Dengue research: a bibliometric analysis of worldwide and Arab publications during 1872-2015
- PMID: 27154247
- PMCID: PMC4859974
- DOI: 10.1186/s12985-016-0534-2
Dengue research: a bibliometric analysis of worldwide and Arab publications during 1872-2015
Abstract
Background: Dengue is an important emerging and re-emerging arboviral infection globally as a rapidly growing and widespread public health problem, with transmission occurring in more than 128 countries in Asia, Americas, southeast Africa, western Pacific, and eastern Mediterranean regions. Therefore, the aim of this study was to characterize and quantify the scientific output of dengue research in Arab countries relative to that worldwide by using a bibliometric analysis.
Methods: The standardized search approach based on the use of the the keyword "dengue" in the title, abstract, and keyword field was used to get research output related to dengue at a global level. All data related to dengue were collected from the past to December 31, 2015.
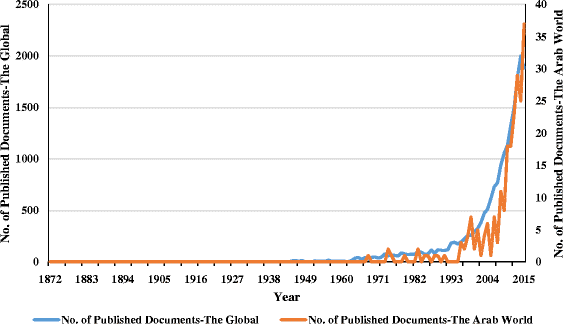
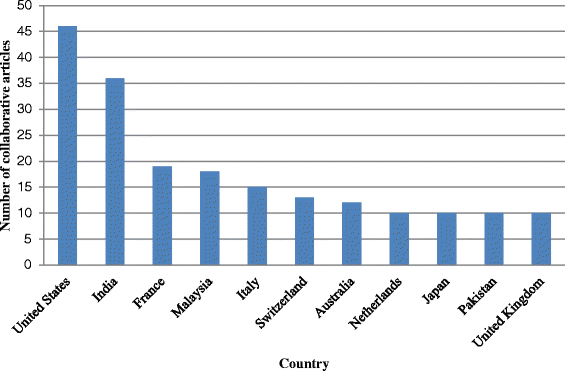
Results: A total of 19,581 dengue-related documents identified in the Scopus database. The results show that the study of dengue exhibits an overall upward trend from 1872 to 2015 with peak publications in 2014. The leading countries in dengue research were the USA (4,709; 24.05 %), India (1,942; 9.92 %), Brazil (1,530; 7.81 %), Thailand (1,260; 6.43 %), the UK (1,129; 5.77 %), and France (1,087; 5.55 %). Only 226 (1.16 % of the overall global research effort in the dengue field) articles were published from the Arab region. The total number of citations for all publications was 352,710, with an average of 18.0 citations per publication. Furthermore, the h-index for all extracted data related to dengue research was 186. Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) was the most productive country in Arab region with 102 documents representing 45.1 %. Furthermore, the h-index for all extracted data related to dengue research was 27. The USA was Arab's most main cooperative partner (46, 20.4 %), followed by India (36, 15.9 %).
Conclusions: The amount of literature related to dengue research has considerably increased over the last decade. This bibliometric analysis has demonstrated the leading role that the USA, India, Brazil, Thailand, the UK, and France play in dengue research. The Arab world produced fewer publications related to dengue with lower quality than other world countries.
Keywords: Arab world; Bibliometric; Citations; Dengue; Scopus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Scientific research publications in dengue: A global and Indian bibliometric analysis from 1997 to 2018.J Vector Borne Dis. 2019 Oct-Dec;56(4):281-287. doi: 10.4103/0972-9062.302029. J Vector Borne Dis. 2019. PMID: 33269726 Review.
-
Arab world's growing contribution to global leishmaniasis research (1998-2017): a bibliometric study.BMC Public Health. 2019 May 22;19(1):625. doi: 10.1186/s12889-019-6969-9. BMC Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31118003 Free PMC article.
-
Benchmarking the scientific output of industrial wastewater research in Arab world by utilizing bibliometric techniques.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016 May;23(10):10288-300. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6434-6. Epub 2016 Mar 21. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016. PMID: 26996912 Free PMC article.
-
Scientific publications from Arab world in leading journals of Integrative and Complementary Medicine: a bibliometric analysis.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015 Sep 4;15:308. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0840-z. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015. PMID: 26341635 Free PMC article.
-
A Scopus-based examination of tobacco use publications in Middle Eastern Arab countries during the period 2003-2012.Harm Reduct J. 2014 May 1;11:14. doi: 10.1186/1477-7517-11-14. Harm Reduct J. 2014. PMID: 24885706 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The bibliometric landscape of infectious disease research in Panama (1990-2019).Dialogues Health. 2023 Feb 24;2:100117. doi: 10.1016/j.dialog.2023.100117. eCollection 2023 Dec. Dialogues Health. 2023. PMID: 38515494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bibliometric Indicators of the Zika Outbreak.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017 Jan 19;11(1):e0005132. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005132. eCollection 2017 Jan. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017. PMID: 28103326 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A Bibliometric Analysis on Dengue Outbreaks in Tropical and Sub-Tropical Climates Worldwide Since 1950.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Mar 19;18(6):3197. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18063197. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33808795 Free PMC article.
-
Dengue fever with bilateral thalamic diffusion restriction lesions: a case report.BMC Neurol. 2025 Apr 26;25(1):185. doi: 10.1186/s12883-025-04197-2. BMC Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40287618 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric Analysis of Ebola Research Indexed in Web of Science and Scopus (2010-2020).Biomed Res Int. 2020 Sep 3;2020:5476567. doi: 10.1155/2020/5476567. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32964036 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilder-Smith A, Byass P. The elusive global burden of dengue. Lancet Infect Dis. 2016. Article in press. - PubMed
-
- Jaenisch T, Tam DT, Kieu NT, Van Ngoc T, Nam NT, Van Kinh N, Yacoub S, Chanpheaktra N, Kumar V, See LL, et al. Clinical evaluation of dengue and identification of risk factors for severe disease: protocol for a multicentre study in 8 countries. BMC Infect Dis. 2016;16:120. doi: 10.1186/s12879-016-1440-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous