43. - PubMed
-
- Uribe M, Gil S, Perez F, Toledo H, Ballesteros A, Garcia‐Ramos G. Successful use of lactitol in acute portal systemic encephalopathy. A double blind controlled trial [abstract]. Hepatology 1984;4:765.
Uribe 1987b {published and unpublished data}
-
- Uribe M, Toledo H, Perez F, Vargas F, Gil S, Garcia‐Ramos G, et al. Lactitol, a second‐generation disaccharide for treatment of chronic portal‐systemic encephalopathy. A double‐blind, crossover, randomized clinical trial. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 1987;32:1345‐53. - PubMed
Watanabe 1997 {published data only}
-
- Suzuki H, Sato S, Suzuki K, Muto Y, Watanabe A, Kuriyama K. Phase III study with lactitol (NS‐4) for the patients of hyperammonemia: comparative study with lactulose. Rinsho Iyaku (Journal of Clinical Therapeutics and Medicines) 1995; Vol. 11:1439‐73. [CN‐00542601]
-
- Watanabe A, Sakai T, Sato S. Does lactulose improve psychometric tests and quality of life in cirrhotic patients with subclinical hepatic encephalopathy? [abstract]. Hepatology 1996;24:452A. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe A, Sakai T, Sato S, Imai F, Ohto M, Arakawa Y, et al. Clinical efficacy of lactulose in cirrhotic patients with and without subclinical hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 1997;26:1410‐4. [PUBMED: 9397979] - PubMed
Wen 2013 {published data only}
-
- Wen J, Liu Q, Song J, Tong M, Peng L, Liang H. Lactulose is highly potential in prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis and upper gastrointestinal bleeding: results of a controlled randomized trial. Digestion 2013;87:132‐8. [PUBMED: 23485720] - PubMed
Xing 2003 {published data only}
-
- Xing Q, Liu L. Research of lactulose in the treatment of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. World Chinese Journal of Digestion 2003;11:108‐9.
Yao 2014 {published data only}
-
- Yao C, Huang G, Wang M, Xia M, Yao F, Niu D, et al. Chinese herbal medicine formula Jieduhuayu granules improves cognitive and neurophysiological functions in patients with cirrhosis who have minimal hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized controlled trial. Complementary Therapies in Medicine 2014;22:977‐85. [PUBMED: 25453517] - PubMed
Zeng 2003 {published data only}
-
- Nie YQ, Zeng Z, Li YY, Sha WH, Ping L, Dai SJ. Long‐term efficacy of lactulose in patients with subclinical hepatic encephalopathy. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 2003;42:261‐3. [PUBMED: 12887812] - PubMed
-
- Zeng Z, Li YY. Effects of lactulose treatment on the course of subclinical hepatic encephalopathy. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2003;83:1126‐9. [PUBMED: 12921628] - PubMed
-
- Zeng Z, Li YY, Jia L, Nie Y‐Q. Influence of lactulose on the cognitive level and quality of life in patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation 2006; Vol. 10:165‐7. [CN‐00613050]
Ziada 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ziada DH, Soliman HH, Yamany SA, Hamisa MF, Hasan AM. Can Lactobacillus acidophilus improve minimal hepatic encephalopathy? A neurometabolite study using magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Arab Journal of Gastroenterology 2013;14:116‐22. [PUBMED: 24206740] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Bajaj 2010a {published data only}
-
- Bajaj JS, Sanyal AJ, Bell D, Gilles H, Heuman DM. Predictors of the recurrence of hepatic encephalopathy in lactulose‐treated patients. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2010;31:1012‐7. [PUBMED: 20136802] - PubMed
Bircher 1971 {published data only}
-
- Bircher J, Haemmerli UP, Scollo‐Lavizzari G, Hoffmann K. Treatment of chronic portal‐systemic encephalopathy with lactulose. Report of six patients and review of the literature. American Journal of Medicine 1971;51:148‐59. [PUBMED: 5095524] - PubMed
Brown 1970 {published data only}
-
- Brown H, Trey C, McDermott WV Jr. Encephalopathy after portacaval shunting managed with lactulose. American Journal of Surgery 1970;119:132‐7. [PUBMED: 5440784] - PubMed
James 1971 {published data only}
Lanthier 1985 {published data only}
Merli 1992 {published data only}
-
- Merli M, Caschera M, Piat C, Pinto G, Diofebi M, Riggio O. The effect of lactulose and lactitol administration on fecal fat excretion in patients with liver cirrhosis. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology 1992; Vol. 15:125‐7. [CN‐00087562] - PubMed
Patil 1987 {published data only}
Piotraschke 1996 {published data only}
-
- Piotraschke J, Berger E, Haag K, Ochs A, Görtelmeyer R, Rössle M. Effect of lactulose on latent hepatic encephalopathy and plasma ammonia concentration in outpatients with TIPS [abstract]. Journal of Hepatology 1996;25:98.
Pockros 2009 {published data only}
-
- Pockros P, Hassanein T, Vierling J, Heuman D, Hillebrand D, Chojkier M. Phase 2, multicenter, randomized study of AST‐120 (spherical carbon adsorbent) vs. lactulose in the treatment of low‐grade hepatic encephalopathy (HE) [abstract]. Journal of Hepatology 2009; Vol. 50:S43. [CN‐00715816]
Quinton 1982 {published data only}
-
- Quinton A, Lamouliatte H, Plane D, Delteil L. Randomized study of mannitol lavage and of a combination of lactulose and kanamycin in prevention and treatment of posthemorrhagic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis [abstract]. Gastroenterologie Clinique et Biologique 1982;6:124A.
Rahimi 2014 {published data only}
Riggio 1990 {published data only}
-
- Riggio O, Varriale M, Testore GP, Rosa R, Rosa E, Merli M, et al. Effect of lactitol and lactulose administration on the fecal flora in cirrhotic patients. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology 1990;12:433‐6. [PUBMED: 2398251] - PubMed
Rorsman 1970 {published data only}
-
- Rorsman G, Sulg I. Lactulose treatment of chronic hepatoportal encephalopathy. A clinical and electroencephalographic study. Acta Medica Scandinavica 1970;187:337‐46. [PUBMED: 5526951] - PubMed
Salerno 1994 {published data only}
-
- Salerno F, Moser P, Maggi A, Vitaliani G, Benetti G. Effects of long‐term administration of low‐dose lactitol in patients with cirrhosis but without overt encephalopathy. Journal of Hepatology 1994;21:1092‐6. [PUBMED: 7699233] - PubMed
Schomerus 1993 {published data only}
-
- Schomerus H, Schreiegg J. Prevalence of latent portasystemic encephalopathy in an unselected population of patients with liver cirrhosis in general practice. Zeitschrift fur Gastroenterologie 1993;31:231‐4. [PUBMED: 8493802] - PubMed
Sharma 2008 {published data only}
-
- Sharma P, Sharma BC, Puri V, Sarin SK. An open‐label randomized controlled trial of lactulose and probiotics in the treatment of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2008;20:506‐11. [PUBMED: 18467909] - PubMed
Sharma 2009a {published data only}
-
- Sharma P, Sharma BC, Sarin SK. Predictors of nonresponse to lactulose for minimal hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis. Liver International 2009;29:1365‐71. [PUBMED: 19555401] - PubMed
Sharma 2010 {published data only}
-
- Sharma P, Sharma BC, Sarin SK. Predictors of nonresponse to lactulose in patients with cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2010;22:526‐31. [PUBMED: 20009938] - PubMed
Sharma 2010a {published data only}
-
- Sharma P, Sharma BC, Sarin SK. Prevalence of abnormal psychometric tests and critical flicker frequency after clinical recovery of overt hepatic encephalopathy. Neurology India 2010;58:220‐4. [PUBMED: 20508339] - PubMed
Sharma 2011a {published data only}
Trovato 1995 {published data only}
-
- Trovato GM, Catalano D, Carpinteri G, Runcio N, Mazzone O. Effects of lactitol on hepatic encephalopathy and plasma amino‐acid imbalance. Recenti Progressi in Medicina 1995;86:299‐303. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Vendemiale 1992 {published data only}
-
- Vendemiale G, Palasciano G, Cirelli F, Altamura M, Vincentiis A, Altomare E. Crystalline lactulose in the therapy of hepatic cirrhosis. Evaluation of clinical and immunological parameters. Preliminary results. Arzneimittel‐Forschung 1992;42:969‐72. [PMID: 1418064] - PubMed
Venturini 2005 {published data only}
-
- Venturini I, Ferrieri A, Farina F, Cosenza F, Avallone R, Corsi L, et al. Evaluation of rifaximin, placebo and lactulose in reducing the levels of benzodiazepine‐like compounds in patients with liver cirrhosis: a pilot study. Drugs under Experimental and Clinical Research 2005;31:161‐8. [PUBMED: 16223206] - PubMed
Zeegen 1970 {published data only}
-
- Zeegen R, Drinkwater JE, Fenton JC, Vince A, Dawson AM. Some observations on the effects of treatment with lactulose on patients with chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Quarterly Journal of Medicine 1970;39:245‐63. [PUBMED: 5449591] - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
Salih 2007 {unpublished data only}
-
- Lactulose for the prevention of hepatic encephalopathy in participants with cirrhosis and upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage. Ongoing study 2007.
