DNA methylation changes facilitated evolution of genes derived from Mutator-like transposable elements
- PMID: 27154274
- PMCID: PMC4858842
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-016-0954-8
DNA methylation changes facilitated evolution of genes derived from Mutator-like transposable elements
Abstract
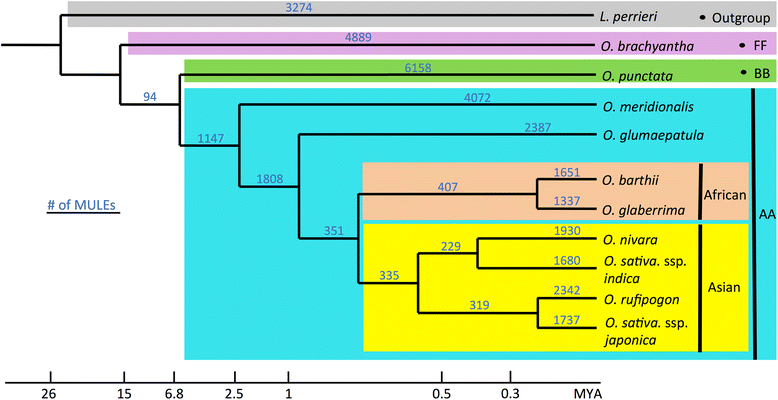
Background: Mutator-like transposable elements, a class of DNA transposons, exist pervasively in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes, with more than 10,000 copies identified in the rice genome. These elements can capture ectopic genomic sequences that lead to the formation of new gene structures. Here, based on whole-genome comparative analyses, we comprehensively investigated processes and mechanisms of the evolution of putative genes derived from Mutator-like transposable elements in ten Oryza species and the outgroup Leersia perieri, bridging ~20 million years of evolutionary history.
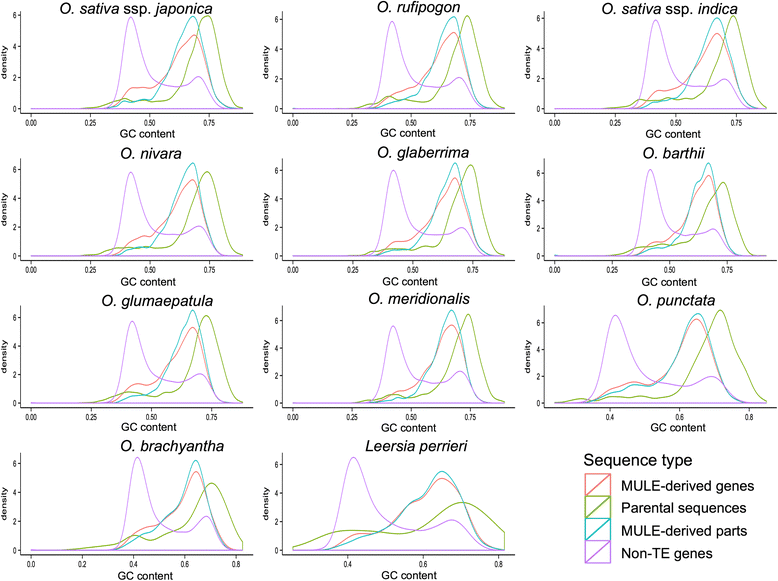
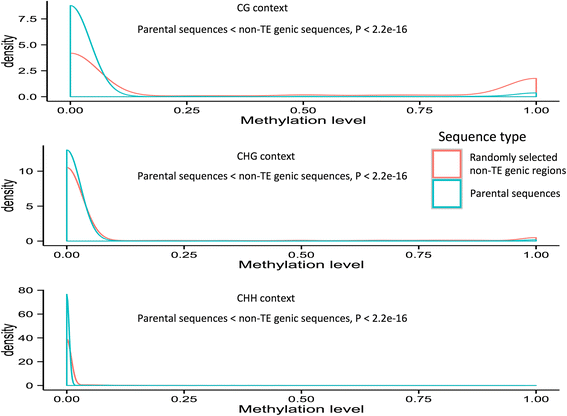
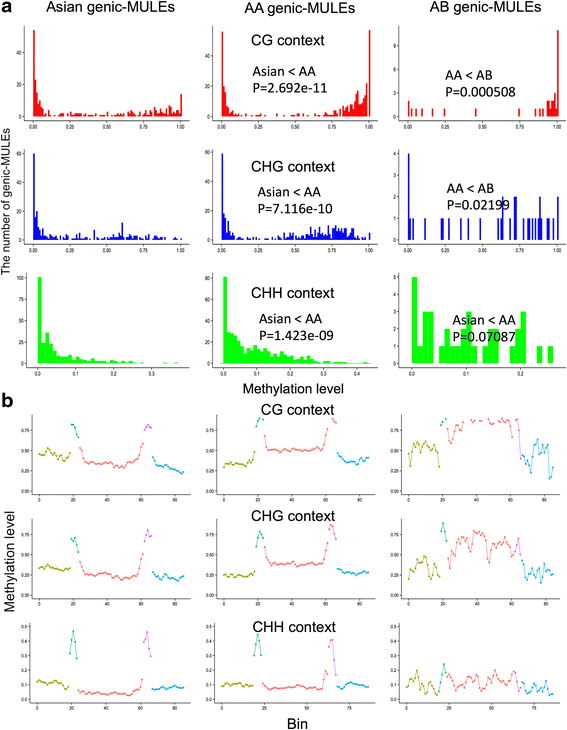
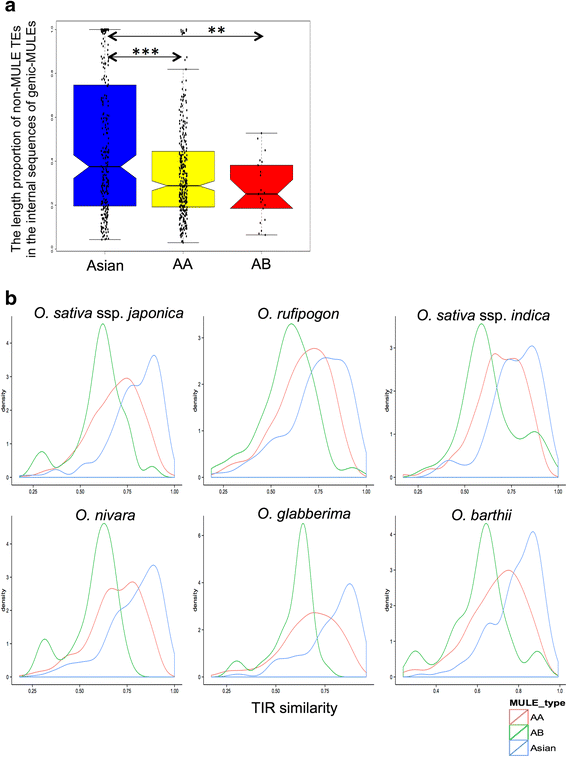
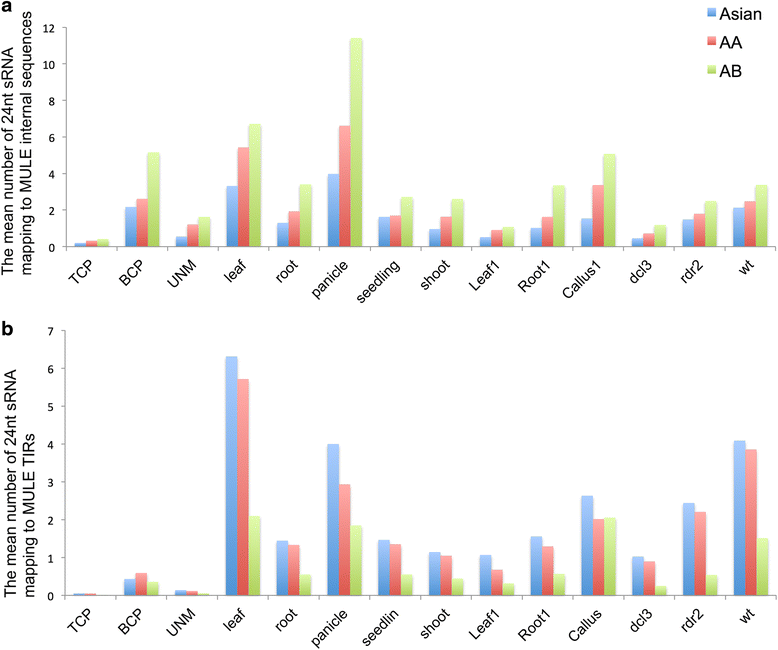
Results: Our analysis identified thousands of putative genes in each of the Oryza species, a large proportion of which have evidence of expression and contain chimeric structures. Consistent with previous reports, we observe that the putative Mutator-like transposable element-derived genes are generally GC-rich and mainly derive from GC-rich parental sequences. Furthermore, we determine that Mutator-like transposable elements capture parental sequences preferentially from genomic regions with low methylation levels and high recombination rates. We explicitly show that methylation levels in the internal and terminated inverted repeat regions of these elements, which might be directed by the 24-nucleotide small RNA-mediated pathway, are different and change dynamically over evolutionary time. Lastly, we demonstrate that putative genes derived from Mutator-like transposable elements tend to be expressed in mature pollen, which have undergone de-methylation programming, thereby providing a permissive expression environment for newly formed/transposable element-derived genes.