Quantum dot-NanoLuc bioluminescence resonance energy transfer enables tumor imaging and lymph node mapping in vivo
- PMID: 27157466
- PMCID: PMC4912020
- DOI: 10.1039/c6cc02764d
Quantum dot-NanoLuc bioluminescence resonance energy transfer enables tumor imaging and lymph node mapping in vivo
Abstract
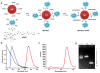
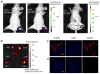
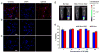
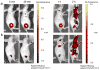
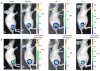
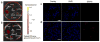
A small luciferase protein (Nluc) was conjugated to QDs as a bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) pair. The conjugate showed 76% BRET efficiency and lymph node mapping was successfully performed. The cRGD peptide was conjugated to QD-Nluc for tumor targeting. The self-illuminating QD-Nluc showed excellent energy transfer in a living system and offered an optimal tumor-to-background ratio (>85).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Self-illuminating quantum dots for highly sensitive in vivo real-time luminescent mapping of sentinel lymph nodes.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:3433-43. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S30709. Epub 2012 Jul 5. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22848169 Free PMC article.
-
An enzymatically-sensitized sequential and concentric energy transfer relay self-assembled around semiconductor quantum dots.Nanoscale. 2015 May 7;7(17):7603-14. doi: 10.1039/c5nr00828j. Nanoscale. 2015. PMID: 25804284
-
Near infrared bioluminescence resonance energy transfer from firefly luciferase--quantum dot bionanoconjugates.Nanotechnology. 2014 Dec 12;25(49):495606. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/25/49/495606. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Nanotechnology. 2014. PMID: 25414169
-
Integration of Nanomaterials and Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer Techniques for Sensing Biomolecules.Biosensors (Basel). 2019 Mar 16;9(1):42. doi: 10.3390/bios9010042. Biosensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30884844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NanoLuc: A Small Luciferase Is Brightening Up the Field of Bioluminescence.Bioconjug Chem. 2016 May 18;27(5):1175-1187. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.6b00112. Epub 2016 Apr 19. Bioconjug Chem. 2016. PMID: 27045664 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chemiluminescence and Bioluminescence Imaging for Biosensing and Therapy: In Vitro and In Vivo Perspectives.Theranostics. 2019 May 31;9(14):4047-4065. doi: 10.7150/thno.33228. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31281531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Creation of different bioluminescence resonance energy transfer based biosensors with high affinity to VEGF.PLoS One. 2020 Mar 26;15(3):e0230344. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230344. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32214330 Free PMC article.
-
Coelenterazine-Dependent Luciferases as a Powerful Analytical Tool for Research and Biomedical Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 10;21(20):7465. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207465. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33050422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current advances in the development of bioluminescent probes toward spatiotemporal trans-scale imaging.Biophys Physicobiol. 2024 Feb 2;21(Supplemental):e211004. doi: 10.2142/biophysico.bppb-v21.s004. eCollection 2024. Biophys Physicobiol. 2024. PMID: 39175853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanobody-Nanoluciferase Fusion Protein-Enabled Immunoassay for Ochratoxin A in Coffee with Enhanced Specificity and Sensitivity.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Oct 19;14(10):713. doi: 10.3390/toxins14100713. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36287981 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

