Pharmacological modulation of lateral habenular dopamine D2 receptors alters the anxiogenic response to cocaine in a runway model of drug self-administration
- PMID: 27155504
- PMCID: PMC4887427
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.05.002
Pharmacological modulation of lateral habenular dopamine D2 receptors alters the anxiogenic response to cocaine in a runway model of drug self-administration
Abstract
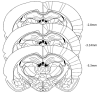
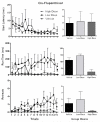
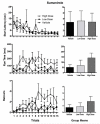
Cocaine has long been known to produce an initial "high" followed by an aversive/anxiogenic "crash". While much is known about the neurobiology of cocaine's positive/rewarding effects, the mechanisms that give rise to the drug's negative/anxiogenic actions remain unclear. Recent research has implicated the lateral habenula (LHb) in the encoding of aversive events including the anxiogenic response to cocaine. Of particular interest in this regard are the reciprocal connections between the LHb and the ventral tegmental area (VTA). VTA-DA neurons innervate different subsets of LHb cells that in turn feedback upon and modulate VTA neuronal activity. Here we examined the impact of D2 receptor activation and inhibition on the anxiogenic response to cocaine using a runway model of self-administration that is sensitive to the dual and opposing effects of the drug. Male rats ran a straight alley for IV cocaine (1.0mg/kg) following bilateral intra-LHb infusions of the D2 receptor antagonist, cis-flupenthixol (0, 7.5 or 15μg/side) or the D2 agonist, sumanirole (0, 5 or 10μg/side). Vehicle-pretreated controls developed approach-avoidance conflict behaviors about goal-box entry reflective of the dual positive and negative effects of cocaine. These behaviors were significantly diminished during LHb-D2 receptor antagonism and increased by the LHb D2 receptor agonist. These results demonstrate that activity at the D2 receptor in the lateral habenula serves to modulate the anxiogenic response to cocaine.
Keywords: anxiety; cis-flupenthixol; cocaine; lateral habenula; runway self-administration; sumanirole.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
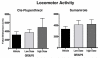
Similar articles
-
Activation of 5-HT1B receptors in the Lateral Habenula attenuates the anxiogenic effects of cocaine.Behav Brain Res. 2019 Jan 14;357-358:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2018.04.014. Epub 2018 Apr 13. Behav Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 29660439 Free PMC article.
-
Entopeduncular Nucleus Projections to the Lateral Habenula Contribute to Cocaine Avoidance.J Neurosci. 2021 Jan 13;41(2):298-306. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0708-20.2020. Epub 2020 Nov 19. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33214316 Free PMC article.
-
D1-like dopamine receptor dysfunction in the lateral habenula nucleus increased anxiety-like behavior in rat.Neuroscience. 2017 Jan 6;340:542-550. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.11.005. Epub 2016 Nov 16. Neuroscience. 2017. PMID: 27865867
-
Habenular connections with the dopaminergic and serotonergic system and their role in stress-related psychiatric disorders.Eur J Neurosci. 2021 Jan;53(1):65-88. doi: 10.1111/ejn.14647. Epub 2019 Dec 27. Eur J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 31833616 Review.
-
The lateral habenula and alcohol: Role of glutamate and M-type potassium channels.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2017 Nov;162:94-102. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2017.06.005. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2017. PMID: 28624587 Review.
Cited by
-
Ethanol Withdrawal Drives Anxiety-Related Behaviors by Reducing M-type Potassium Channel Activity in the Lateral Habenula.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2017 Aug;42(9):1813-1824. doi: 10.1038/npp.2017.68. Epub 2017 Apr 7. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28387223 Free PMC article.
-
Lateral habenular norepinephrine contributes to states of arousal and anxiety in male rats.Behav Brain Res. 2018 Jul 16;347:108-115. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2018.03.012. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Behav Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 29526789 Free PMC article.
-
Review of the cytology and connections of the lateral habenula, an avatar of adaptive behaving.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2017 Nov;162:3-21. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2017.06.004. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2017. PMID: 28647565 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allen Institute for Brain Science © Allen Mouse Brain Atlas [Internet] 2015 Available from: http://mouse.brain-map.org.
-
- Amat J, Sparks PD, Matus-Amat P, Griggs J, Watkins LR, Maier SF. The role of the habenular complex in the elevation of dorsal raphé nucleus serotonin and the changes in the behavioral responses produced by uncontrollable stress. Brain Research. 2001;917:118–126. - PubMed
-
- Anthony JC, Tien AY, Petronis KR. Epidemiologic evidence on cocaine use and panic attacks. American Journal of Epidemiology. 1989;129:543–549. - PubMed
-
- Aston-Jones G, Harris GC. Brain substrates for increased drug seeking during protracted withdrawal. Neuropharmacology. 2004;47(Suppl 1):167–179. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