Wang 2012 {unpublished data only}
-
- Impact of lactulose treatment on cognition, assessment of quality of life and changes of intestinal flora in minimal hepatic encephalopathy participants: a multicentre, randomised, open‐label and controlled clinical study. Ongoing study 2012.
Additional references
Bajaj 2008
-
- Bajaj JS, Hafeezullah M, Franco J, Varma RR, Hoffmann RG, Knox JF, et al. Inhibitory control test for the diagnosis of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterology 2008;135:1591‐600. [PUBMED: 18723018] - PubMed
Bajaj 2009
-
- Bajaj JS, Wade JB, Sanyal AJ. Spectrum of neurocognitive impairment in cirrhosis: implications for the assessment of hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2009;50:2014‐21. [PUBMED: 19787808] - PubMed
Bajaj 2010b
Bajaj 2010c
-
- Bajaj JS, Sanyal AJ, Bell D, Gilles H, Heuman DM. Predictors of the recurrence of hepatic encephalopathy in lactulose‐treated patients. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2010;31:1012‐7. [PUBMED: 20136802] - PubMed
Bajaj 2011a
-
- Bajaj JS, Cordoba J, Mullen KD, Amodio P, Shawcross DL, Butterworth RF, et al. Review article: the design of clinical trials in hepatic encephalopathy‐‐an International Society for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen Metabolism (ISHEN) consensus statement. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2011;33:739‐47. [PUBMED: 21306407] - PMC - PubMed
Bajaj 2011b
Bajaj 2012
-
- Bajaj JS, Gillevet PM, Patel NR, Ahluwalia V, Ridlon JM, Kettenmann B, et al. A longitudinal systems biology analysis of lactulose withdrawal in hepatic encephalopathy. Metabolic Brain Disease 2012;27:205‐15. [PUBMED: 22527995] - PubMed
Berding 2009
-
- Berding G, Banati RB, Buchert R, Chierichetti F, Grover VP, Kato A, et al. Radiotracer imaging studies in hepatic encephalopathy: ISHEN practice guidelines. Liver International 2009;29:621‐8. [PUBMED: 19413665] - PubMed
Bircher 1966
-
- Bircher J, Müller J, Guggenheim P, Haemmerli UP. Treatment of chronic portal‐systemic encephalopathy with lactulose. Lancet 1966;1:890. - PubMed
Blanc 1992
-
- Blanc P, Daures JP, Rouillon JM, Peray P, Pierrugues R, Larrey D, et al. Lactitol or lactulose in the treatment of chronic hepatic encephalopathy: results of a meta‐analysis. Hepatology 1992;15:222‐8. [PUBMED: 1531204] - PubMed
Brown 2006
Bustamante 1999
-
- Bustamante J, Rimola A, Ventura PJ, Navasa M, Cirera I, Reggiardo V, et al. Prognostic significance of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis. Journal of Hepatology 1999;30:890‐5. [PUBMED: 10365817] - PubMed
Butterworth 2014
-
- Butterworth RF. Hepatic encephalopathy in alcoholic cirrhosis. Handbook of Clinical Neurology 2014;125:589‐602. [PUBMED: 25307598] - PubMed
Cadranel 2001
-
- Cadranel JF, Lebiez E, Martino V, Bernard B, Koury S, Tourbah A, et al. Focal neurological signs in hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients: an underestimated entity?. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2001;96:515‐8. [PUBMED: 11232699] - PubMed
Camma 1993
-
- Camma C, Fiorello F, Tine F, Marchesini G, Fabbri A, Pagliaro L. Lactitol in treatment of chronic hepatic encephalopathy. A meta‐analysis. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 1993;38:916‐22. [PUBMED: 8482191] - PubMed
Chu 1997
-
- Chu NS, Yang SS, Liaw YF. Evoked potentials in liver diseases. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 1997;12:S288‐93. [PUBMED: 9407349] - PubMed
