Mutations in DNMT3B Modify Epigenetic Repression of the D4Z4 Repeat and the Penetrance of Facioscapulohumeral Dystrophy
- PMID: 27153398
- PMCID: PMC4863565
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.03.013
Mutations in DNMT3B Modify Epigenetic Repression of the D4Z4 Repeat and the Penetrance of Facioscapulohumeral Dystrophy
Abstract
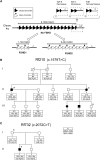
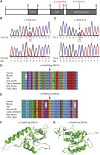
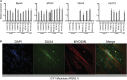
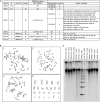
Facioscapulohumeral dystrophy (FSHD) is associated with somatic chromatin relaxation of the D4Z4 repeat array and derepression of the D4Z4-encoded DUX4 retrogene coding for a germline transcription factor. Somatic DUX4 derepression is caused either by a 1-10 unit repeat-array contraction (FSHD1) or by mutations in SMCHD1, which encodes a chromatin repressor that binds to D4Z4 (FSHD2). Here, we show that heterozygous mutations in DNA methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) are a likely cause of D4Z4 derepression associated with low levels of DUX4 expression from the D4Z4 repeat and increased penetrance of FSHD. Recessive mutations in DNMT3B were previously shown to cause immunodeficiency, centromeric instability, and facial anomalies (ICF) syndrome. This study suggests that transcription of DUX4 in somatic cells is modified by variations in its epigenetic state and provides a basis for understanding the reduced penetrance of FSHD within families.
Copyright © 2016 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Padberg G.W., Lunt P.W., Koch M., Fardeau M. Diagnostic criteria for facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy. Neuromuscul. Disord. 1991;1:231–234. - PubMed
-
- van Deutekom J.C., Wijmenga C., van Tienhoven E.A., Gruter A.M., Hewitt J.E., Padberg G.W., van Ommen G.J., Hofker M.H., Frants R.R. FSHD associated DNA rearrangements are due to deletions of integral copies of a 3.2 kb tandemly repeated unit. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1993;2:2037–2042. - PubMed
-
- Wijmenga C., Hewitt J.E., Sandkuijl L.A., Clark L.N., Wright T.J., Dauwerse H.G., Gruter A.M., Hofker M.H., Moerer P., Williamson R. Chromosome 4q DNA rearrangements associated with facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy. Nat. Genet. 1992;2:26–30. - PubMed
-
- Lemmers R.J., Wohlgemuth M., van der Gaag K.J., van der Vliet P.J., van Teijlingen C.M., de Knijff P., Padberg G.W., Frants R.R., van der Maarel S.M. Specific sequence variations within the 4q35 region are associated with facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007;81:884–894. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

