Update on management of Barrett's esophagus
- PMID: 27158538
- PMCID: PMC4848245
- DOI: 10.4292/wjgpt.v7.i2.227
Update on management of Barrett's esophagus
Abstract
Barrett's esophagus (BE) is a common condition that develops as a consequence of gastroesophageal reflux disease. The significance of Barrett's metaplasia is that predisposes to cancer development. This article provides a current evidence-based review for the management of BE and related early neoplasia. Controversial issues that impact the management of patients with BE, including definition, screening, clinical aspects, diagnosis, surveillance, and management of dysplasia and early cancer have been assessed.
Keywords: Barrett metaplasia; Barrett’s esophagus; Esophageal adenocarcinoma; Gastroesophageal reflux disease; Radiofrequency ablation.
Figures
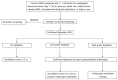
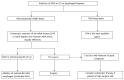
References
-
- Barrett NR. Chronic peptic ulcer of the oesophagus and “oesophagitis”. Br J Surg. 1950;38:175–182. - PubMed
-
- Spechler SJ, Sharma P, Souza RF, Inadomi JM, Shaheen NJ. American Gastroenterological Association medical position statement on the management of Barrett’s esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:1084–1091. - PubMed
-
- Fitzgerald RC, di Pietro M, Ragunath K, Ang Y, Kang JY, Watson P, Trudgill N, Patel P, Kaye PV, Sanders S, et al. British Society of Gastroenterology guidelines on the diagnosis and management of Barrett’s oesophagus. Gut. 2014;63:7–42. - PubMed
-
- Riddell RH, Odze RD. Definition of Barrett’s esophagus: time for a rethink--is intestinal metaplasia dead? Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:2588–2594. - PubMed
-
- Ronkainen J, Aro P, Storskrubb T, Johansson SE, Lind T, Bolling-Sternevald E, Vieth M, Stolte M, Talley NJ, Agréus L. Prevalence of Barrett’s esophagus in the general population: an endoscopic study. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:1825–1831. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