Conn 1977
-
- Conn HO, Leevy CM, Vlahcevic ZR, Rodgers JB, Maddrey WC, Seeff L, et al. Comparison of lactulose and neomycin in the treatment of chronic portal‐systemic encephalopathy. A double blind controlled trial. Gastroenterology 1977;72:573‐83. [PUBMED: 14049] - PubMed
D'Amico 1986
-
- D'Amico G, Morabito A, Pagliaro L, Marubini E. Survival and prognostic indicators in compensated and decompensated cirrhosis. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 1986;31:468‐75. [PUBMED: 3009109] - PubMed
D'Amico 2006
-
- D'Amico G, Garcia‐Tsao G, Pagliaro L. Natural history and prognostic indicators of survival in cirrhosis: a systematic review of 118 studies. Journal of Hepatology 2006;44:217‐31. - PubMed
de Jongh 1992
-
- Jongh FE, Janssen HL, Man RA, Hop WC, Schalm SW, Blankenstein M. Survival and prognostic indicators in hepatitis B surface antigen‐positive cirrhosis of the liver. Gastroenterology 1992;103:1630‐5. [PUBMED: 1426884] - PubMed
Dwan 2008
EASL and AASLD guideline 2014a
-
- Anonymous. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the European Association for the Study of the Liver and the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Journal of Hepatology 2014;61:642‐59. [PUBMED: 25015420] - PubMed
EASL and AASLD guideline 2014b
-
- Vilstrup H, Amodio P, Bajaj J, Cordoba J, Ferenci P, Mullen KD, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology 2014;60:715‐35. [PUBMED: 25042402] - PubMed
Ferenci 2002
-
- Ferenci P, Lockwood A, Mullen K, Tarter R, Weissenborn K, Blei AT. Hepatic encephalopathy‐‐definition, nomenclature, diagnosis, and quantification: final report of the working party at the 11th World Congresses of Gastroenterology, Vienna, 1998. Hepatology 2002;35:716‐21. [PUBMED: 11870389] - PubMed
Gilson 1975
Gluud 2015
-
- Gluud C, Nikolova D, Klingenberg SL. Cochrane Hepato‐Biliary Group. About Cochrane (Cochrane Review Groups (CRGs)) 2015, Issue 2. Art. No.: LIVER.
GRADEpro [Computer program]
-
- Brozek J, Oxman A, Schünemann H. GRADEpro. Version 3.2 for Windows. Grade Working Group, 2008.
Groeneweg 1998
-
- Groeneweg M, Quero JC, Bruijn I, Hartmann IJ, Essink‐bot ML, Hop WC, et al. Subclinical hepatic encephalopathy impairs daily functioning. Hepatology 1998;28:45‐9. [PUBMED: 9657095] - PubMed
Grover 2006
Guérit 2009
-
- Guérit JM, Amantini A, Fischer C, Kaplan PW, Mecarelli O, Schnitzler A, et al. Neurophysiological investigations of hepatic encephalopathy: ISHEN practice guidelines. Liver International 2009;29:789‐96. [PUBMED: 19638107] - PubMed
Harbord 2006
-
- Harbord RM, Egger M, Sterne JA. A modified test for small‐study effects in meta‐analyses of controlled trials with binary endpoints. Statistics in Medicine 2006;25:3443‐57. [PUBMED: 16345038] - PubMed
Haussinger 2000
-
- Haussinger D, Kircheis G, Fischer R, Schliess F, vom Dahl S. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: a clinical manifestation of astrocyte swelling and low‐grade cerebral edema?. Journal of Hepatology 2000;32:1035‐8. [PUBMED: 10898326] - PubMed
Higgins 2008
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
ICH‐GCP 2007
-
- International Conference on Harmonisation Expert Working Group. International conference on harmonisation of technical requirements for registration of pharmaceuticals for human use. ICH harmonised tripartite guideline. Guideline for good clinical practice CFR & ICH Guidelines. Vol. 1, Pennsylvania: Barnett International/PAREXEL, 1997.
