Force Generation by Membrane-Associated Myosin-I
- PMID: 27156719
- PMCID: PMC4860596
- DOI: 10.1038/srep25524
Force Generation by Membrane-Associated Myosin-I
Abstract
Vertebrate myosin-IC (Myo1c) is a type-1 myosin that links cell membranes to the cytoskeleton via its actin-binding motor domain and its phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P2)-binding tail domain. While it is known that Myo1c bound to PtdIns(4,5)P2 in fluid-lipid bilayers can propel actin filaments in an unloaded motility assay, its ability to develop forces against external load on actin while bound to fluid bilayers has not been explored. Using optical tweezers, we measured the diffusion coefficient of single membrane-bound Myo1c molecules by force-relaxation experiments, and the ability of ensembles of membrane-bound Myo1c molecules to develop and sustain forces. To interpret our results, we developed a computational model that recapitulates the basic features of our experimental ensemble data and suggests that Myo1c ensembles can generate forces parallel to lipid bilayers, with larger forces achieved when the myosin works away from the plane of the membrane or when anchored to slowly diffusing regions.
Figures
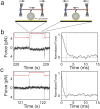

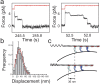
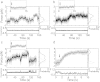

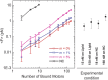

 in Table 3, also see Supplementary Information).
in Table 3, also see Supplementary Information).Similar articles
-
Membrane-bound myo1c powers asymmetric motility of actin filaments.Curr Biol. 2012 Sep 25;22(18):1688-92. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.06.069. Epub 2012 Aug 2. Curr Biol. 2012. PMID: 22863317 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane-bound myosin IC drives the chiral rotation of the gliding actin filament around its longitudinal axis.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 14;13(1):19908. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-47125-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37963943 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics of the interaction of myo1c with phosphoinositides.J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 16;284(42):28650-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.049791. Epub 2009 Aug 25. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19706607 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging the membrane - cytoskeleton interface with myosin-1.Trends Cell Biol. 2010 Jul;20(7):418-26. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2010.04.004. Epub 2010 May 12. Trends Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20471271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myosin-I molecular motors at a glance.J Cell Sci. 2016 Jul 15;129(14):2689-95. doi: 10.1242/jcs.186403. Epub 2016 Jul 11. J Cell Sci. 2016. PMID: 27401928 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SH3BGRL3 binds to myosin 1c in a calcium dependent manner and modulates migration in the MDA-MB-231 cell line.BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2021 Aug 11;22(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s12860-021-00379-1. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34380438 Free PMC article.
-
Switch-2 determines Mg2+ADP-release kinetics and fine-tunes the duty ratio of Dictyostelium class-1 myosins.Front Physiol. 2024 Jun 3;15:1393952. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1393952. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38887318 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanochemical properties of human myosin-1C are modulated by isoform-specific differences in the N-terminal extension.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100128. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015187. Epub 2020 Dec 3. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33257319 Free PMC article.
-
Supported lipid bilayer platforms to probe cell mechanobiology.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2017 Sep;1859(9 Pt A):1465-1482. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2017.05.005. Epub 2017 May 11. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2017. PMID: 28502789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemomechanical regulation of myosin Ic cross-bridges: Deducing the elastic properties of an ensemble from single-molecule mechanisms.PLoS Comput Biol. 2017 May 26;13(5):e1005566. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005566. eCollection 2017 May. PLoS Comput Biol. 2017. PMID: 28549064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yin H. L. & Janmey P. A. Phosphoinositide regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. Annu Rev Physiol 65, 761–89 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

