Whole exome sequencing in patients with white matter abnormalities
- PMID: 27159321
- PMCID: PMC5354169
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.24650
Whole exome sequencing in patients with white matter abnormalities
Abstract
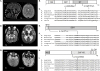
Here we report whole exome sequencing (WES) on a cohort of 71 patients with persistently unresolved white matter abnormalities with a suspected diagnosis of leukodystrophy or genetic leukoencephalopathy. WES analyses were performed on trio, or greater, family groups. Diagnostic pathogenic variants were identified in 35% (25 of 71) of patients. Potentially pathogenic variants were identified in clinically relevant genes in a further 7% (5 of 71) of cases, giving a total yield of clinical diagnoses in 42% of individuals. These findings provide evidence that WES can substantially decrease the number of unresolved white matter cases. Ann Neurol 2016;79:1031-1037.
© 2016 American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
AV receives funding from Illumina, Inc., Gilead Sciences Inc., Eli Lilly & Co. and Shire Plc. AK, VR, ER, SC, TH, and RJT are employees of Illumina, Inc. The rest of the authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Vanderver A, Tonduti D, Schiffmann R, Schmidt J, Van der Knaap MS. Leukodystrophy Overview. In: Pagon RA, Adam MP, Bird TD, Dolan CR, Fong CT, Smith RJH, et al., editors. GeneReviews(R) Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 2014. All rights reserved. - PubMed
-
- van der Knaap MS, Breiter SN, Naidu S, Hart AA, Valk J. Defining and categorizing leukoencephalopathies of unknown origin: MR imaging approach. Radiology. 1999 Oct;213(1):121–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