Johanson 2007
Katz 1963
-
- Katz MM, Lyerly SB. Methods for measuring adjustment and social behavior in the community: i. Rationale, description, discriminative validity and scale development. Psychological Reports 1963;13:503‐35.
Kimer 2015
-
- Kimer N, Krag A, Møller S, Bendtsen F, Gluud L. Rifaximin for people with hepatic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011585] - DOI
Kircheis 2002
-
- Kircheis G, Wettstein M, Timmermann L, Schnitzler A, Haussinger D. Critical flicker frequency for quantification of low‐grade hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2002;35:357‐66. [PUBMED: 11826409] - PubMed
Kircheis 2009
-
- Kircheis G, Knoche A, Hilger N, Manhart F, Schnitzler A, Schulze H, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy and fitness to drive. Gastroenterology 2009;137:1706‐15. [PUBMED: 19686744] - PubMed
Lauridsen 2011
-
- Lauridsen MM, Jepsen P, Vilstrup H. Critical flicker frequency and continuous reaction times for the diagnosis of minimal hepatic encephalopathy: a comparative study of 154 patients with liver disease. Metabolic Brain Disease 2011;26:135‐9. [PUBMED: 21484318] - PubMed
Miller 2014
Montagnese 2004
-
- Montagnese S, Amodio P, Morgan MY. Methods for diagnosing hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: a multidimensional approach. Metabolic Brain Disease 2004;19:281‐312. [PUBMED: 15554423] - PubMed
Montgomery 1929
-
- Montgomery E, Hudson CS. Transformation of lactose to a new disaccharide, lactulose. Science 1929;69:556.
Neff 2010
-
- Neff G. Pharmacoeconomics of hepatic encephalopathy. Pharmacotherapy 2010;30:28S‐32S. [PUBMED: 20412038] - PubMed
O'Carroll 1991
-
- O'Carroll RE, Hayes PC, Ebmeier KP, Dougall N, Murray C, Best JJ, et al. Regional cerebral blood flow and cognitive function in patients with chronic liver disease. Lancet 1991;337:1250‐3. [PUBMED: 1674063] - PubMed
Page 2014
-
- Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Kirkham J, Dwan K, Kramer S, Green S, et al. Bias due to selective inclusion and reporting of outcomes and analyses in systematic reviews of randomised trials of healthcare interventions. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2014, Issue 10. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.MR000035.pub2; MR000035] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Parsons‐Smith 1957
-
- Parsons‐Smith BG, Summerskill WH, Dawson AM, Sherlock S. The electroencephalograph in liver disease. Lancet 1957;273:867‐71. [PUBMED: 13482229] - PubMed
Patidar 2014
Poordad 2007
-
- Poordad FF. Review article: the burden of hepatic encephalopathy. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2007;25:3‐9. [PUBMED: 17295846] - PubMed
Qin 2014
-
- Qin N, Yang F, Li A, Prifti E, Chen Y, Shao L, et al. Alterations of the human gut microbiome in liver cirrhosis. Nature 2014;513(7516):59‐64. [PUBMED: 25079328] - PubMed
Randolph 2009
-
- Randolph C, Hilsabeck R, Kato A, Kharbanda P, Li YY, Mapelli D, et al. Neuropsychological assessment of hepatic encephalopathy: ISHEN practice guidelines. Liver International 2009;29:629‐35. [PUBMED: 19302444] - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Riggio 1990b
-
- Riggio O, Varriale M, Testore GP, Rosa R, Rosa E, Merli M, et al. Effect of lactitol and lactulose administration on the fecal flora in cirrhotic patients. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology 1990;12(4):433‐6. [PUBMED: 2398251] - PubMed
Roman 2011
-
- Roman E, Córdoba J, Torrens M, Torras X, Villanueva C, Vargas V, et al. Minimal hepatic encephalopathy is associated with falls. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2011;106:476‐82. - PubMed
Saunders 1981
Savovic 2012
-
- Savovic J, Jones HE, Altman DG, Harris RJ, Juni P, Pildal J, et al. Influence of reported study design characteristics on intervention effect estimates from randomized, controlled trials. Annals of Internal Medicine 2012;157:429‐38. [PUBMED: 22945832] - PubMed
Schomerus 1981
-
- Schomerus H, Hamster W, Blunck H, Reinhard U, Mayer K, Dolle W. Latent portosystemic encephalopathy. I. Nature of cerebral functional defects and their effect on fitness to drive. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 1981;26:622‐30. [PUBMED: 7249898] - PubMed
Schomerus 1998
-
- Schomerus H, Hamster W. Neuropsychological aspects of portal‐systemic encephalopathy. Metabolic Brain Disease 1998;13:361‐77. [PUBMED: 10206827] - PubMed
SF 36 questionnaire
-
- Short Form 36 questionnaire (SF 36). www.sf‐36.org (accessed 20 November 2014).
Sotil 2009
-
- Sotil EU, Gottstein J, Ayala E, Randolph C, Blei AT. Impact of preoperative overt hepatic encephalopathy on neurocognitive function after liver transplantation. Liver Transplantation 2009;15:184‐92. - PubMed
Stata [Computer program]
-
- Stata Corp, Texas, USA. Stata 13. Stata Corp, Texas, USA, 2007.
Stepanova 2012
-
- Stepanova M, Mishra A, Venkatesan C, Younossi ZM. In‐hospital mortality and economic burden associated with hepatic encephalopathy in the United States from 2005 to 2009. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2012;10:1034‐41. [PUBMED: 22642955] - PubMed
Stewart 2007
-
- Stewart CA, Malinchoc M, Kim WR, Kamath PS. Hepatic encephalopathy as a predictor of survival in patients with end‐stage liver disease. Liver Transplantation 2007;13:1366‐71. - PubMed
Taylor‐Robinson 1994
-
- Taylor‐Robinson SD, Sargentoni J, Marcus CD, Morgan MY, Bryant DJ. Regional variations in cerebral proton spectroscopy in patients with chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Metabolic Brain Disease 1994;9:347‐59. [PUBMED: 7898401] - PubMed
Teasdale 1974
-
- Teasdale G, Jennett B. Assessment of coma and impaired consciousness. A practical scale. Lancet 1974;2:81‐4. [PUBMED: 4136544] - PubMed
Thorlund 2011
-
- Thorlund K, Engstrøm J, Wetterslev J, Brok J, Imberger G, Gluud C. User manual for Trial Sequential Analysis (TSA). ctu.dk/tsa/files/tsa_manual.pdf 2011 (accessed 6 June 2015).
TSA 2011 [Computer program]
-
- Copenhagen Trial Unit. TSA ‐ Trial Sequential Analysis. Version 0.9 Beta. Copenhagen: Copenhagen Trial Unit, 2011.
Victor 1965
-
- Victor M, Adams RD, Cole M. The acquired (non‐Wilsonian) type of chronic hepatocerebral degeneration. Medicine 1965;44:345‐96. [PUBMED: 5318075] - PubMed
Volk 2012
Weissenborn 1998
-
- Weissenborn K. Diagnosis of encephalopathy. Digestion 1998;59(Suppl 2):22‐4. - PubMed
Weissenborn 2001
-
- Weissenborn K, Ennen JC, Schomerus H, Ruckert N, Hecker H. Neuropsychological characterization of hepatic encephalopathy. Journal of Hepatology 2001;34:768‐73. [PUBMED: 11434627] - PubMed
WHOQOL 1998
-
- The WHOQOL Group. Development of the World Health Organization WHOQOL‐BREF quality of life assessment. Psychological Medicine 1998;28:551‐8. [PUBMED: 9626712] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Als‐Nielsen 2000
Als‐Nielsen 2004a
Als‐Nielsen 2004b
Als‐Nielsen 2005
-
- Als‐Nielsen BE, Gluud LL, Gluud CN. Nonabsorbable disaccharides for the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy‐‐a systemic review of randomized clinical trials‐‐a secondary publication. Ugeskrift for Laeger 2005;167:179‐82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

