Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: A Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 27158575
- PMCID: PMC4846395
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.546
Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
Introduction Anaplastic large cell lymphoma is a very rare T-cell lymphoma that has only recently been found to be associated with breast implants. It has been described in the literature mainly in the form of case reports. This article focuses on the imaging characteristics of this rare disease. We hope to increase awareness of breast imagers and referring physicians to improve early detection rates. Case Report We present the case of a 32-year-old female who presented with several weeks of pain and firmness in her right breast. MRI and ultrasound demonstrated a peri-implant fluid collection. Ultrasound-guided aspiration revealed anaplastic large cell lymphoma. The patient was treated with implant removal alone and has now been in remission for 3 years. Conclusion Anaplastic large cell lymphoma of the breast is a very rare entity that has mainly been described in the literature as case reports. As in the case of our patient, imaging findings can be very non-specific, and it is important for surgeons, breast imagers, and oncologists to be aware of this rare disease to ensure prompt diagnosis.
Keywords: Breast; anaplastic large cell lymphoma; mri; peri-implant fluid collection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
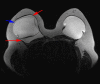
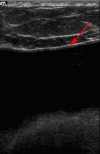
Similar articles
-
The First Confirmed Case of Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma in Hawai'i.Hawaii J Health Soc Welf. 2019 Nov;78(11):338-340. Hawaii J Health Soc Welf. 2019. PMID: 31723941 Free PMC article.
-
Breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma, an under-recognised entity.J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2019 Oct;63(5):630-638. doi: 10.1111/1754-9485.12905. Epub 2019 Jun 7. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31173460 Review.
-
Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma associated with breast implants: a unique entity within the spectrum of peri-implant effusions.Diagn Cytopathol. 2014 Nov;42(11):929-38. doi: 10.1002/dc.23152. Epub 2014 Mar 31. Diagn Cytopathol. 2014. PMID: 24687769
-
Variable presentation of anaplastic large-cell lymphoma in patients with breast implants.ANZ J Surg. 2017 Oct;87(10):789-794. doi: 10.1111/ans.13074. Epub 2015 Apr 1. ANZ J Surg. 2017. PMID: 25827224
-
Primary breast lymphoma in a patient with silicone breast implants: a case report and review of the literature.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2008 Jul;61(7):822-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2007.03.027. Epub 2007 May 16. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2008. PMID: 17509956 Review.
Cited by
-
[Understanding Silicone Breast Implant-Associated Complications for Radiologists].Taehan Yongsang Uihakhoe Chi. 2021 Jan;82(1):49-65. doi: 10.3348/jksr.2020.0208. Epub 2021 Jan 31. Taehan Yongsang Uihakhoe Chi. 2021. PMID: 36237459 Free PMC article. Review. Korean.
-
Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma: Current Understanding and Recommendations for Management.Plast Surg (Oakv). 2020 May;28(2):117-126. doi: 10.1177/2292550320925906. Epub 2020 May 21. Plast Surg (Oakv). 2020. PMID: 32596187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Description of Two Cases of Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Associated with a Breast Implant.Case Rep Radiol. 2019 Jun 27;2019:6137198. doi: 10.1155/2019/6137198. eCollection 2019. Case Rep Radiol. 2019. PMID: 31346484 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) in women with breast implants: Preliminary FDA findings and analyses. [Dec;2015 ];Large Large. http://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/ProductsandMedicalProcedures/Implantsa... 2011
-
- Breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma: a case report and literature review. Hwang MJ, Brown H, Murrin R, Momtahan N, Sterne GD. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2015;39:391–395. - PubMed
-
- Coming of age: Breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma after 18 years of investigation. Clemens MW, Miranda RN. Clin Plast Surg. 2015;42:605–613. - PubMed
-
- Lymphomas associated with breast implants: A review of the literature. Rupani A, Frame JD, Kamel D. Aesthet Surg J. 2015;35:533–544. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
