New approaches in the diagnosis, pathophysiology, and treatment of pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy
- PMID: 27156964
- PMCID: PMC5710737
- DOI: 10.1016/j.transci.2016.04.007
New approaches in the diagnosis, pathophysiology, and treatment of pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy
Abstract
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT)-associated thrombotic microangiopathy (TA-TMA) is an understudied complication of HSCT that significantly affects transplant-related morbidity and mortality. Over the past several decades, the cause of TA-TMA has remained unknown, limiting treatment options to non-specific therapies adapted from other diseases. Recent prospective studies dedicated to the study of TA-TMA have provided new insights into the pathogenesis of, and genetic susceptibility to TA-TMA, raising awareness of this important transplant complication and allowing for the identification of potentially novel therapeutic targets. Specifically, many patients with TA-TMA develop multi-organ tissue injury through endothelial damage mediated by the activation of the complement pathway, leading to rational therapeutic strategies including complement blockade. This new knowledge has the potential to favorably influence clinical practice and change the standard of care for how patients with TA-TMA are managed. In this review, we summarize novel approaches to the recognition and management of TA-TMA, using case examples to illustrate key clinical points that hopefully lead to improved short and long-term outcomes for these complex HSCT patients, who remain at significant risk for treatment-related morbidity and mortality.
Keywords: Complement; Eculizumab; Hematopoietic stem cell transplant; TA-TMA; Thrombotic microangiopathy.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
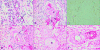

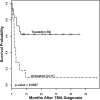
References
-
- Elsallabi O, Bhatt VR, Dhakal P, Foster KW, Tendulkar KK. Hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2016;22:12–20. - PubMed
-
- Ho VT, Cutler C, Carter S, Martin P, Adams R, Horowitz M, et al. Blood and marrow transplant clinical trials network toxicity committee consensus summary: thrombotic microangiopathy after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2005;11:571–5. - PubMed
-
- Ruutu T, Barosi G, Benjamin RJ, Clark RE, George JN, Gratwohl A, et al. Diagnostic criteria for hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated microangiopathy: results of a consensus process by an International Working Group. Haematologica. 2007;92:95–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

