Regulation of astrocyte glutamate transporter-1 (GLT1) and aquaporin-4 (AQP4) expression in a model of epilepsy
- PMID: 27155358
- PMCID: PMC4992641
- DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2016.05.003
Regulation of astrocyte glutamate transporter-1 (GLT1) and aquaporin-4 (AQP4) expression in a model of epilepsy
Abstract
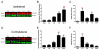
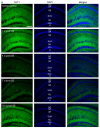
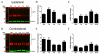
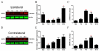
Astrocytes regulate extracellular glutamate and water homeostasis through the astrocyte-specific membrane proteins glutamate transporter-1 (GLT1) and aquaporin-4 (AQP4), respectively. The role of astrocytes and the regulation of GLT1 and AQP4 in epilepsy are not fully understood. In this study, we investigated the expression of GLT1 and AQP4 in the intrahippocampal kainic acid (IHKA) model of temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE). We used real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), Western blot, and immunohistochemical analysis at 1, 4, 7, and 30days after kainic acid-induced status epilepticus (SE) to determine hippocampal glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP, a marker for reactive astrocytes), GLT1, and AQP4 expression changes during the development of epilepsy (epileptogenesis). Following IHKA, all mice had SE and progressive increases in GFAP immunoreactivity and GFAP protein expression out to 30days post-SE. A significant initial increase in dorsal hippocampal GLT1 immunoreactivity and protein levels were observed 1day post SE and followed by a marked downregulation at 4 and 7days post SE with a return to near control levels by 30days post SE. AQP4 dorsal hippocampal protein expression was significantly downregulated at 1day post SE and was followed by a gradual return to baseline levels with a significant increase in ipsilateral protein levels by 30days post SE. Transient increases in GFAP and AQP4 mRNA were also observed. Our findings suggest that specific molecular changes in astrocyte glutamate transporters and water channels occur during epileptogenesis in this model, and suggest the novel therapeutic strategy of restoring glutamate and water homeostasis.
Keywords: AQP4; Aquaporin; Astrocyte; EAAT2; Epilepsy; GFAP; GLT1; Glutamate transporter-1; Kainic acid; Seizure.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Alvestad S, Hammer J, Hoddevik EH, Skare O, Sonnewald U, Amiry-Moghaddam M, Ottersen OP. Mislocalization of AQP4 precedes chronic seizures in the kainate model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2013;105:30–41. - PubMed
-
- Amiry-Moghaddam M, Ottersen OP. The molecular basis of water transport in the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003;4:991–1001. - PubMed
-
- Arabadzisz D, Antal K, Parpan F, Emri Z, Fritschy JM. Epileptogenesis and chronic seizures in a mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy are associated with distinct EEG patterns and selective neurochemical alterations in the contralateral hippocampus. Exp. Neurol. 2005;194:76–90. - PubMed
-
- Araque A, Parpura V, Sanzgiri RP, Haydon PG. Tripartite synapses: glia, the unacknowledged partner. Trends Neurosci. 1999;22:208–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

