Aerobic and anaerobic cellulase production by Cellulomonas uda
- PMID: 27154570
- PMCID: PMC4995238
- DOI: 10.1007/s00203-016-1230-8
Aerobic and anaerobic cellulase production by Cellulomonas uda
Abstract
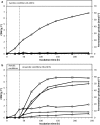
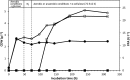
Cellulomonas uda (DSM 20108/ATCC 21399) is one of the few described cellulolytic facultative anaerobes. Based on these characteristics, we initiated a physiological study of C. uda with the aim to exploit it for cellulase production in simple bioreactors with no or sporadic aeration. Growth, cellulase activity and fermentation product formation were evaluated in different media under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions and in experiments where C. uda was exposed to alternating aerobic/anaerobic growth conditions. Here we show that C. uda behaves as a true facultative anaerobe when cultivated on soluble substrates such as glucose and cellobiose, but for reasons unknown cellulase activity is only induced under aerobic conditions on insoluble cellulosic substrates and not under anaerobic conditions. These findings enhance knowledge on the limited number of described facultative cellulolytic anaerobes, and in addition it greatly limits the utility of C. uda as an 'easy to handle' cellulase producer with low aeration demands.
Keywords: Aerobic/anaerobic; Cellulase; Cellulomonas uda; Cellulose degradation; Facultative anaerobe.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Beguin P, Eisen H, Roupas A. Free and cellulose-bound cellulases in a Cellulomonas species. J Gen Microbiol. 1977;101:191–196. doi: 10.1099/00221287-101-2-191. - DOI
-
- Bower CE, Holmhansen T. A salicylate-hypochlorite method for determining ammonia in seawater. Can J Fish Aquat Sci. 1980;37:794–798. doi: 10.1139/f80-106. - DOI
-
- Christopherson MR, Suen G, Bramhacharya S, Jewell KA, Aylward FO, Mead D, Brumm PJ. The genome sequences of Cellulomonas fimi and “Cellvibrio gilvus” reveal the cellulolytic strategies of two facultative anaerobes, transfer of “Cellvibrio gilvus” to the genus Cellulomonas, and proposal of Cellulomonas gilvus sp nov. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e53954. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053954. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clemmer JE, Tseng CL. Identification of the major anaerobic end products of Cellulomonas Sp (Atcc-21399) Biotechnol Lett. 1986;8:823–826. doi: 10.1007/BF01020832. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

