Histamine 1 receptor-Gβγ-cAMP/PKA-CFTR pathway mediates the histamine-induced resetting of the suprachiasmatic circadian clock
- PMID: 27153809
- PMCID: PMC4858891
- DOI: 10.1186/s13041-016-0227-1
Histamine 1 receptor-Gβγ-cAMP/PKA-CFTR pathway mediates the histamine-induced resetting of the suprachiasmatic circadian clock
Abstract
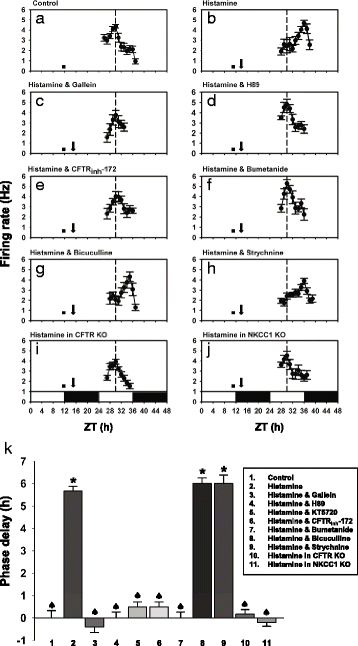
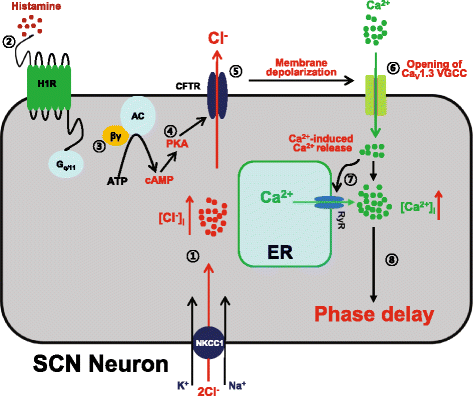
Background: Recent evidence indicates that histamine, acting on histamine 1 receptor (H1R), resets the circadian clock in the mouse suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) by increasing intracellular Ca(2+) concentration ([Ca(2+)]i) through the activation of CaV1.3 L-type Ca(2+) channels and Ca(2+)-induced Ca(2+) release from ryanodine receptor-mediated internal stores.
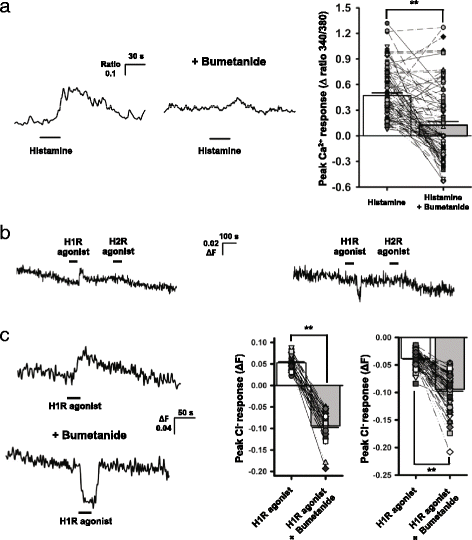
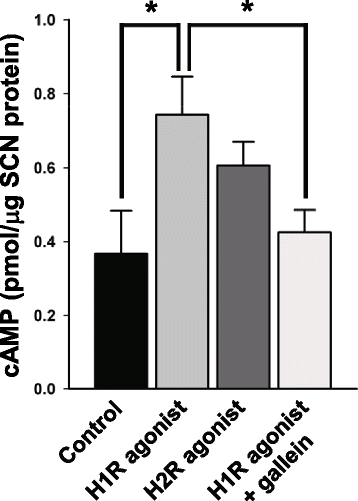
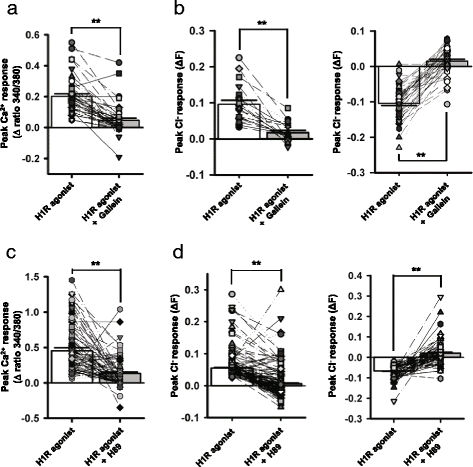
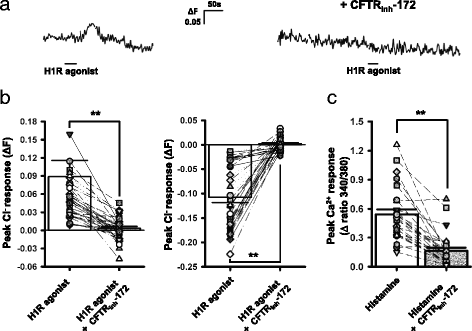
Results: In the current study, we explored the underlying mechanisms with various techniques including Ca(2+)- and Cl(-)-imaging and extracellular single-unit recording. Our hypothesis was that histamine causes Cl(-) efflux through cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) to elicit membrane depolarization needed for the activation of CaV1.3 Ca(2+) channels in SCN neurons. We found that histamine elicited Cl(-) efflux and increased [Ca(2+)]i in dissociated mouse SCN cells. Both of these events were suppressed by bumetanide [Na(+)-K(+)-2Cl(-) cotransporter isotype 1 (NKCC1) blocker], CFTRinh-172 (CFTR inhibitor), gallein (Gβγ protein inhibitor) and H89 [protein kinase A (PKA) inhibitor]. By itself, H1R activation with 2-pyridylethylamine increased the level of cAMP in the SCN and this regulation was prevented by gallein. Finally, histamine-evoked phase shifts of the circadian neural activity rhythm in the mouse SCN slice were blocked by bumetanide, CFTRinh-172, gallein or H89 and were not observed in NKCC1 or CFTR KO mice.
Conclusions: Taken together, these results indicate that histamine recruits the H1R-Gβγ-cAMP/PKA pathway in the SCN neurons to activate CaV1.3 channels through CFTR-mediated Cl(-) efflux and ultimately to phase-shift the circadian clock. This pathway and NKCC1 may well be potential targets for agents designed to treat problems resulting from the disturbance of the circadian system.
Keywords: CFTR; Calcium; Chloride; Circadian rhythm; Histamine; NKCC1; Suprachiasmatic nucleus.
Figures
References
-
- Watanabe T, Taguchi Y, Shiosaka S, Tanaka J, Kubota H, Terano Y, et al. Distribution of the histaminergic neuron system in the central nervous system of rats - A fluorescent immunohistochemical analysis with histidine-decarboxylase as a marker. Brain Res. 1984;295(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90811-4. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