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that DNA methylation may be a primary mechanism to facilitate the origination, survival, and regulation of genes derived from Mutator-like transposable elements, thus contributing to the evolution of gene innovation and novelty in plant genomes.
Keywords: Comparative genomics; DNA methylation; GC content; MULEs; Molecular evolution; New genes; Oryza; Recombination rate.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Selective acquisition and retention of genomic sequences by Pack-Mutator-like elements based on guanine-cytosine content and the breadth of expression.Plant Physiol. 2013 Nov;163(3):1419-32. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.223271. Epub 2013 Sep 12. Plant Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24028844 Free PMC article.
-
Autotetraploid rice methylome analysis reveals methylation variation of transposable elements and their effects on gene expression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Dec 15;112(50):E7022-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1515170112. Epub 2015 Nov 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26621743 Free PMC article.
-
Survey of transposable elements from rice genomic sequences.Plant J. 2001 Jan;25(2):169-79. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.00945.x. Plant J. 2001. PMID: 11169193
-
Miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements: discovery, distribution, and activity.Genome. 2013 Sep;56(9):475-86. doi: 10.1139/gen-2012-0174. Epub 2013 Mar 8. Genome. 2013. PMID: 24168668 Review.
-
Intertwined evolution of plant epigenomes and genomes.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2021 Jun;61:101990. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2020.101990. Epub 2021 Jan 11. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 33445143 Review.
Cited by
-
Domestication of rice has reduced the occurrence of transposable elements within gene coding regions.BMC Genomics. 2017 Jan 9;18(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3454-z. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28068923 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Characterization of Virulence Factors and Related Proteins in Enterococcus Strains from Dairy and Fermented Food Products.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 19;23(18):10971. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810971. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142880 Free PMC article.
-
Maize DNA Methylation in Response to Drought Stress Is Involved in Target Gene Expression and Alternative Splicing.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 31;22(15):8285. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158285. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34361051 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Characterization of Antibiotic Resistance in Listeria and Production of Antimicrobial and Virulence Factors.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 29;22(15):8141. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158141. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360905 Free PMC article.
-
CsMYB60 is a key regulator of flavonols and proanthocyanidans that determine the colour of fruit spines in cucumber.J Exp Bot. 2019 Jan 1;70(1):69-84. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery336. J Exp Bot. 2019. PMID: 30256979 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Robertson DS. Characterization of a Mutator system in maize. Mutat Res. 1978;51:21–28. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(78)90004-0. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

